 在 TensorFlow.org 上查看 在 TensorFlow.org 上查看
|
 在 Google Colab 中运行 在 Google Colab 中运行
|
 在 GitHub 上查看源代码 在 GitHub 上查看源代码
|
 下载笔记本 下载笔记本
|
本教程提供了如何使用 TensorFlow 处理 CSV 数据的示例。
这主要分为两个部分
- 从磁盘加载数据
- 将其预处理成适合训练的形式。
本教程重点介绍加载,并提供了一些预处理的快速示例。要详细了解预处理方面,请查看 使用预处理层 指南和 使用 Keras 预处理层对结构化数据进行分类 教程。
设置
import pandas as pd
import numpy as np
# Make numpy values easier to read.
np.set_printoptions(precision=3, suppress=True)
import tensorflow as tf
from tensorflow.keras import layers
2024-07-13 05:31:36.932819: E external/local_xla/xla/stream_executor/cuda/cuda_fft.cc:479] Unable to register cuFFT factory: Attempting to register factory for plugin cuFFT when one has already been registered 2024-07-13 05:31:36.958817: E external/local_xla/xla/stream_executor/cuda/cuda_dnn.cc:10575] Unable to register cuDNN factory: Attempting to register factory for plugin cuDNN when one has already been registered 2024-07-13 05:31:36.958856: E external/local_xla/xla/stream_executor/cuda/cuda_blas.cc:1442] Unable to register cuBLAS factory: Attempting to register factory for plugin cuBLAS when one has already been registered
内存中的数据
对于任何小型 CSV 数据集,在 TensorFlow 模型上训练它的最简单方法是将其加载到内存中,作为 pandas DataFrame 或 NumPy 数组。
一个比较简单的例子是 鲍鱼数据集。
- 数据集很小。
- 所有输入特征都是有限范围的浮点值。
以下是将数据下载到 DataFrame 中的方法
abalone_train = pd.read_csv(
"https://storage.googleapis.com/download.tensorflow.org/data/abalone_train.csv",
names=["Length", "Diameter", "Height", "Whole weight", "Shucked weight",
"Viscera weight", "Shell weight", "Age"])
abalone_train.head()
数据集包含一组对 鲍鱼(一种海蜗牛)的测量值。

“鲍鱼壳”(作者 Nicki Dugan Pogue,CC BY-SA 2.0)
这个数据集的标称任务是从其他测量值中预测年龄,因此将特征和标签分开以进行训练
abalone_features = abalone_train.copy()
abalone_labels = abalone_features.pop('Age')
对于这个数据集,您将以相同的方式处理所有特征。将特征打包到单个 NumPy 数组中。
abalone_features = np.array(abalone_features)
abalone_features
array([[0.435, 0.335, 0.11 , ..., 0.136, 0.077, 0.097],
[0.585, 0.45 , 0.125, ..., 0.354, 0.207, 0.225],
[0.655, 0.51 , 0.16 , ..., 0.396, 0.282, 0.37 ],
...,
[0.53 , 0.42 , 0.13 , ..., 0.374, 0.167, 0.249],
[0.395, 0.315, 0.105, ..., 0.118, 0.091, 0.119],
[0.45 , 0.355, 0.12 , ..., 0.115, 0.067, 0.16 ]])
接下来,创建一个回归模型来预测年龄。由于只有一个输入张量,因此 tf.keras.Sequential 模型在这里就足够了。
abalone_model = tf.keras.Sequential([
layers.Dense(64, activation='relu'),
layers.Dense(1)
])
abalone_model.compile(loss = tf.keras.losses.MeanSquaredError(),
optimizer = tf.keras.optimizers.Adam())
要训练该模型,请将特征和标签传递给 Model.fit
abalone_model.fit(abalone_features, abalone_labels, epochs=10)
Epoch 1/10 WARNING: All log messages before absl::InitializeLog() is called are written to STDERR I0000 00:00:1720848701.706380 451497 service.cc:145] XLA service 0x7f9e70006580 initialized for platform CUDA (this does not guarantee that XLA will be used). Devices: I0000 00:00:1720848701.706434 451497 service.cc:153] StreamExecutor device (0): Tesla T4, Compute Capability 7.5 I0000 00:00:1720848701.706438 451497 service.cc:153] StreamExecutor device (1): Tesla T4, Compute Capability 7.5 I0000 00:00:1720848701.706441 451497 service.cc:153] StreamExecutor device (2): Tesla T4, Compute Capability 7.5 I0000 00:00:1720848701.706444 451497 service.cc:153] StreamExecutor device (3): Tesla T4, Compute Capability 7.5 94/104 ━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━ 0s 1ms/step - loss: 96.5334 I0000 00:00:1720848702.122367 451497 device_compiler.h:188] Compiled cluster using XLA! This line is logged at most once for the lifetime of the process. 