 在 TensorFlow.org 上查看 在 TensorFlow.org 上查看
|
 在 Google Colab 中运行 在 Google Colab 中运行
|
 在 GitHub 上查看源代码 在 GitHub 上查看源代码
|
 下载笔记本 下载笔记本
|
概述
此笔记本展示了如何使用 TensorFlow Compression 压缩模型。
在下面的示例中,我们将 MNIST 分类器的权重压缩到比其浮点表示小得多的尺寸,同时保持分类精度。这通过基于论文 Scalable Model Compression by Entropy Penalized Reparameterization 的两步过程完成。
在训练期间使用显式的熵惩罚训练“可压缩”模型,这鼓励模型参数的可压缩性。此惩罚的权重 \(\lambda\) 使得能够连续控制压缩模型大小与其精度之间的权衡。
使用与惩罚相匹配的编码方案将可压缩模型编码为压缩模型,这意味着惩罚是模型大小的良好预测器。这确保了该方法不需要多次训练、压缩和重新训练模型以进行微调。
此方法严格关注压缩模型大小,而不是计算复杂度。它可以与模型修剪等技术结合使用以减少大小和复杂度。
各种模型的示例压缩结果
| 模型(数据集) | 模型大小 | 压缩率 | Top-1 错误压缩(未压缩) |
|---|---|---|---|
| LeNet300-100 (MNIST) | 8.56 KB | 124x | 1.9% (1.6%) |
| LeNet5-Caffe (MNIST) | 2.84 KB | 606x | 1.0% (0.7%) |
| VGG-16 (CIFAR-10) | 101 KB | 590x | 10.0% (6.6%) |
| ResNet-20-4 (CIFAR-10) | 128 KB | 134x | 8.8% (5.0%) |
| ResNet-18 (ImageNet) | 1.97 MB | 24x | 30.0% (30.0%) |
| ResNet-50 (ImageNet) | 5.49 MB | 19x | 26.0% (25.0%) |
应用包括
- 大规模将模型部署/广播到边缘设备,节省传输带宽。
- 在联邦学习中将全局模型状态传达给客户端。模型架构(隐藏单元数量等)与初始模型保持一致,客户端可以继续在解压缩模型上学习。
- 在内存极其有限的客户端上执行推理。在推理期间,可以按顺序解压缩每一层的权重,并在计算激活后立即丢弃。
设置
通过 pip 安装 Tensorflow Compression。
# Installs the latest version of TFC compatible with the installed TF version.read MAJOR MINOR <<< "$(pip show tensorflow | perl -p -0777 -e 's/.*Version: (\d+)\.(\d+).*/\1 \2/sg')"pip install "tensorflow-compression<$MAJOR.$(($MINOR+1))"
ERROR: pip's dependency resolver does not currently take into account all the packages that are installed. This behaviour is the source of the following dependency conflicts. tf-keras 2.16.0 requires tensorflow<2.17,>=2.16, but you have tensorflow 2.14.1 which is incompatible.
导入库依赖项。
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import tensorflow as tf
import tensorflow_compression as tfc
import tensorflow_datasets as tfds
2024-07-13 06:14:49.769559: E tensorflow/compiler/xla/stream_executor/cuda/cuda_dnn.cc:9342] Unable to register cuDNN factory: Attempting to register factory for plugin cuDNN when one has already been registered 2024-07-13 06:14:49.769599: E tensorflow/compiler/xla/stream_executor/cuda/cuda_fft.cc:609] Unable to register cuFFT factory: Attempting to register factory for plugin cuFFT when one has already been registered 2024-07-13 06:14:49.769638: E tensorflow/compiler/xla/stream_executor/cuda/cuda_blas.cc:1518] Unable to register cuBLAS factory: Attempting to register factory for plugin cuBLAS when one has already been registered
定义和训练一个基本的 MNIST 分类器
为了有效地压缩密集层和卷积层,我们需要定义自定义层类。这些类似于 tf.keras.layers 下的层,但我们将在稍后对其进行子类化以有效地实现熵惩罚重新参数化 (EPR)。为此,我们还添加了一个复制构造函数。
首先,我们定义一个标准的密集层
class CustomDense(tf.keras.layers.Layer):
def __init__(self, filters, name="dense"):
super().__init__(name=name)
self.filters = filters
@classmethod
def copy(cls, other, **kwargs):
"""Returns an instantiated and built layer, initialized from `other`."""
self = cls(filters=other.filters, name=other.name, **kwargs)
self.build(None, other=other)
return self
def build(self, input_shape, other=None):
"""Instantiates weights, optionally initializing them from `other`."""
