 在 TensorFlow.org 上查看 在 TensorFlow.org 上查看
|
 在 Google Colab 中运行 在 Google Colab 中运行
|
 在 GitHub 上查看源代码 在 GitHub 上查看源代码
|
 下载笔记本 下载笔记本
|
本教程演示了使用 UCF101 动作识别数据集训练 3D 卷积神经网络 (CNN) 进行视频分类。3D CNN 使用三维滤波器执行卷积。内核能够在三个方向上滑动,而在 2D CNN 中,它只能在两个维度上滑动。该模型基于 D. Tran 等人 (2017) 在 深入探究时空卷积在动作识别中的应用 中发表的论文。在本教程中,您将
- 构建输入管道
- 使用 Keras 函数式 API 构建具有残差连接的 3D 卷积神经网络模型
- 训练模型
- 评估和测试模型
本视频分类教程是 TensorFlow 视频教程系列的第二部分。以下是另外三个教程
- 加载视频数据:本教程解释了本文档中使用的许多代码。
- 用于流式动作识别的 MoViNet:熟悉 TF Hub 上可用的 MoViNet 模型。
- 使用 MoViNet 进行视频分类的迁移学习:本教程解释了如何使用在不同数据集上训练的预训练视频分类模型与 UCF-101 数据集一起使用。
设置
首先,安装并导入一些必要的库,包括:remotezip 用于检查 ZIP 文件的内容,tqdm 用于使用进度条,OpenCV 用于处理视频文件,einops 用于执行更复杂的张量操作,以及 tensorflow_docs 用于在 Jupyter 笔记本中嵌入数据。
pip install remotezip tqdm opencv-python einopspip install -U tensorflow keras
import tqdm
import random
import pathlib
import itertools
import collections
import cv2
import einops
import numpy as np
import remotezip as rz
import seaborn as sns
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import tensorflow as tf
import keras
from keras import layers
2024-07-13 04:45:46.026708: E external/local_xla/xla/stream_executor/cuda/cuda_fft.cc:485] Unable to register cuFFT factory: Attempting to register factory for plugin cuFFT when one has already been registered 2024-07-13 04:45:46.048378: E external/local_xla/xla/stream_executor/cuda/cuda_dnn.cc:8454] Unable to register cuDNN factory: Attempting to register factory for plugin cuDNN when one has already been registered 2024-07-13 04:45:46.054995: E external/local_xla/xla/stream_executor/cuda/cuda_blas.cc:1452] Unable to register cuBLAS factory: Attempting to register factory for plugin cuBLAS when one has already been registered
加载和预处理视频数据
下面的隐藏单元格定义了辅助函数,用于从 UCF-101 数据集中下载数据片段,并将其加载到 tf.data.Dataset 中。您可以在 加载视频数据教程 中了解更多关于特定预处理步骤的信息,该教程更详细地介绍了这段代码。
隐藏块末尾的 FrameGenerator 类是这里最重要的工具。它创建一个可迭代对象,可以将数据馈送到 TensorFlow 数据管道。具体来说,这个类包含一个 Python 生成器,它加载视频帧及其编码标签。生成器 (__call__) 函数生成由 frames_from_video_file 生成的帧数组和与帧集关联的标签的独热编码向量。
URL = 'https://storage.googleapis.com/thumos14_files/UCF101_videos.zip'
download_dir = pathlib.Path('./UCF101_subset/')
subset_paths = download_ufc_101_subset(URL,
num_classes = 10,
splits = {"train": 30, "val": 10, "test": 10},
download_dir = download_dir)
train : 100%|██████████| 300/300 [00:25<00:00, 11.66it/s] val : 100%|██████████| 100/100 [00:11<00:00, 8.86it/s] test : 100%|██████████| 100/100 [00:07<00:00, 12.55it/s]
创建训练集、验证集和测试集 (train_ds、val_ds 和 test_ds)。