104/104 ━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━ 2s 4ms/step - loss: 94.9891 Epoch 2/10 104/104 ━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━ 0s 1ms/step - loss: 31.2786 Epoch 3/10 104/104 ━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━ 0s 1ms/step - loss: 8.3721 Epoch 4/10 104/104 ━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━ 0s 1ms/step - loss: 8.1522 Epoch 5/10 104/104 ━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━ 0s 1ms/step - loss: 7.7770 Epoch 6/10 104/104 ━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━ 0s 1ms/step - loss: 7.0686 Epoch 7/10 104/104 ━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━ 0s 1ms/step - loss: 6.6384 Epoch 8/10 104/104 ━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━ 0s 1ms/step - loss: 6.5113 Epoch 9/10 104/104 ━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━ 0s 1ms/step - loss: 7.2517 Epoch 10/10 104/104 ━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━ 0s 1ms/step - loss: 6.0659 <keras.src.callbacks.history.History at 0x7fa03002be80>
您刚刚看到了使用 CSV 数据训练模型的最基本方法。接下来,您将学习如何应用预处理来规范化数值列。
基本预处理
将输入规范化到您的模型是一个好习惯。Keras 预处理层提供了一种将这种规范化构建到您的模型中的便捷方法。
The tf.keras.layers.Normalization 层预先计算每列的均值和方差,并使用它们来规范化数据。
首先,创建该层
normalize = layers.Normalization()
然后,使用 Normalization.adapt 方法使规范化层适应您的数据。
normalize.adapt(abalone_features)
然后,在您的模型中使用规范化层
norm_abalone_model = tf.keras.Sequential([
normalize,
layers.Dense(64, activation='relu'),
layers.Dense(1)
])
norm_abalone_model.compile(loss = tf.keras.losses.MeanSquaredError(),
optimizer = tf.keras.optimizers.Adam())
norm_abalone_model.fit(abalone_features, abalone_labels, epochs=10)
Epoch 1/10 104/104 ━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━ 1s 3ms/step - loss: 93.6417 Epoch 2/10 104/104 ━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━ 0s 1ms/step - loss: 48.7377 Epoch 3/10 104/104 ━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━ 0s 1ms/step - loss: 26.9893 Epoch 4/10 104/104 ━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━ 0s 1ms/step - loss: 18.4746 Epoch 5/10 104/104 ━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━ 0s 1ms/step - loss: 11.3473 Epoch 6/10 104/104 ━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━ 0s 1ms/step - loss: 7.5720 Epoch 7/10 104/104 ━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━ 0s 1ms/step - loss: 6.3920 Epoch 8/10 104/104 ━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━ 0s 1ms/step - loss: 6.4452 Epoch 9/10 104/104 ━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━ 0s 1ms/step - loss: 5.8708 Epoch 10/10 104/104 ━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━ 0s 1ms/step - loss: 5.8409 <keras.src.callbacks.history.History at 0x7fa0280efee0>
混合数据类型
在前面的部分中,您使用了一个所有特征都是有限范围浮点值的数据集。但并非所有数据集都限于单一数据类型。
“泰坦尼克号”数据集包含有关泰坦尼克号乘客的信息。该数据集的标称任务是预测谁幸存下来。

图片 来自维基百科
原始数据可以轻松地作为 Pandas DataFrame 加载,但不能立即用作 TensorFlow 模型的输入。
titanic = pd.read_csv("https://storage.googleapis.com/tf-datasets/titanic/train.csv")
titanic.head()
titanic_features = titanic.copy()
titanic_labels = titanic_features.pop('survived')
由于数据类型和范围不同,您不能简单地将特征堆叠到 NumPy 数组中并将其传递给 tf.keras.Sequential 模型。每列都需要单独处理。
作为一种选择,您可以离线预处理您的数据(使用您喜欢的任何工具)将分类列转换为数值列,然后将处理后的输出传递给您的 TensorFlow 模型。这种方法的缺点是,如果您保存和导出您的模型,预处理不会与它一起保存。Keras 预处理层避免了这个问题,因为它们是模型的一部分。
在本例中,您将构建一个使用 Keras 函数式 API 实现预处理逻辑的模型。您也可以通过 子类化 来实现。
函数式 API 在“符号”张量上运行。普通的“急切”张量具有值。相反,这些“符号”张量没有值。相反,它们跟踪对它们执行的操作,并构建计算的表示,您可以稍后运行。以下是一个快速示例
# Create a symbolic input
input = tf.keras.Input(shape=(), dtype=tf.float32)
# Perform a calculation using the input
result = 2*input + 1
# the result doesn't have a value
result
<KerasTensor shape=(None,), dtype=float32, sparse=False, name=keras_tensor_9>
calc = tf.keras.Model(inputs=input, outputs=result)
print(calc(np.array([1])).numpy())
print(calc(np.array([2])).numpy())
[3.] [5.]
要构建预处理模型,首先构建一组符号 tf.keras.Input 对象,匹配 CSV 列的名称和数据类型。
inputs = {}
for name, column in titanic_features.items():
dtype = column.dtype
if dtype == object:
dtype = tf.string
else:
dtype = tf.float32
inputs[name] = tf.keras.Input(shape=(1,), name=name, dtype=dtype)
inputs
{'sex': <KerasTensor shape=(None, 1), dtype=string, sparse=None, name=sex>,