if other is None:
kernel_shape = (input_shape[-1], self.filters)
kernel = tf.keras.initializers.GlorotUniform()(shape=kernel_shape)
bias = tf.keras.initializers.Zeros()(shape=(self.filters,))
else:
kernel, bias = other.kernel, other.bias
self.kernel = tf.Variable(
tf.cast(kernel, self.variable_dtype), name="kernel")
self.bias = tf.Variable(
tf.cast(bias, self.variable_dtype), name="bias")
self.built = True
def call(self, inputs):
outputs = tf.linalg.matvec(self.kernel, inputs, transpose_a=True)
outputs = tf.nn.bias_add(outputs, self.bias)
return tf.nn.leaky_relu(outputs)
类似地,一个二维卷积层
class CustomConv2D(tf.keras.layers.Layer):
def __init__(self, filters, kernel_size,
strides=1, padding="SAME", name="conv2d"):
super().__init__(name=name)
self.filters = filters
self.kernel_size = kernel_size
self.strides = strides
self.padding = padding
@classmethod
def copy(cls, other, **kwargs):
"""Returns an instantiated and built layer, initialized from `other`."""
self = cls(filters=other.filters, kernel_size=other.kernel_size,
strides=other.strides, padding=other.padding, name=other.name,
**kwargs)
self.build(None, other=other)
return self
def build(self, input_shape, other=None):
"""Instantiates weights, optionally initializing them from `other`."""
if other is None:
kernel_shape = 2 * (self.kernel_size,) + (input_shape[-1], self.filters)
kernel = tf.keras.initializers.GlorotUniform()(shape=kernel_shape)
bias = tf.keras.initializers.Zeros()(shape=(self.filters,))
else:
kernel, bias = other.kernel, other.bias
self.kernel = tf.Variable(
tf.cast(kernel, self.variable_dtype), name="kernel")
self.bias = tf.Variable(
tf.cast(bias, self.variable_dtype), name="bias")
self.built = True
def call(self, inputs):
outputs = tf.nn.convolution(
inputs, self.kernel, strides=self.strides, padding=self.padding)
outputs = tf.nn.bias_add(outputs, self.bias)
return tf.nn.leaky_relu(outputs)
在我们继续进行模型压缩之前,让我们检查一下我们是否可以成功地训练一个常规分类器。
定义模型架构
classifier = tf.keras.Sequential([
CustomConv2D(20, 5, strides=2, name="conv_1"),
CustomConv2D(50, 5, strides=2, name="conv_2"),
tf.keras.layers.Flatten(),
CustomDense(500, name="fc_1"),
CustomDense(10, name="fc_2"),
], name="classifier")
2024-07-13 06:14:53.116748: W tensorflow/core/common_runtime/gpu/gpu_device.cc:2211] Cannot dlopen some GPU libraries. Please make sure the missing libraries mentioned above are installed properly if you would like to use GPU. Follow the guide at https://tensorflowcn.cn/install/gpu for how to download and setup the required libraries for your platform. Skipping registering GPU devices...
加载训练数据
def normalize_img(image, label):
"""Normalizes images: `uint8` -> `float32`."""
return tf.cast(image, tf.float32) / 255., label
training_dataset, validation_dataset = tfds.load(
"mnist",
split=["train", "test"],
shuffle_files=True,
as_supervised=True,
with_info=False,
)
training_dataset = training_dataset.map(normalize_img)
validation_dataset = validation_dataset.map(normalize_img)
最后,训练模型
def train_model(model, training_data, validation_data, **kwargs):
model.compile(
optimizer=tf.keras.optimizers.Adam(learning_rate=1e-3),
loss=tf.keras.losses.SparseCategoricalCrossentropy(from_logits=True),
metrics=[tf.keras.metrics.SparseCategoricalAccuracy()],
# Uncomment this to ease debugging:
# run_eagerly=True,
)
