在 TensorFlow.org 上查看 在 TensorFlow.org 上查看
|
 在 Google Colab 中运行 在 Google Colab 中运行
|
 在 GitHub 上查看 在 GitHub 上查看
|
 下载笔记本 下载笔记本
|
 查看 TF Hub 模型 查看 TF Hub 模型
|
YAMNet 是一种深度网络,可以从其训练的 AudioSet-YouTube 语料库 中预测 521 个音频事件 类别。它采用 Mobilenet_v1 深度可分离卷积架构。
import tensorflow as tf
import tensorflow_hub as hub
import numpy as np
import csv
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from IPython.display import Audio
from scipy.io import wavfile
从 TensorFlow Hub 加载模型。
# Load the model.
model = hub.load('https://tfhub.dev/google/yamnet/1')
2024-03-09 14:52:27.405707: E external/local_xla/xla/stream_executor/cuda/cuda_driver.cc:282] failed call to cuInit: CUDA_ERROR_NO_DEVICE: no CUDA-capable device is detected
标签文件将从模型的资产中加载,位于 model.class_map_path()。您将在 class_names 变量中加载它。
# Find the name of the class with the top score when mean-aggregated across frames.
def class_names_from_csv(class_map_csv_text):
"""Returns list of class names corresponding to score vector."""
class_names = []
with tf.io.gfile.GFile(class_map_csv_text) as csvfile:
reader = csv.DictReader(csvfile)
for row in reader:
class_names.append(row['display_name'])
return class_names
class_map_path = model.class_map_path().numpy()
class_names = class_names_from_csv(class_map_path)
添加一个方法来验证和转换加载的音频是否具有正确的采样率 (16K),否则会影响模型的结果。
def ensure_sample_rate(original_sample_rate, waveform,
desired_sample_rate=16000):
"""Resample waveform if required."""
if original_sample_rate != desired_sample_rate:
desired_length = int(round(float(len(waveform)) /
original_sample_rate * desired_sample_rate))
waveform = scipy.signal.resample(waveform, desired_length)
return desired_sample_rate, waveform
下载和准备声音文件
在这里,您将下载一个 wav 文件并收听它。如果您已经有一个文件可用,只需将其上传到 colab 并使用它即可。
curl -O https://storage.googleapis.com/audioset/speech_whistling2.wav
% Total % Received % Xferd Average Speed Time Time Time Current
Dload Upload Total Spent Left Speed
100 153k 100 153k 0 0 1220k 0 --:--:-- --:--:-- --:--:-- 1220k
curl -O https://storage.googleapis.com/audioset/miaow_16k.wav
% Total % Received % Xferd Average Speed Time Time Time Current
Dload Upload Total Spent Left Speed
100 210k 100 210k 0 0 1913k 0 --:--:-- --:--:-- --:--:-- 1913k
# wav_file_name = 'speech_whistling2.wav'
wav_file_name = 'miaow_16k.wav'
sample_rate, wav_data = wavfile.read(wav_file_name, 'rb')
sample_rate, wav_data = ensure_sample_rate(sample_rate, wav_data)
# Show some basic information about the audio.
duration = len(wav_data)/sample_rate
print(f'Sample rate: {sample_rate} Hz')
print(f'Total duration: {duration:.2f}s')
print(f'Size of the input: {len(wav_data)}')
# Listening to the wav file.
Audio(wav_data, rate=sample_rate)
Sample rate: 16000 Hz Total duration: 6.73s Size of the input: 107698 /tmpfs/tmp/ipykernel_101715/2211628228.py:3: WavFileWarning: Chunk (non-data) not understood, skipping it. sample_rate, wav_data = wavfile.read(wav_file_name, 'rb')
wav_data 需要规范化为 [-1.0, 1.0] 之间的值(如模型的 文档 中所述)。
waveform = wav_data / tf.int16.max
执行模型
现在最简单的一步:使用已经准备好的数据,您只需调用模型并获取:分数、嵌入和频谱图。
分数是您将使用的主要结果。频谱图将用于稍后进行一些可视化。
# Run the model, check the output.
scores, embeddings, spectrogram = model(waveform)
scores_np = scores.numpy()
spectrogram_np = spectrogram.numpy()
infered_class = class_names[scores_np.mean(axis=0).argmax()]
print(f'The main sound is: {infered_class}')
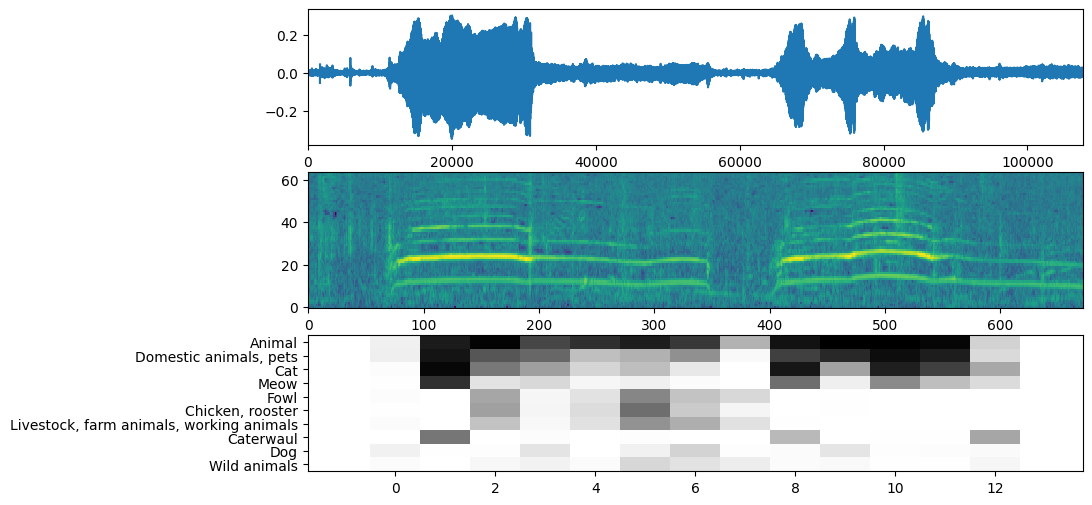
The main sound is: Animal
可视化
YAMNet 还返回了一些其他信息,我们可以用它来进行可视化。让我们看看波形、频谱图和推断出的前几个类别。
plt.figure(figsize=(10, 6))
# Plot the waveform.
plt.subplot(3, 1, 1)
plt.plot(waveform)
plt.xlim([0, len(waveform)])
# Plot the log-mel spectrogram (returned by the model).
plt.subplot(3, 1, 2)
plt.imshow(spectrogram_np.T, aspect='auto', interpolation='nearest', origin='lower')
# Plot and label the model output scores for the top-scoring classes.
mean_scores = np.mean(scores, axis=0)
top_n = 10
top_class_indices = np.argsort(mean_scores)[::-1][:top_n]
plt.subplot(3, 1, 3)
plt.imshow(scores_np[:, top_class_indices].T, aspect='auto', interpolation='nearest', cmap='gray_r')
# patch_padding = (PATCH_WINDOW_SECONDS / 2) / PATCH_HOP_SECONDS
# values from the model documentation
patch_padding = (0.025 / 2) / 0.01
plt.xlim([-patch_padding-0.5, scores.shape[0] + patch_padding-0.5])
# Label the top_N classes.
yticks = range(0, top_n, 1)
plt.yticks(yticks, [class_names[top_class_indices[x]] for x in yticks])
_ = plt.ylim(-0.5 + np.array([top_n, 0]))