'age': <KerasTensor shape=(None, 1), dtype=float32, sparse=None, name=age>,
'n_siblings_spouses': <KerasTensor shape=(None, 1), dtype=float32, sparse=None, name=n_siblings_spouses>,
'parch': <KerasTensor shape=(None, 1), dtype=float32, sparse=None, name=parch>,
'fare': <KerasTensor shape=(None, 1), dtype=float32, sparse=None, name=fare>,
'class': <KerasTensor shape=(None, 1), dtype=string, sparse=None, name=class>,
'deck': <KerasTensor shape=(None, 1), dtype=string, sparse=None, name=deck>,
'embark_town': <KerasTensor shape=(None, 1), dtype=string, sparse=None, name=embark_town>,
'alone': <KerasTensor shape=(None, 1), dtype=string, sparse=None, name=alone>}
预处理逻辑中的第一步是将数值输入连接在一起,并将其通过规范化层运行
numeric_inputs = {name:input for name,input in inputs.items()
if input.dtype==tf.float32}
x = layers.Concatenate()(list(numeric_inputs.values()))
norm = layers.Normalization()
norm.adapt(np.array(titanic[numeric_inputs.keys()]))
all_numeric_inputs = norm(x)
all_numeric_inputs
<KerasTensor shape=(None, 4), dtype=float32, sparse=False, name=keras_tensor_11>
收集所有符号预处理结果,以便稍后将它们连接起来
preprocessed_inputs = [all_numeric_inputs]
对于字符串输入,使用 tf.keras.layers.StringLookup 函数将字符串映射到词汇表中的整数索引。接下来,使用 tf.keras.layers.CategoryEncoding 将索引转换为 float32 数据,适合模型。
The tf.keras.layers.CategoryEncoding 层的默认设置为每个输入创建一个独热向量。一个 tf.keras.layers.Embedding 也可以工作。查看 使用预处理层 指南和 使用 Keras 预处理层对结构化数据进行分类 教程以了解更多信息。
for name, input in inputs.items():
if input.dtype == tf.float32:
continue
lookup = layers.StringLookup(vocabulary=np.unique(titanic_features[name]))
one_hot = layers.CategoryEncoding(num_tokens=lookup.vocabulary_size())
x = lookup(input)
x = one_hot(x)
preprocessed_inputs.append(x)
有了 inputs 和 preprocessed_inputs 的集合,您可以将所有预处理的输入连接在一起,并构建一个处理预处理的模型
preprocessed_inputs_cat = layers.Concatenate()(preprocessed_inputs)
titanic_preprocessing = tf.keras.Model(inputs, preprocessed_inputs_cat)
tf.keras.utils.plot_model(model = titanic_preprocessing , rankdir="LR", dpi=72, show_shapes=True)
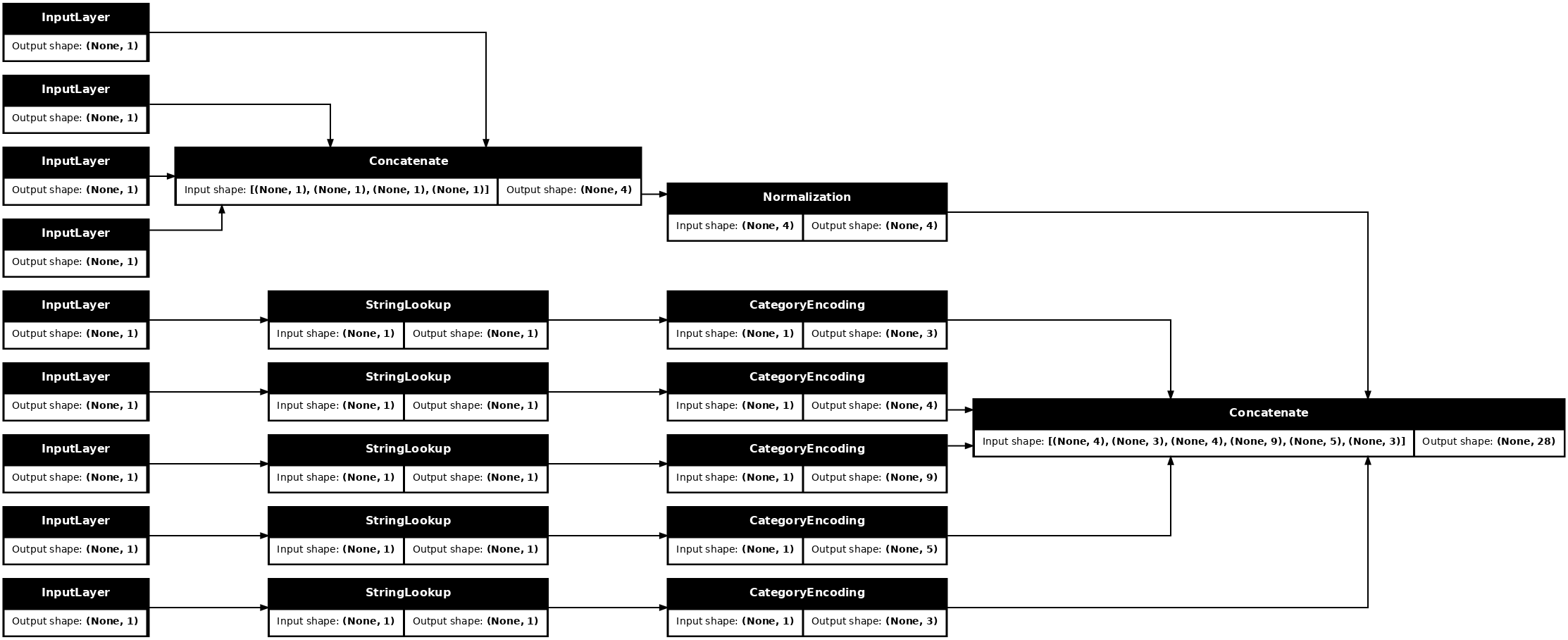
此模型只包含输入预处理。您可以运行它以查看它对您的数据做了什么。Keras 模型不会自动转换 pandas DataFrame,因为它不清楚应该将其转换为一个张量还是转换为张量字典。因此,将其转换为张量字典
titanic_features_dict = {name: np.array(value)
for name, value in titanic_features.items()}
切出第一个训练示例并将其传递给此预处理模型,您将看到数值特征和字符串独热向量都连接在一起
features_dict = {name:values[:1] for name, values in titanic_features_dict.items()}
titanic_preprocessing(features_dict)
<tf.Tensor: shape=(1, 28), dtype=float32, numpy=
array([[-0.61 , 0.395, -0.479, -0.497, 0. , 0. , 1. , 0. ,
0. , 0. , 1. , 0. , 0. , 0. , 0. , 0. ,
0. , 0. , 0. , 1. , 0. , 0. , 0. , 1. ,
0. , 0. , 1. , 0. ]], dtype=float32)>
现在,在此基础上构建模型
def titanic_model(preprocessing_head, inputs):
body = tf.keras.Sequential([
layers.Dense(64, activation='relu'),
layers.Dense(1)
])
preprocessed_inputs = preprocessing_head(inputs)
result = body(preprocessed_inputs)
model = tf.keras.Model(inputs, result)
model.compile(loss=tf.keras.losses.BinaryCrossentropy(from_logits=True),
optimizer=tf.keras.optimizers.Adam())
return model
titanic_model = titanic_model(titanic_preprocessing, inputs)
当您训练模型时,将特征字典作为 x 传递,将标签作为 y 传递。
titanic_model.fit(x=titanic_features_dict, y=titanic_labels, epochs=10)
Epoch 1/10 20/20 ━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━ 2s 3ms/step - loss: 0.6619 Epoch 2/10 20/20 ━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━ 0s 3ms/step - loss: 0.5967 Epoch 3/10 20/20 ━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━ 0s 3ms/step - loss: 0.5366 Epoch 4/10 20/20 ━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━ 0s 3ms/step - loss: 0.4809 Epoch 5/10 20/20 ━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━ 0s 3ms/step - loss: 0.5004 Epoch 6/10 20/20 ━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━ 0s 3ms/step - loss: 0.4659 Epoch 7/10 20/20 ━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━ 0s 3ms/step - loss: 0.4474 Epoch 8/10 20/20 ━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━ 0s 3ms/step - loss: 0.4304 Epoch 9/10 20/20 ━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━ 0s 3ms/step - loss: 0.3952 Epoch 10/10 20/20 ━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━ 0s 3ms/step - loss: 0.4256 <keras.src.callbacks.history.History at 0x7fa153fe5280>