kwargs.setdefault("epochs", 5)
kwargs.setdefault("verbose", 1)
log = model.fit(
training_data.batch(128).prefetch(8),
validation_data=validation_data.batch(128).cache(),
validation_freq=1,
**kwargs,
)
return log.history["val_sparse_categorical_accuracy"][-1]
classifier_accuracy = train_model(
classifier, training_dataset, validation_dataset)
print(f"Accuracy: {classifier_accuracy:0.4f}")
Epoch 1/5 469/469 [==============================] - 51s 106ms/step - loss: 0.2019 - sparse_categorical_accuracy: 0.9396 - val_loss: 0.0729 - val_sparse_categorical_accuracy: 0.9771 Epoch 2/5 469/469 [==============================] - 49s 105ms/step - loss: 0.0638 - sparse_categorical_accuracy: 0.9806 - val_loss: 0.0647 - val_sparse_categorical_accuracy: 0.9774 Epoch 3/5 469/469 [==============================] - 49s 105ms/step - loss: 0.0440 - sparse_categorical_accuracy: 0.9864 - val_loss: 0.0518 - val_sparse_categorical_accuracy: 0.9828 Epoch 4/5 469/469 [==============================] - 49s 105ms/step - loss: 0.0323 - sparse_categorical_accuracy: 0.9904 - val_loss: 0.0564 - val_sparse_categorical_accuracy: 0.9830 Epoch 5/5 469/469 [==============================] - 49s 105ms/step - loss: 0.0258 - sparse_categorical_accuracy: 0.9919 - val_loss: 0.0611 - val_sparse_categorical_accuracy: 0.9840 Accuracy: 0.9840
成功!该模型训练良好,并在 5 个 epoch 内在验证集上达到了超过 98% 的准确率。
训练一个可压缩的分类器
熵惩罚重新参数化 (EPR) 有两个主要成分
在训练期间对模型权重应用惩罚,该惩罚对应于它们在概率模型下的熵,该模型与权重的编码方案相匹配。下面,我们定义了一个 Keras
Regularizer来实现此惩罚。重新参数化权重,即将其带入更可压缩的潜在表示(在可压缩性和模型性能之间取得更好的权衡)。对于卷积核,已经证明 傅立叶域是一个很好的表示。对于其他参数,以下示例只是使用具有不同量化步长的标量量化(舍入)。
首先,定义惩罚。
以下示例使用在 tfc.PowerLawEntropyModel 类中实现的代码/概率模型,灵感来自论文 Optimizing the Communication-Accuracy Trade-off in Federated Learning with Rate-Distortion Theory。惩罚定义为
\[ \log \Bigl(\frac {|x| + \alpha} \alpha\Bigr), \]
其中 \(x\) 是模型参数或其潜在表示的一个元素,而 \(\alpha\) 是一个小的常数,用于在 0 附近的值的数值稳定性。
_ = tf.linspace(-5., 5., 501)
plt.plot(_, tfc.PowerLawEntropyModel(0).penalty(_));
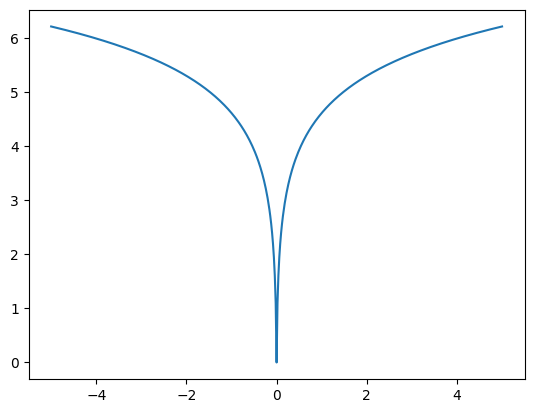
惩罚实际上是一个正则化损失(有时称为“权重损失”)。它在零处具有尖点的凹性鼓励权重稀疏性。用于压缩权重的编码方案,即 Elias gamma 编码,为元素的大小生成长度为 \( 1 + \lfloor \log_2 |x| \rfloor \) 位的代码。也就是说,它与惩罚相匹配,因此应用惩罚会最小化预期代码长度。
class PowerLawRegularizer(tf.keras.regularizers.Regularizer):
def __init__(self, lmbda):
super().__init__()
self.lmbda = lmbda
def __call__(self, variable):
em = tfc.PowerLawEntropyModel(coding_rank=variable.shape.rank)
return self.lmbda * em.penalty(variable)
# Normalizing the weight of the penalty by the number of model parameters is a
# good rule of thumb to produce comparable results across models.
regularizer = PowerLawRegularizer(lmbda=2./classifier.count_params())
其次,定义 CustomDense 和 CustomConv2D 的子类,它们具有以下附加功能
- 它们接受上述正则化器的实例,并在训练期间将其应用于内核和偏差。
- 它们将内核和偏差定义为
@property,只要访问变量,它们就会执行具有直通梯度的量化。这准确地反映了稍后在压缩模型中执行的计算。 - 它们定义了额外的
log_step变量,它们表示量化步长大小的对数。量化越粗糙,模型大小越小,但精度越低。量化步长大小对于每个模型参数都是可训练的,因此对惩罚损失函数执行优化将确定哪个量化步长大小是最好的。
量化步长定义如下
def quantize(latent, log_step):
step = tf.exp(log_step)
return tfc.round_st(latent / step) * step
有了它,我们可以定义密集层
class CompressibleDense(CustomDense):
def __init__(self, regularizer, *args, **kwargs):
super().__init__(*args, **kwargs)
self.regularizer = regularizer
def build(self, input_shape, other=None):
"""Instantiates weights, optionally initializing them from `other`."""