WARNING: All log messages before absl::InitializeLog() is called are written to STDERR I0000 00:00:1720845994.489541 108593 cuda_executor.cc:1015] successful NUMA node read from SysFS had negative value (-1), but there must be at least one NUMA node, so returning NUMA node zero. See more at https://github.com/torvalds/linux/blob/v6.0/Documentation/ABI/testing/sysfs-bus-pci#L344-L355 I0000 00:00:1720845994.492942 108593 cuda_executor.cc:1015] successful NUMA node read from SysFS had negative value (-1), but there must be at least one NUMA node, so returning NUMA node zero. See more at https://github.com/torvalds/linux/blob/v6.0/Documentation/ABI/testing/sysfs-bus-pci#L344-L355 I0000 00:00:1720845994.496622 108593 cuda_executor.cc:1015] successful NUMA node read from SysFS had negative value (-1), but there must be at least one NUMA node, so returning NUMA node zero. See more at https://github.com/torvalds/linux/blob/v6.0/Documentation/ABI/testing/sysfs-bus-pci#L344-L355 I0000 00:00:1720845994.500437 108593 cuda_executor.cc:1015] successful NUMA node read from SysFS had negative value (-1), but there must be at least one NUMA node, so returning NUMA node zero. See more at https://github.com/torvalds/linux/blob/v6.0/Documentation/ABI/testing/sysfs-bus-pci#L344-L355 I0000 00:00:1720845994.511719 108593 cuda_executor.cc:1015] successful NUMA node read from SysFS had negative value (-1), but there must be at least one NUMA node, so returning NUMA node zero. See more at https://github.com/torvalds/linux/blob/v6.0/Documentation/ABI/testing/sysfs-bus-pci#L344-L355 I0000 00:00:1720845994.514756 108593 cuda_executor.cc:1015] successful NUMA node read from SysFS had negative value (-1), but there must be at least one NUMA node, so returning NUMA node zero. See more at https://github.com/torvalds/linux/blob/v6.0/Documentation/ABI/testing/sysfs-bus-pci#L344-L355 I0000 00:00:1720845994.518313 108593 cuda_executor.cc:1015] successful NUMA node read from SysFS had negative value (-1), but there must be at least one NUMA node, so returning NUMA node zero. See more at https://github.com/torvalds/linux/blob/v6.0/Documentation/ABI/testing/sysfs-bus-pci#L344-L355 I0000 00:00:1720845994.521868 108593 cuda_executor.cc:1015] successful NUMA node read from SysFS had negative value (-1), but there must be at least one NUMA node, so returning NUMA node zero. See more at https://github.com/torvalds/linux/blob/v6.0/Documentation/ABI/testing/sysfs-bus-pci#L344-L355 I0000 00:00:1720845994.525390 108593 cuda_executor.cc:1015] successful NUMA node read from SysFS had negative value (-1), but there must be at least one NUMA node, so returning NUMA node zero. See more at https://github.com/torvalds/linux/blob/v6.0/Documentation/ABI/testing/sysfs-bus-pci#L344-L355 I0000 00:00:1720845994.528375 108593 cuda_executor.cc:1015] successful NUMA node read from SysFS had negative value (-1), but there must be at least one NUMA node, so returning NUMA node zero. See more at https://github.com/torvalds/linux/blob/v6.0/Documentation/ABI/testing/sysfs-bus-pci#L344-L355 I0000 00:00:1720845994.531903 108593 cuda_executor.cc:1015] successful NUMA node read from SysFS had negative value (-1), but there must be at least one NUMA node, so returning NUMA node