由于预处理是模型的一部分,因此您可以保存模型并在其他地方重新加载它,并获得相同的结果
titanic_model.save('test.keras')
reloaded = tf.keras.models.load_model('test.keras')
features_dict = {name:values[:1] for name, values in titanic_features_dict.items()}
before = titanic_model(features_dict)
after = reloaded(features_dict)
assert (before-after)<1e-3
print(before)
print(after)
tf.Tensor([[-1.932]], shape=(1, 1), dtype=float32) tf.Tensor([[-1.932]], shape=(1, 1), dtype=float32)
使用 tf.data
在上一节中,您在训练模型时依赖于模型的内置数据混洗和批处理。
如果您需要更多地控制输入数据管道,或者需要使用不适合内存的数据:使用 tf.data。
有关更多示例,请参阅 tf.data:构建 TensorFlow 输入管道 指南。
关于内存数据
作为将 tf.data 应用于 CSV 数据的第一个示例,请考虑以下代码以手动将上一节中的特征字典切片。对于每个索引,它都会获取每个特征的该索引
import itertools
def slices(features):
for i in itertools.count():
# For each feature take index `i`
example = {name:values[i] for name, values in features.items()}
yield example
运行此代码并打印第一个示例
for example in slices(titanic_features_dict):
for name, value in example.items():
print(f"{name:19s}: {value}")
break
sex : male age : 22.0 n_siblings_spouses : 1 parch : 0 fare : 7.25 class : Third deck : unknown embark_town : Southampton alone : n
内存数据加载器中最基本的 tf.data.Dataset 是 Dataset.from_tensor_slices 构造函数。这将返回一个 tf.data.Dataset,它在 TensorFlow 中实现了上述 slices 函数的通用版本。
features_ds = tf.data.Dataset.from_tensor_slices(titanic_features_dict)
您可以像任何其他 python 可迭代对象一样迭代 tf.data.Dataset
for example in features_ds:
for name, value in example.items():
print(f"{name:19s}: {value}")
break
sex : b'male' age : 22.0 n_siblings_spouses : 1 parch : 0 fare : 7.25 class : b'Third' deck : b'unknown' embark_town : b'Southampton' alone : b'n'
The from_tensor_slices 函数可以处理任何嵌套字典或元组的结构。以下代码创建了一个 (features_dict, labels) 对的数据集
titanic_ds = tf.data.Dataset.from_tensor_slices((titanic_features_dict, titanic_labels))
要使用此 Dataset 训练模型,您至少需要 shuffle 和 batch 数据。
titanic_batches = titanic_ds.shuffle(len(titanic_labels)).batch(32)
不要将 features 和 labels 传递给 Model.fit,而是传递数据集
titanic_model.fit(titanic_batches, epochs=5)
Epoch 1/5 20/20 ━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━ 0s 3ms/step - loss: 0.4309 Epoch 2/5 20/20 ━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━ 0s 3ms/step - loss: 0.4024 Epoch 3/5 20/20 ━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━ 0s 3ms/step - loss: 0.4184 Epoch 4/5 20/20 ━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━ 0s 3ms/step - loss: 0.3813 Epoch 5/5 20/20 ━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━ 0s 3ms/step - loss: 0.3939 <keras.src.callbacks.history.History at 0x7fa153fe73d0>
从单个文件
到目前为止,本教程一直在使用内存数据。 tf.data 是一个高度可扩展的工具包,用于构建数据管道,并提供一些用于加载 CSV 文件的函数。
titanic_file_path = tf.keras.utils.get_file("train.csv", "https://storage.googleapis.com/tf-datasets/titanic/train.csv")
Downloading data from https://storage.googleapis.com/tf-datasets/titanic/train.csv 30874/30874 ━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━ 0s 0us/step
现在从文件中读取 CSV 数据并创建一个 tf.data.Dataset。
(有关完整文档,请参阅 tf.data.experimental.make_csv_dataset)
titanic_csv_ds = tf.data.experimental.make_csv_dataset(
titanic_file_path,
batch_size=5, # Artificially small to make examples easier to show.
label_name='survived',
num_epochs=1,
ignore_errors=True,)
WARNING:tensorflow:From /tmpfs/src/tf_docs_env/lib/python3.9/site-packages/tensorflow/python/data/experimental/ops/readers.py:572: ignore_errors (from tensorflow.python.data.experimental.ops.error_ops) is deprecated and will be removed in a future version. Instructions for updating: Use `tf.data.Dataset.ignore_errors` instead.