super().build(input_shape, other=other)
if other is not None and hasattr(other, "kernel_log_step"):
kernel_log_step = other.kernel_log_step
bias_log_step = other.bias_log_step
else:
kernel_log_step = bias_log_step = -4.
self.kernel_log_step = tf.Variable(
tf.cast(kernel_log_step, self.variable_dtype), name="kernel_log_step")
self.bias_log_step = tf.Variable(
tf.cast(bias_log_step, self.variable_dtype), name="bias_log_step")
self.add_loss(lambda: self.regularizer(
self.kernel_latent / tf.exp(self.kernel_log_step)))
self.add_loss(lambda: self.regularizer(
self.bias_latent / tf.exp(self.bias_log_step)))
@property
def kernel(self):
return quantize(self.kernel_latent, self.kernel_log_step)
@kernel.setter
def kernel(self, kernel):
self.kernel_latent = tf.Variable(kernel, name="kernel_latent")
@property
def bias(self):
return quantize(self.bias_latent, self.bias_log_step)
@bias.setter
def bias(self, bias):
self.bias_latent = tf.Variable(bias, name="bias_latent")
卷积层类似。此外,只要设置内核,卷积内核就会以其实值离散傅立叶变换 (RDFT) 的形式存储,并且只要使用内核,就会对变换进行反转。由于内核的不同频率分量往往或多或少地可压缩,因此每个分量都分配了它自己的量化步长大小。
定义傅立叶变换及其逆如下
def to_rdft(kernel, kernel_size):
# The kernel has shape (H, W, I, O) -> transpose to take DFT over last two
# dimensions.
kernel = tf.transpose(kernel, (2, 3, 0, 1))
# The RDFT has type complex64 and shape (I, O, FH, FW).
kernel_rdft = tf.signal.rfft2d(kernel)
# Map real and imaginary parts into regular floats. The result is float32
# and has shape (I, O, FH, FW, 2).
kernel_rdft = tf.stack(
[tf.math.real(kernel_rdft), tf.math.imag(kernel_rdft)], axis=-1)
# Divide by kernel size to make the DFT orthonormal (length-preserving).
return kernel_rdft / kernel_size
def from_rdft(kernel_rdft, kernel_size):
# Undoes the transformations in to_rdft.
kernel_rdft *= kernel_size
kernel_rdft = tf.dtypes.complex(*tf.unstack(kernel_rdft, axis=-1))
kernel = tf.signal.irfft2d(kernel_rdft, fft_length=2 * (kernel_size,))
return tf.transpose(kernel, (2, 3, 0, 1))
有了它,将卷积层定义为
class CompressibleConv2D(CustomConv2D):
def __init__(self, regularizer, *args, **kwargs):
super().__init__(*args, **kwargs)
self.regularizer = regularizer
def build(self, input_shape, other=None):
"""Instantiates weights, optionally initializing them from `other`."""
super().build(input_shape, other=other)
if other is not None and hasattr(other, "kernel_log_step"):
kernel_log_step = other.kernel_log_step
bias_log_step = other.bias_log_step
else:
kernel_log_step = tf.fill(self.kernel_latent.shape[2:], -4.)
bias_log_step = -4.