zero. See more at https://github.com/torvalds/linux/blob/v6.0/Documentation/ABI/testing/sysfs-bus-pci#L344-L355 I0000 00:00:1720845994.535205 108593 cuda_executor.cc:1015] successful NUMA node read from SysFS had negative value (-1), but there must be at least one NUMA node, so returning NUMA node zero. See more at https://github.com/torvalds/linux/blob/v6.0/Documentation/ABI/testing/sysfs-bus-pci#L344-L355 I0000 00:00:1720845995.758719 108593 cuda_executor.cc:1015] successful NUMA node read from SysFS had negative value (-1), but there must be at least one NUMA node, so returning NUMA node zero. See more at https://github.com/torvalds/linux/blob/v6.0/Documentation/ABI/testing/sysfs-bus-pci#L344-L355 I0000 00:00:1720845995.760793 108593 cuda_executor.cc:1015] successful NUMA node read from SysFS had negative value (-1), but there must be at least one NUMA node, so returning NUMA node zero. See more at https://github.com/torvalds/linux/blob/v6.0/Documentation/ABI/testing/sysfs-bus-pci#L344-L355 I0000 00:00:1720845995.762854 108593 cuda_executor.cc:1015] successful NUMA node read from SysFS had negative value (-1), but there must be at least one NUMA node, so returning NUMA node zero. See more at https://github.com/torvalds/linux/blob/v6.0/Documentation/ABI/testing/sysfs-bus-pci#L344-L355 I0000 00:00:1720845995.764914 108593 cuda_executor.cc:1015] successful NUMA node read from SysFS had negative value (-1), but there must be at least one NUMA node, so returning NUMA node zero. See more at https://github.com/torvalds/linux/blob/v6.0/Documentation/ABI/testing/sysfs-bus-pci#L344-L355 I0000 00:00:1720845995.766958 108593 cuda_executor.cc:1015] successful NUMA node read from SysFS had negative value (-1), but there must be at least one NUMA node, so returning NUMA node zero. See more at https://github.com/torvalds/linux/blob/v6.0/Documentation/ABI/testing/sysfs-bus-pci#L344-L355 I0000 00:00:1720845995.768836 108593 cuda_executor.cc:1015] successful NUMA node read from SysFS had negative value (-1), but there must be at least one NUMA node, so returning NUMA node zero. See more at https://github.com/torvalds/linux/blob/v6.0/Documentation/ABI/testing/sysfs-bus-pci#L344-L355 I0000 00:00:1720845995.770780 108593 cuda_executor.cc:1015] successful NUMA node read from SysFS had negative value (-1), but there must be at least one NUMA node, so returning NUMA node zero. See more at https://github.com/torvalds/linux/blob/v6.0/Documentation/ABI/testing/sysfs-bus-pci#L344-L355 I0000 00:00:1720845995.772725 108593 cuda_executor.cc:1015] successful NUMA node read from SysFS had negative value (-1), but there must be at least one NUMA node, so returning NUMA node zero. See more at https://github.com/torvalds/linux/blob/v6.0/Documentation/ABI/testing/sysfs-bus-pci#L344-L355 I0000 00:00:1720845995.774676 108593 cuda_executor.cc:1015] successful