此函数包含许多便捷功能,因此数据易于使用。这包括
- 使用列标题作为字典键。
- 自动确定每列的类型。
for batch, label in titanic_csv_ds.take(1):
for key, value in batch.items():
print(f"{key:20s}: {value}")
print()
print(f"{'label':20s}: {label}")
sex : [b'female' b'male' b'male' b'male' b'male'] age : [ 2. 28. 18. 32. 28.] n_siblings_spouses : [0 0 1 0 0] parch : [1 0 0 0 0] fare : [ 12.288 7.896 108.9 30.5 13. ] class : [b'Third' b'Third' b'First' b'First' b'Second'] deck : [b'unknown' b'unknown' b'C' b'B' b'unknown'] embark_town : [b'Southampton' b'Southampton' b'Cherbourg' b'Cherbourg' b'Southampton'] alone : [b'n' b'y' b'n' b'y' b'y'] label : [1 0 0 1 1] 2024-07-13 05:31:51.519261: W tensorflow/core/framework/local_rendezvous.cc:404] Local rendezvous is aborting with status: OUT_OF_RANGE: End of sequence
它还可以动态解压缩数据。这是一个包含 城市间交通量数据集 的压缩 CSV 文件。

图片 来自维基百科
traffic_volume_csv_gz = tf.keras.utils.get_file(
'Metro_Interstate_Traffic_Volume.csv.gz',
"https://archive.ics.uci.edu/ml/machine-learning-databases/00492/Metro_Interstate_Traffic_Volume.csv.gz",
cache_dir='.', cache_subdir='traffic')
Downloading data from https://archive.ics.uci.edu/ml/machine-learning-databases/00492/Metro_Interstate_Traffic_Volume.csv.gz 335872/Unknown 0s 1us/step
设置 compression_type 参数以直接从压缩文件中读取
traffic_volume_csv_gz_ds = tf.data.experimental.make_csv_dataset(
traffic_volume_csv_gz,
batch_size=256,
label_name='traffic_volume',
num_epochs=1,
compression_type="GZIP")
for batch, label in traffic_volume_csv_gz_ds.take(1):
for key, value in batch.items():
print(f"{key:20s}: {value[:5]}")
print()
print(f"{'label':20s}: {label[:5]}")
holiday : [b'None' b'None' b'None' b'None' b'None'] temp : [288.99 294.07 262.2 284.58 295.89] rain_1h : [0. 0. 0. 0. 0.] snow_1h : [0. 0. 0. 0. 0.] clouds_all : [ 0 56 90 90 1] weather_main : [b'Clear' b'Clouds' b'Clouds' b'Rain' b'Clear'] weather_description : [b'Sky is Clear' b'broken clouds' b'overcast clouds' b'light rain' b'sky is clear'] date_time : [b'2013-08-08 07:00:00' b'2013-07-15 04:00:00' b'2013-02-21 19:00:00' b'2013-05-10 13:00:00' b'2013-04-28 16:00:00'] label : [6771 828 3431 5457 4475] 2024-07-13 05:31:52.189408: W tensorflow/core/framework/local_rendezvous.cc:404] Local rendezvous is aborting with status: OUT_OF_RANGE: End of sequence
缓存
解析 CSV 数据会产生一些开销。对于小型模型,这可能是训练的瓶颈。
根据您的用例,使用 Dataset.cache 或 tf.data.Dataset.snapshot 可能是一个好主意,这样 CSV 数据只会在第一个时期解析一次。
The cache 和 snapshot 方法的主要区别在于,cache 文件只能由创建它们的 TensorFlow 进程使用,而 snapshot 文件可以由其他进程读取。
例如,迭代 traffic_volume_csv_gz_ds 20 次,如果不使用缓存,可能需要大约 15 秒,而使用缓存则需要大约 2 秒。
%%time
for i, (batch, label) in enumerate(traffic_volume_csv_gz_ds.repeat(20)):
if i % 40 == 0:
print('.', end='')
print()
............................................................................................... CPU times: user 13.3 s, sys: 2.27 s, total: 15.6 s Wall time: 9.8 s 2024-07-13 05:32:01.991227: W tensorflow/core/framework/local_rendezvous.cc:404] Local rendezvous is aborting with status: OUT_OF_RANGE: End of sequence
%%time
caching = traffic_volume_csv_gz_ds.cache().shuffle(1000)
for i, (batch, label) in enumerate(caching.shuffle(1000).repeat(20)):
if i % 40 == 0:
print('.', end='')
print()
............................................................................................... CPU times: user 1.85 s, sys: 200 ms, total: 2.05 s Wall time: 1.75 s 2024-07-13 05:32:03.764820: W tensorflow/core/framework/local_rendezvous.cc:404] Local rendezvous is aborting with status: OUT_OF_RANGE: End of sequence
%%time
snapshotting = traffic_volume_csv_gz_ds.snapshot('titanic.tfsnap').shuffle(1000)
for i, (batch, label) in enumerate(snapshotting.shuffle(1000).repeat(20)):
if i % 40 == 0:
print('.', end='')
print()
............................................................................................... CPU times: user 2.75 s, sys: 583 ms, total: 3.33 s Wall time: 2.05 s 2024-07-13 05:32:05.819285: W tensorflow/core/framework/local_rendezvous.cc:404] Local rendezvous is aborting with status: OUT_OF_RANGE: End of sequence
如果您的数据加载速度因加载 CSV 文件而变慢,并且 Dataset.cache 和 tf.data.Dataset.snapshot 不足以满足您的用例,请考虑将您的数据重新编码为更简化的格式。
多个文件
本节中到目前为止的所有示例都可以轻松地在没有 tf.data 的情况下完成。在处理文件集合时,tf.data 可以真正简化操作。
例如,字符字体图像 数据集以一组 CSV 文件的形式分发,每个字体一个文件。

图像由 Willi Heidelbach 从 Pixabay 提供
下载数据集并查看其中的文件
fonts_zip = tf.keras.utils.get_file(
'fonts.zip', "https://archive.ics.uci.edu/ml/machine-learning-databases/00417/fonts.zip",