self.kernel_log_step = tf.Variable(
tf.cast(kernel_log_step, self.variable_dtype), name="kernel_log_step")
self.bias_log_step = tf.Variable(
tf.cast(bias_log_step, self.variable_dtype), name="bias_log_step")
self.add_loss(lambda: self.regularizer(
self.kernel_latent / tf.exp(self.kernel_log_step)))
self.add_loss(lambda: self.regularizer(
self.bias_latent / tf.exp(self.bias_log_step)))
@property
def kernel(self):
kernel_rdft = quantize(self.kernel_latent, self.kernel_log_step)
return from_rdft(kernel_rdft, self.kernel_size)
@kernel.setter
def kernel(self, kernel):
kernel_rdft = to_rdft(kernel, self.kernel_size)
self.kernel_latent = tf.Variable(kernel_rdft, name="kernel_latent")
@property
def bias(self):
return quantize(self.bias_latent, self.bias_log_step)
@bias.setter
def bias(self, bias):
self.bias_latent = tf.Variable(bias, name="bias_latent")
定义一个与上述架构相同的分类器模型,但使用这些修改后的层
def make_mnist_classifier(regularizer):
return tf.keras.Sequential([
CompressibleConv2D(regularizer, 20, 5, strides=2, name="conv_1"),
CompressibleConv2D(regularizer, 50, 5, strides=2, name="conv_2"),
tf.keras.layers.Flatten(),
CompressibleDense(regularizer, 500, name="fc_1"),
CompressibleDense(regularizer, 10, name="fc_2"),
], name="classifier")
compressible_classifier = make_mnist_classifier(regularizer)
并训练模型
penalized_accuracy = train_model(
compressible_classifier, training_dataset, validation_dataset)
print(f"Accuracy: {penalized_accuracy:0.4f}")
Epoch 1/5 469/469 [==============================] - 55s 113ms/step - loss: 3.7981 - sparse_categorical_accuracy: 0.9287 - val_loss: 2.1786 - val_sparse_categorical_accuracy: 0.9713 Epoch 2/5 469/469 [==============================] - 53s 112ms/step - loss: 1.6769 - sparse_categorical_accuracy: 0.9763 - val_loss: 1.3201 - val_sparse_categorical_accuracy: 0.9791 Epoch 3/5 469/469 [==============================] - 53s 113ms/step - loss: 1.0883 - sparse_categorical_accuracy: 0.9836 - val_loss: 0.9567 - val_sparse_categorical_accuracy: 0.9826 Epoch 4/5 469/469 [==============================] - 53s 113ms/step - loss: 0.8137 - sparse_categorical_accuracy: 0.9865 - val_loss: 0.7832 - val_sparse_categorical_accuracy: 0.9835 Epoch 5/5 469/469 [==============================] - 53s 113ms/step - loss: 0.6752 - sparse_categorical_accuracy: 0.9881 - val_loss: 0.7038 - val_sparse_categorical_accuracy: 0.9836 Accuracy: 0.9836
可压缩模型已达到与普通分类器相似的精度。
但是,该模型尚未真正压缩。为此,我们定义了另一组子类,它们以压缩形式(作为一系列位)存储内核和偏差。
压缩分类器
下面定义的 CustomDense 和 CustomConv2D 的子类将可压缩密集层的权重转换为二进制字符串。此外,它们以半精度存储量化步长大小的对数以节省空间。只要通过 @property 访问内核或偏差,它们就会从其字符串表示中解压缩并解量化。
首先,定义压缩和解压缩模型参数的函数
def compress_latent(latent, log_step, name):
em = tfc.PowerLawEntropyModel(latent.shape.rank)
compressed = em.compress(latent / tf.exp(log_step))
compressed = tf.Variable(compressed, name=f"{name}_compressed")
log_step = tf.cast(log_step, tf.float16)
log_step = tf.Variable(log_step, name=f"{name}_log_step")
return compressed, log_step
def decompress_latent(compressed, shape, log_step):
latent = tfc.PowerLawEntropyModel(len(shape)).decompress(compressed, shape)
step = tf.exp(tf.cast(log_step, latent.dtype))
return latent * step
有了这些,我们可以定义 CompressedDense
class CompressedDense(CustomDense):
def build(self, input_shape, other=None):
assert isinstance(other, CompressibleDense)
self.input_channels = other.kernel.shape[0]
self.kernel_compressed, self.kernel_log_step = compress_latent(
other.kernel_latent, other.kernel_log_step, "kernel")
self.bias_compressed, self.bias_log_step = compress_latent(
other.bias_latent, other.bias_log_step, "bias")
self.built = True
@property
def kernel(self):
kernel_shape = (self.input_channels, self.filters)
return decompress_latent(
self.kernel_compressed, kernel_shape, self.kernel_log_step)
@property
def bias(self):
bias_shape = (self.filters,)
return decompress_latent(
self.bias_compressed, bias_shape, self.bias_log_step)
卷积层类类似于上述内容。
class CompressedConv2D(CustomConv2D):
def build(self, input_shape, other=None):
assert isinstance(other, CompressibleConv2D)
self.input_channels = other.kernel.shape[2]
self.kernel_compressed, self.kernel_log_step = compress_latent(
other.kernel_latent, other.kernel_log_step, "kernel")
self.bias_compressed, self.bias_log_step = compress_latent(
other.bias_latent, other.bias_log_step, "bias")
self.built = True
@property
def kernel(self):
rdft_shape = (self.input_channels, self.filters,