NUMA node read from SysFS had negative value (-1), but there must be at least one NUMA node, so returning NUMA node zero. See more at https://github.com/torvalds/linux/blob/v6.0/Documentation/ABI/testing/sysfs-bus-pci#L344-L355 I0000 00:00:1720845995.776556 108593 cuda_executor.cc:1015] successful NUMA node read from SysFS had negative value (-1), but there must be at least one NUMA node, so returning NUMA node zero. See more at https://github.com/torvalds/linux/blob/v6.0/Documentation/ABI/testing/sysfs-bus-pci#L344-L355 I0000 00:00:1720845995.778542 108593 cuda_executor.cc:1015] successful NUMA node read from SysFS had negative value (-1), but there must be at least one NUMA node, so returning NUMA node zero. See more at https://github.com/torvalds/linux/blob/v6.0/Documentation/ABI/testing/sysfs-bus-pci#L344-L355 I0000 00:00:1720845995.780459 108593 cuda_executor.cc:1015] successful NUMA node read from SysFS had negative value (-1), but there must be at least one NUMA node, so returning NUMA node zero. See more at https://github.com/torvalds/linux/blob/v6.0/Documentation/ABI/testing/sysfs-bus-pci#L344-L355 I0000 00:00:1720845995.818786 108593 cuda_executor.cc:1015] successful NUMA node read from SysFS had negative value (-1), but there must be at least one NUMA node, so returning NUMA node zero. See more at https://github.com/torvalds/linux/blob/v6.0/Documentation/ABI/testing/sysfs-bus-pci#L344-L355 I0000 00:00:1720845995.820761 108593 cuda_executor.cc:1015] successful NUMA node read from SysFS had negative value (-1), but there must be at least one NUMA node, so returning NUMA node zero. See more at https://github.com/torvalds/linux/blob/v6.0/Documentation/ABI/testing/sysfs-bus-pci#L344-L355 I0000 00:00:1720845995.822757 108593 cuda_executor.cc:1015] successful NUMA node read from SysFS had negative value (-1), but there must be at least one NUMA node, so returning NUMA node zero. See more at https://github.com/torvalds/linux/blob/v6.0/Documentation/ABI/testing/sysfs-bus-pci#L344-L355 I0000 00:00:1720845995.824858 108593 cuda_executor.cc:1015] successful NUMA node read from SysFS had negative value (-1), but there must be at least one NUMA node, so returning NUMA node zero. See more at https://github.com/torvalds/linux/blob/v6.0/Documentation/ABI/testing/sysfs-bus-pci#L344-L355 I0000 00:00:1720845995.826813 108593 cuda_executor.cc:1015] successful NUMA node read from SysFS had negative value (-1), but there must be at least one NUMA node, so returning NUMA node zero. See more at https://github.com/torvalds/linux/blob/v6.0/Documentation/ABI/testing/sysfs-bus-pci#L344-L355 I0000 00:00:1720845995.828694 108593 cuda_executor.cc:1015] successful NUMA node read from SysFS had negative value (-1), but there must be at least one NUMA node, so returning NUMA node zero. See more at