cache_dir='.', cache_subdir='fonts',
extract=True)
Downloading data from https://archive.ics.uci.edu/ml/machine-learning-databases/00417/fonts.zip 159481856/Unknown 4s 0us/step
import pathlib
font_csvs = sorted(str(p) for p in pathlib.Path('fonts').glob("*.csv"))
font_csvs[:10]
['fonts/AGENCY.csv', 'fonts/ARIAL.csv', 'fonts/BAITI.csv', 'fonts/BANKGOTHIC.csv', 'fonts/BASKERVILLE.csv', 'fonts/BAUHAUS.csv', 'fonts/BELL.csv', 'fonts/BERLIN.csv', 'fonts/BERNARD.csv', 'fonts/BITSTREAMVERA.csv']
len(font_csvs)
153
在处理大量文件时,您可以将 glob 样式的 file_pattern 传递给 tf.data.experimental.make_csv_dataset 函数。文件的顺序在每次迭代时都会被混洗。
使用 num_parallel_reads 参数设置并行读取和交织在一起的文件数量。
fonts_ds = tf.data.experimental.make_csv_dataset(
file_pattern = "fonts/*.csv",
batch_size=10, num_epochs=1,
num_parallel_reads=20,
shuffle_buffer_size=10000)
这些 CSV 文件将图像展平为单行。列名格式为 r{row}c{column}。以下是第一批
for features in fonts_ds.take(1):
for i, (name, value) in enumerate(features.items()):
if i>15:
break
print(f"{name:20s}: {value}")
print('...')
print(f"[total: {len(features)} features]")
font : [b'BODONI' b'PHAGSPA' b'PLAYBILL' b'EDWARDIAN' b'EDWARDIAN' b'BOOK' b'HAETTENSCHWEILER' b'CENTAUR' b'CENTAUR' b'LEELAWADEE'] fontVariant : [b'BODONI MT POSTER COMPRESSED' b'MICROSOFT PHAGSPA' b'PLAYBILL' b'EDWARDIAN SCRIPT ITC' b'EDWARDIAN SCRIPT ITC' b'BOOK ANTIQUA' b'HAETTENSCHWEILER' b'CENTAUR' b'CENTAUR' b'LEELAWADEE UI SEMILIGHT'] m_label : [ 114 8254 93 100 710 1084 1025 8224 338 9723] strength : [0.4 0.4 0.4 0.4 0.4 0.4 0.4 0.4 0.4 0.4] italic : [1 0 1 0 1 0 0 0 1 0] orientation : [0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0.] m_top : [47 40 30 44 49 53 27 33 34 50] m_left : [20 20 20 23 46 21 21 21 28 29] originalH : [35 4 56 34 8 31 55 53 44 39] originalW : [27 28 28 32 16 44 20 19 68 39] h : [20 20 20 20 20 20 20 20 20 20] w : [20 20 20 20 20 20 20 20 20 20] r0c0 : [ 1 255 1 1 0 255 1 1 1 255] r0c1 : [ 1 255 1 1 0 255 1 1 1 255] r0c2 : [ 1 255 1 1 0 255 1 1 1 255] r0c3 : [ 1 255 1 1 0 255 163 1 1 255] ... [total: 412 features] 2024-07-13 05:32:17.807571: W tensorflow/core/framework/local_rendezvous.cc:404] Local rendezvous is aborting with status: OUT_OF_RANGE: End of sequence
可选:打包字段
您可能不想像这样在单独的列中处理每个像素。在尝试使用此数据集之前,请确保将像素打包到图像张量中。
以下是解析列名以构建每个示例的图像的代码
import re
def make_images(features):
image = [None]*400
new_feats = {}
for name, value in features.items():
match = re.match('r(\d+)c(\d+)', name)
if match:
image[int(match.group(1))*20+int(match.group(2))] = value
else:
new_feats[name] = value
image = tf.stack(image, axis=0)
image = tf.reshape(image, [20, 20, -1])
new_feats['image'] = image
return new_feats
将该函数应用于数据集中的每个批次
fonts_image_ds = fonts_ds.map(make_images)
for features in fonts_image_ds.take(1):
break
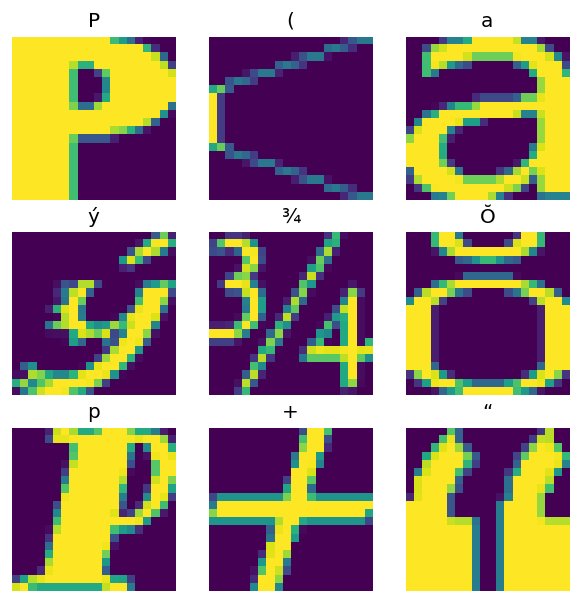
绘制生成的图像
from matplotlib import pyplot as plt
plt.figure(figsize=(6,6), dpi=120)
for n in range(9):
plt.subplot(3,3,n+1)
plt.imshow(features['image'][..., n])
plt.title(chr(features['m_label'][n]))
plt.axis('off')
低级函数
到目前为止,本教程重点介绍了用于读取 csv 数据的最高级实用程序。对于高级用户,如果您的用例不符合基本模式,还有另外两个 API 可能会有所帮助。
tf.io.decode_csv:用于将文本行解析为 CSV 列张量列表的函数。tf.data.experimental.CsvDataset:一个低级的 CSV 数据集构造函数。
本节重新创建了 tf.data.experimental.make_csv_dataset 提供的功能,以演示如何使用此低级功能。
tf.io.decode_csv
此函数将字符串或字符串列表解码为列列表。
与 tf.data.experimental.make_csv_dataset 不同,此函数不会尝试猜测列数据类型。您可以通过提供一个包含每个列的正确类型值的 record_defaults 列表来指定列类型。
要使用 tf.io.decode_csv 以字符串形式读取泰坦尼克号数据,您应该说
text = pathlib.Path(titanic_file_path).read_text()
lines = text.split('\n')[1:-1]
all_strings = [str()]*10
all_strings
['', '', '', '', '', '', '', '', '', '']
features = tf.io.decode_csv(lines, record_defaults=all_strings)
for f in features:
print(f"type: {f.dtype.name}, shape: {f.shape}")
type: string, shape: (627,) type: string, shape: (627,) type: string, shape: (627,) type: string, shape: (627,) type: string, shape: (627,) type: string, shape: (627,) type: string, shape: (627,) type: string, shape: (627,) type: string, shape: (627,) type: string, shape: (627,)
要使用它们的实际类型进行解析,请创建一个包含相应类型的 record_defaults 列表
print(lines[0])
0,male,22.0,1,0,7.25,Third,unknown,Southampton,n
titanic_types = [int(), str(), float(), int(), int(), float(), str(), str(), str(), str()]
titanic_types
[0, '', 0.0, 0, 0, 0.0, '', '', '', '']
features = tf.io.decode_csv(lines, record_defaults=titanic_types)
for f in features:
print(f"type: {f.dtype.name}, shape: {f.shape}")