self.kernel_size, self.kernel_size // 2 + 1, 2)
kernel_rdft = decompress_latent(
self.kernel_compressed, rdft_shape, self.kernel_log_step)
return from_rdft(kernel_rdft, self.kernel_size)
@property
def bias(self):
bias_shape = (self.filters,)
return decompress_latent(
self.bias_compressed, bias_shape, self.bias_log_step)
为了将可压缩模型转换为压缩模型,我们可以方便地使用 clone_model 函数。 compress_layer 将任何可压缩层转换为压缩层,并简单地传递任何其他类型的层(例如 Flatten 等)。
def compress_layer(layer):
if isinstance(layer, CompressibleDense):
return CompressedDense.copy(layer)
if isinstance(layer, CompressibleConv2D):
return CompressedConv2D.copy(layer)
return type(layer).from_config(layer.get_config())
compressed_classifier = tf.keras.models.clone_model(
compressible_classifier, clone_function=compress_layer)
现在,让我们验证压缩模型是否按预期执行
compressed_classifier.compile(metrics=[tf.keras.metrics.SparseCategoricalAccuracy()])
_, compressed_accuracy = compressed_classifier.evaluate(validation_dataset.batch(128))
print(f"Accuracy of the compressible classifier: {penalized_accuracy:0.4f}")
print(f"Accuracy of the compressed classifier: {compressed_accuracy:0.4f}")
79/79 [==============================] - 1s 10ms/step - loss: 0.0000e+00 - sparse_categorical_accuracy: 0.9836 Accuracy of the compressible classifier: 0.9836 Accuracy of the compressed classifier: 0.9836
压缩模型的分类精度与训练期间达到的精度相同!
此外,压缩模型权重的大小远小于原始模型大小
def get_weight_size_in_bytes(weight):
if weight.dtype == tf.string:
return tf.reduce_sum(tf.strings.length(weight, unit="BYTE"))
else:
return tf.size(weight) * weight.dtype.size
original_size = sum(map(get_weight_size_in_bytes, classifier.weights))
compressed_size = sum(map(get_weight_size_in_bytes, compressed_classifier.weights))
print(f"Size of original model weights: {original_size} bytes")
print(f"Size of compressed model weights: {compressed_size} bytes")
print(f"Compression ratio: {(original_size/compressed_size):0.0f}x")
Size of original model weights: 5024320 bytes Size of compressed model weights: 19458 bytes Compression ratio: 258x
在磁盘上存储模型需要一些开销来存储模型架构、函数图等。
ZIP 等无损压缩方法擅长压缩此类数据,但不能压缩权重本身。这就是为什么在应用 ZIP 压缩后,即使在计算包含该开销的模型大小后,EPR 仍然具有显著优势的原因
import os
import shutil
def get_disk_size(model, path):
model.save(path)
zip_path = shutil.make_archive(path, "zip", path)
return os.path.getsize(zip_path)
original_zip_size = get_disk_size(classifier, "/tmp/classifier")
compressed_zip_size = get_disk_size(
compressed_classifier, "/tmp/compressed_classifier")
print(f"Original on-disk size (ZIP compressed): {original_zip_size} bytes")
print(f"Compressed on-disk size (ZIP compressed): {compressed_zip_size} bytes")
print(f"Compression ratio: {(original_zip_size/compressed_zip_size):0.0f}x")
INFO:tensorflow:Assets written to: /tmp/classifier/assets INFO:tensorflow:Assets written to: /tmp/classifier/assets INFO:tensorflow:Assets written to: /tmp/compressed_classifier/assets INFO:tensorflow:Assets written to: /tmp/compressed_classifier/assets Original on-disk size (ZIP compressed): 13906612 bytes Compressed on-disk size (ZIP compressed): 61588 bytes Compression ratio: 226x
正则化效果和大小-精度权衡
上面,\(\lambda\) 超参数设置为 2(按模型中参数的数量进行归一化)。随着我们增加 \(\lambda\),模型权重因可压缩性而受到越来越大的惩罚。
对于较低的值,惩罚可以像权重正则化器一样起作用。它实际上对分类器的泛化性能有益,并且可以导致验证数据集上的精度略微提高
Accuracy of the vanilla classifier: 0.9840 Accuracy of the penalized classifier: 0.9836
对于较高的值,我们看到模型大小越来越小,但精度也逐渐下降。为了看到这一点,让我们训练几个模型并绘制它们的大小与精度
def compress_and_evaluate_model(lmbda):
print(f"lambda={lmbda:0.0f}: training...", flush=True)
regularizer = PowerLawRegularizer(lmbda=lmbda/classifier.count_params())
compressible_classifier = make_mnist_classifier(regularizer)
train_model(
compressible_classifier, training_dataset, validation_dataset, verbose=0)
print("compressing...", flush=True)
compressed_classifier = tf.keras.models.clone_model(
compressible_classifier, clone_function=compress_layer)
compressed_size = sum(map(
get_weight_size_in_bytes, compressed_classifier.weights))
compressed_zip_size = float(get_disk_size(
compressed_classifier, "/tmp/compressed_classifier"))
print("evaluating...", flush=True)
compressed_classifier = tf.keras.models.load_model(
"/tmp/compressed_classifier")
compressed_classifier.compile(
metrics=[tf.keras.metrics.SparseCategoricalAccuracy()])
_, compressed_accuracy = compressed_classifier.evaluate(
validation_dataset.batch(128), verbose=0)
print()
return compressed_size, compressed_zip_size, compressed_accuracy
lambdas = (2., 5., 10., 20., 50.)
metrics = [compress_and_evaluate_model(l) for l in lambdas]
metrics = tf.convert_to_tensor(metrics, tf.float32)
lambda=2: training... compressing... WARNING:tensorflow:Compiled the loaded model, but the compiled metrics have yet to be built. `model.compile_metrics` will be empty until you train or evaluate the model. WARNING:tensorflow:Compiled the loaded model, but the compiled metrics have yet to be built. `model.compile_metrics` will be empty until you train or evaluate the model. INFO:tensorflow:Assets written to: /tmp/compressed_classifier/assets INFO:tensorflow:Assets written to: /tmp/compressed_classifier/assets evaluating... WARNING:tensorflow:No training configuration found in save file, so the model was *not* compiled. Compile it manually. WARNING:tensorflow:No training configuration found in save file, so the model was *not* compiled. Compile it manually. lambda=5: training... compressing... WARNING:tensorflow:Compiled the loaded model, but the compiled metrics have yet to be built. `model.compile_metrics` will be empty until you train or evaluate the model. WARNING:tensorflow:Compiled the loaded model, but the compiled metrics have yet to be built. `model.compile_metrics` will be empty until you train or evaluate the model. INFO:tensorflow:Assets written to: /tmp/compressed_classifier/assets INFO:tensorflow:Assets written to: /tmp/compressed_classifier/assets evaluating... WARNING:tensorflow:No training configuration found in save file, so the model was *not* compiled. Compile it manually. WARNING:tensorflow:No training configuration found in save file, so the model was *not* compiled. Compile it manually. lambda=10: training... compressing... WARNING:tensorflow:Compiled the loaded model, but the compiled metrics have yet to be built. `model.compile_metrics` will be empty until you train or evaluate the model. WARNING:tensorflow:Compiled the loaded model, but the compiled metrics have yet to be built. `model.compile_metrics` will be empty until you train or evaluate the model. INFO:tensorflow:Assets written to: /tmp/compressed_classifier/assets INFO:tensorflow:Assets written to: /tmp/compressed_classifier/assets evaluating... WARNING:tensorflow:No training configuration found in save file, so the model was *not* compiled. Compile it manually. WARNING:tensorflow:No training configuration found in save file, so the model was *not* compiled. Compile it manually. lambda=20: training... compressing... WARNING:tensorflow:Compiled the loaded model, but the compiled metrics have yet to be built. `model.compile_metrics` will be empty until you train or evaluate the model. WARNING:tensorflow:Compiled the loaded model, but the compiled metrics have yet to be built. `model.compile_metrics` will be empty until you train or evaluate the model. INFO:tensorflow:Assets written to: /tmp/compressed_classifier/assets INFO:tensorflow:Assets written to: /tmp/compressed_classifier/assets evaluating... WARNING:tensorflow:No training configuration found in save file, so the model was *not* compiled. Compile it manually. WARNING:tensorflow:No training configuration found in save file, so the model was *not* compiled. Compile it manually. lambda=50: training... compressing... WARNING:tensorflow:Compiled the loaded model, but the compiled metrics have yet to be built. `model.compile_metrics` will be empty until you train or evaluate the model. WARNING:tensorflow:Compiled the loaded model, but the compiled metrics have yet to be built. `model.compile_metrics` will be empty until you train or evaluate the model. INFO:tensorflow:Assets written to: /tmp/compressed_classifier/assets INFO:tensorflow:Assets written to: /tmp/compressed_classifier/assets evaluating... WARNING:tensorflow:No training configuration found in save file, so the model was *not* compiled. Compile it manually. WARNING:tensorflow:No training configuration found in save file, so the model was *not* compiled. Compile it manually.