type: int32, shape: (627,) type: string, shape: (627,) type: float32, shape: (627,) type: int32, shape: (627,) type: int32, shape: (627,) type: float32, shape: (627,) type: string, shape: (627,) type: string, shape: (627,) type: string, shape: (627,) type: string, shape: (627,)
tf.data.experimental.CsvDataset
tf.data.experimental.CsvDataset 类提供了一个最小的 CSV Dataset 接口,没有 tf.data.experimental.make_csv_dataset 函数的便利功能:列标题解析、列类型推断、自动混洗、文件交织。
此构造函数使用 record_defaults 的方式与 tf.io.decode_csv 相同
simple_titanic = tf.data.experimental.CsvDataset(titanic_file_path, record_defaults=titanic_types, header=True)
for example in simple_titanic.take(1):
print([e.numpy() for e in example])
[0, b'male', 22.0, 1, 0, 7.25, b'Third', b'unknown', b'Southampton', b'n'] 2024-07-13 05:32:20.987770: W tensorflow/core/framework/local_rendezvous.cc:404] Local rendezvous is aborting with status: OUT_OF_RANGE: End of sequence
上面的代码基本上等效于
def decode_titanic_line(line):
return tf.io.decode_csv(line, titanic_types)
manual_titanic = (
# Load the lines of text
tf.data.TextLineDataset(titanic_file_path)
# Skip the header row.
.skip(1)
# Decode the line.
.map(decode_titanic_line)
)
for example in manual_titanic.take(1):
print([e.numpy() for e in example])
[0, b'male', 22.0, 1, 0, 7.25, b'Third', b'unknown', b'Southampton', b'n'] 2024-07-13 05:32:21.082269: W tensorflow/core/framework/local_rendezvous.cc:404] Local rendezvous is aborting with status: OUT_OF_RANGE: End of sequence
多个文件
要使用 tf.data.experimental.CsvDataset 解析字体数据集,您首先需要确定 record_defaults 的列类型。从检查一个文件的首行开始
font_line = pathlib.Path(font_csvs[0]).read_text().splitlines()[1]
print(font_line)
AGENCY,AGENCY FB,64258,0.400000,0,0.000000,35,21,51,22,20,20,1,1,1,21,101,210,255,255,255,255,255,255,255,255,255,255,255,255,255,255,1,1,1,93,255,255,255,176,146,146,146,146,146,146,146,146,216,255,255,255,1,1,1,93,255,255,255,70,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,163,255,255,255,1,1,1,93,255,255,255,70,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,163,255,255,255,1,1,1,93,255,255,255,70,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,163,255,255,255,1,1,1,93,255,255,255,70,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,163,255,255,255,1,1,1,93,255,255,255,70,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,163,255,255,255,141,141,141,182,255,255,255,172,141,141,141,115,1,1,1,1,163,255,255,255,255,255,255,255,255,255,255,255,255,255,255,209,1,1,1,1,163,255,255,255,6,6,6,96,255,255,255,74,6,6,6,5,1,1,1,1,163,255,255,255,1,1,1,93,255,255,255,70,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,163,255,255,255,1,1,1,93,255,255,255,70,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,163,255,255,255,1,1,1,93,255,255,255,70,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,163,255,255,255,1,1,1,93,255,255,255,70,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,163,255,255,255,1,1,1,93,255,255,255,70,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,163,255,255,255,1,1,1,93,255,255,255,70,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,163,255,255,255,1,1,1,93,255,255,255,70,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,163,255,255,255,1,1,1,93,255,255,255,70,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,163,255,255,255,1,1,1,93,255,255,255,70,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,163,255,255,255,1,1,1,93,255,255,255,70,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,163,255,255,255
只有前两个字段是字符串,其余是整数或浮点数,您可以通过计算逗号来获得特征总数
num_font_features = font_line.count(',')+1
font_column_types = [str(), str()] + [float()]*(num_font_features-2)
tf.data.experimental.CsvDataset 构造函数可以接受一个输入文件列表,但会按顺序读取它们。CSV 列表中的第一个文件是 AGENCY.csv
font_csvs[0]
'fonts/AGENCY.csv'
因此,当您将文件列表传递给 CsvDataset 时,首先读取 AGENCY.csv 中的记录
simple_font_ds = tf.data.experimental.CsvDataset(
font_csvs,
record_defaults=font_column_types,
header=True)
for row in simple_font_ds.take(10):
print(row[0].numpy())
b'AGENCY' b'AGENCY' b'AGENCY' b'AGENCY' b'AGENCY' b'AGENCY' b'AGENCY' b'AGENCY' b'AGENCY' b'AGENCY' 2024-07-13 05:32:21.216095: W tensorflow/core/framework/local_rendezvous.cc:404] Local rendezvous is aborting with status: OUT_OF_RANGE: End of sequence
要交织多个文件,请使用 Dataset.interleave。
以下是一个包含 CSV 文件名的初始数据集
font_files = tf.data.Dataset.list_files("fonts/*.csv")
这会在每个 epoch 中混洗文件名
print('Epoch 1:')
for f in list(font_files)[:5]:
print(" ", f.numpy())
print(' ...')
print()
print('Epoch 2:')
for f in list(font_files)[:5]:
print(" ", f.numpy())
print(' ...')
Epoch 1:
b'fonts/GIGI.csv'
b'fonts/NUMERICS.csv'
b'fonts/COPPERPLATE.csv'
b'fonts/PHAGSPA.csv'
b'fonts/ROMAN.csv'
...
Epoch 2:
b'fonts/MV_BOLI.csv'
b'fonts/PROXY.csv'
b'fonts/MONOTXT.csv'
b'fonts/MAIANDRA.csv'
b'fonts/PALACE.csv'
...
2024-07-13 05:32:21.557274: W tensorflow/core/framework/local_rendezvous.cc:404] Local rendezvous is aborting with status: OUT_OF_RANGE: End of sequence
2024-07-13 05:32:21.573293: W tensorflow/core/framework/local_rendezvous.cc:404] Local rendezvous is aborting with status: OUT_OF_RANGE: End of sequence
interleave 方法接受一个 map_func,该函数为父 Dataset 的每个元素创建一个子 Dataset。
在这里,您希望从文件数据集的每个元素创建一个 tf.data.experimental.CsvDataset
def make_font_csv_ds(path):
return tf.data.experimental.CsvDataset(
path,
record_defaults=font_column_types,
header=True)
由 interleave 返回的 Dataset 通过循环遍历多个子 Dataset 来返回元素。请注意,在下面,数据集如何循环遍历 cycle_length=3 三个字体文件
font_rows = font_files.interleave(make_font_csv_ds,
cycle_length=3)
fonts_dict = {'font_name':[], 'character':[]}
for row in font_rows.take(10):
fonts_dict['font_name'].append(row[0].numpy().decode())
fonts_dict['character'].append(chr(int(row[2].numpy())))
pd.DataFrame(fonts_dict)
2024-07-13 05:32:21.931277: W tensorflow/core/framework/local_rendezvous.cc:404] Local rendezvous is aborting with status: OUT_OF_RANGE: End of sequence
性能
之前已经提到,tf.io.decode_csv 在对一批字符串运行时效率更高。
在使用大型批次大小时,可以利用这一事实来提高 CSV 加载性能(但请先尝试 缓存)。
使用内置加载器,20 个包含 2048 个示例的批次大约需要 17 秒。
BATCH_SIZE=2048
fonts_ds = tf.data.experimental.make_csv_dataset(
file_pattern = "fonts/*.csv",
batch_size=BATCH_SIZE, num_epochs=1,
num_parallel_reads=100)
%%time
for i,batch in enumerate(fonts_ds.take(20)):
print('.',end='')
print()
.................... CPU times: user 44.6 s, sys: 4.21 s, total: 48.9 s Wall time: 20.6 s 2024-07-13 05:32:43.296482: W tensorflow/core/framework/local_rendezvous.cc:404] Local rendezvous is aborting with status: OUT_OF_RANGE: End of sequence
将文本行批次传递给 decode_csv 运行速度更快,大约需要 5 秒
fonts_files = tf.data.Dataset.list_files("fonts/*.csv")
fonts_lines = fonts_files.interleave(
lambda fname:tf.data.TextLineDataset(fname).skip(1),
cycle_length=100).batch(BATCH_SIZE)
fonts_fast = fonts_lines.map(lambda x: tf.io.decode_csv(x, record_defaults=font_column_types))
%%time
for i,batch in enumerate(fonts_fast.take(20)):
print('.',end='')
print()
.................... CPU times: user 3.35 s, sys: 111 ms, total: 3.47 s Wall time: 752 ms 2024-07-13 05:32:44.690941: W tensorflow/core/framework/local_rendezvous.cc:404] Local rendezvous is aborting with status: OUT_OF_RANGE: End of sequence
有关通过使用大型批次来提高 CSV 性能的另一个示例,请参阅 过度拟合和欠拟合教程。
这种方法可能有效,但请考虑其他选项,例如 Dataset.cache 和 tf.data.Dataset.snapshot,或者将您的数据重新编码为更简化的格式。