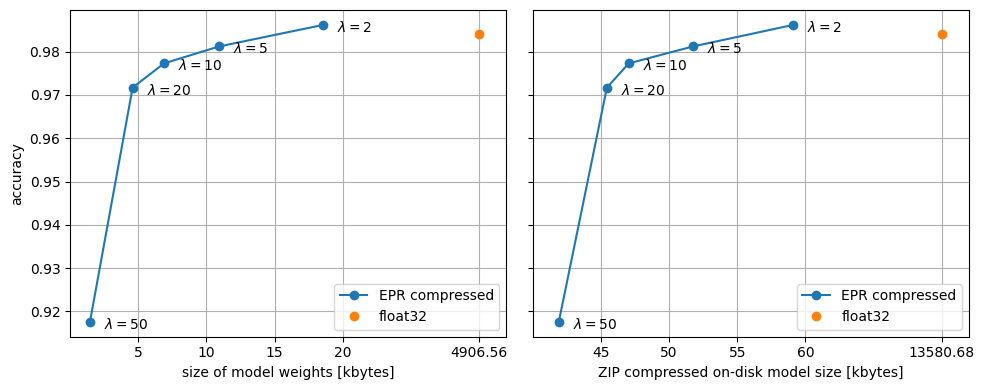
该图应该理想地显示出肘部形状的大小-精度权衡,但精度指标有些嘈杂是正常的。根据初始化,曲线可能会出现一些扭结。
由于正则化效果,对于 \(\lambda\) 的较小值,EPR 压缩模型在测试集上的精度高于原始模型。即使我们比较 ZIP 压缩后的尺寸,EPR 压缩模型也小得多。
解压缩分类器
CompressedDense 和 CompressedConv2D 在每次前向传递时都会解压缩它们的权重。这使得它们非常适合内存有限的设备,但解压缩在计算上可能很昂贵,尤其是对于较小的批次大小。
为了解压缩模型一次,并将其用于进一步训练或推理,我们可以将其转换回使用常规层或可压缩层的模型。这在模型部署或联邦学习场景中可能很有用。
首先,转换回普通模型,我们可以进行推理,以及/或者继续进行没有压缩惩罚的常规训练
def decompress_layer(layer):
if isinstance(layer, CompressedDense):
return CustomDense.copy(layer)
if isinstance(layer, CompressedConv2D):
return CustomConv2D.copy(layer)
return type(layer).from_config(layer.get_config())
decompressed_classifier = tf.keras.models.clone_model(
compressed_classifier, clone_function=decompress_layer)
decompressed_accuracy = train_model(
decompressed_classifier, training_dataset, validation_dataset, epochs=1)
print(f"Accuracy of the compressed classifier: {compressed_accuracy:0.4f}")
print(f"Accuracy of the decompressed classifier after one more epoch of training: {decompressed_accuracy:0.4f}")
469/469 [==============================] - 50s 106ms/step - loss: 0.0851 - sparse_categorical_accuracy: 0.9749 - val_loss: 0.0695 - val_sparse_categorical_accuracy: 0.9759 Accuracy of the compressed classifier: 0.9836 Accuracy of the decompressed classifier after one more epoch of training: 0.9759
请注意,在额外训练一个 epoch 后,验证精度下降,因为训练是在没有正则化的情况下完成的。
或者,我们可以将模型转换回“可压缩”模型,用于推理以及/或者使用压缩惩罚进行进一步训练
def decompress_layer_with_penalty(layer):
if isinstance(layer, CompressedDense):
return CompressibleDense.copy(layer, regularizer=regularizer)
if isinstance(layer, CompressedConv2D):
return CompressibleConv2D.copy(layer, regularizer=regularizer)
return type(layer).from_config(layer.get_config())
decompressed_classifier = tf.keras.models.clone_model(
compressed_classifier, clone_function=decompress_layer_with_penalty)
decompressed_accuracy = train_model(
decompressed_classifier, training_dataset, validation_dataset, epochs=1)
print(f"Accuracy of the compressed classifier: {compressed_accuracy:0.4f}")
print(f"Accuracy of the decompressed classifier after one more epoch of training: {decompressed_accuracy:0.4f}")
469/469 [==============================] - 55s 113ms/step - loss: 0.8058 - sparse_categorical_accuracy: 0.9901 - val_loss: 0.8403 - val_sparse_categorical_accuracy: 0.9866 Accuracy of the compressed classifier: 0.9836 Accuracy of the decompressed classifier after one more epoch of training: 0.9866
在这里,在额外训练一个 epoch 后,精度提高了。