https://github.com/torvalds/linux/blob/v6.0/Documentation/ABI/testing/sysfs-bus-pci#L344-L355 I0000 00:00:1720845995.830617 108593 cuda_executor.cc:1015] successful NUMA node read from SysFS had negative value (-1), but there must be at least one NUMA node, so returning NUMA node zero. See more at https://github.com/torvalds/linux/blob/v6.0/Documentation/ABI/testing/sysfs-bus-pci#L344-L355 I0000 00:00:1720845995.832571 108593 cuda_executor.cc:1015] successful NUMA node read from SysFS had negative value (-1), but there must be at least one NUMA node, so returning NUMA node zero. See more at https://github.com/torvalds/linux/blob/v6.0/Documentation/ABI/testing/sysfs-bus-pci#L344-L355 I0000 00:00:1720845995.834553 108593 cuda_executor.cc:1015] successful NUMA node read from SysFS had negative value (-1), but there must be at least one NUMA node, so returning NUMA node zero. See more at https://github.com/torvalds/linux/blob/v6.0/Documentation/ABI/testing/sysfs-bus-pci#L344-L355 I0000 00:00:1720845995.836944 108593 cuda_executor.cc:1015] successful NUMA node read from SysFS had negative value (-1), but there must be at least one NUMA node, so returning NUMA node zero. See more at https://github.com/torvalds/linux/blob/v6.0/Documentation/ABI/testing/sysfs-bus-pci#L344-L355 I0000 00:00:1720845995.839317 108593 cuda_executor.cc:1015] successful NUMA node read from SysFS had negative value (-1), but there must be at least one NUMA node, so returning NUMA node zero. See more at https://github.com/torvalds/linux/blob/v6.0/Documentation/ABI/testing/sysfs-bus-pci#L344-L355 I0000 00:00:1720845995.841708 108593 cuda_executor.cc:1015] successful NUMA node read from SysFS had negative value (-1), but there must be at least one NUMA node, so returning NUMA node zero. See more at https://github.com/torvalds/linux/blob/v6.0/Documentation/ABI/testing/sysfs-bus-pci#L344-L355
创建模型
以下 3D 卷积神经网络模型基于 D. Tran 等人 (2017) 的论文 A Closer Look at Spatiotemporal Convolutions for Action Recognition。该论文比较了 3D ResNets 的几个版本。这些网络不是像标准 ResNets 那样对具有 (height, width) 维度的单个图像进行操作,而是对 (time, height, width) 的视频体积进行操作。解决这个问题最明显的方法是用 3D 卷积 (layers.Conv3D) 替换每个 2D 卷积 (layers.Conv2D)。
本教程使用具有 残差连接 的 (2 + 1)D 卷积。 (2 + 1)D 卷积允许对空间和时间维度进行分解,因此创建了两个独立的步骤。这种方法的一个优点是,将卷积分解为空间和时间维度可以节省参数。
对于每个输出位置,3D 卷积将来自体积的 3D 补丁中的所有向量组合起来,以在输出体积中创建一个向量。
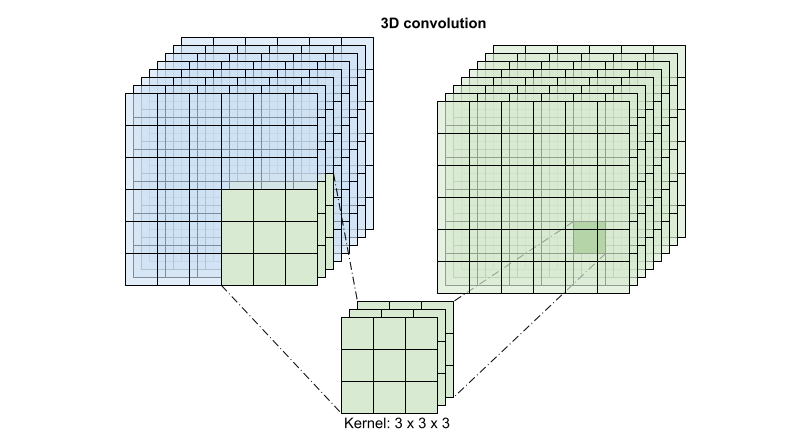
此操作需要 time * height * width * channels 个输入,并产生 channels 个输出(假设输入和输出通道的数量相同。因此,具有 (3 x 3 x 3) 核大小的 3D 卷积层需要一个具有 27 * channels ** 2 个条目的权重矩阵。参考论文发现,更有效和高效的方法是对卷积进行分解。他们建议使用 "(2+1)D" 卷积,它分别处理空间和时间维度,而不是使用单个 3D 卷积来处理时间和空间维度。下图显示了 (2 + 1)D 卷积的分解空间和时间卷积。
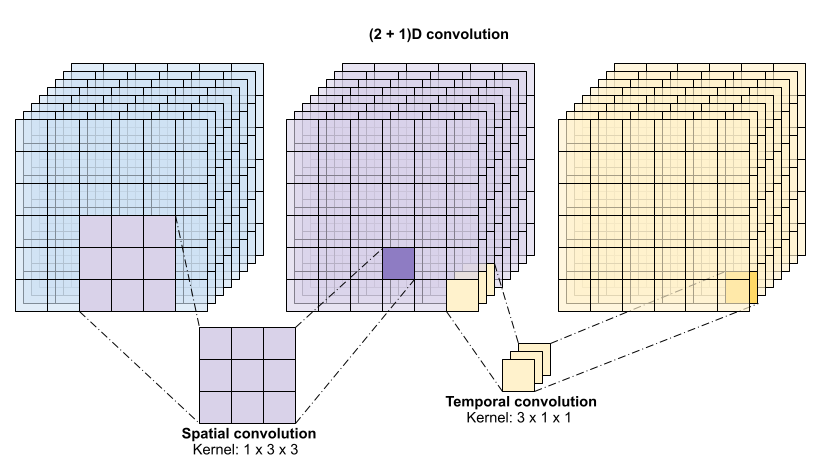
这种方法的主要优点是减少了参数数量。在 (2 + 1)D 卷积中,空间卷积接收形状为 (1, width, height) 的数据,而时间卷积接收形状为 (time, 1, 1) 的数据。例如,具有 (3 x 3 x 3) 核大小的 (2 + 1)D 卷积需要大小为 (9 * channels**2) + (3 * channels**2) 的权重矩阵,不到完整 3D 卷积的一半。本教程实现了 (2 + 1)D ResNet18,其中 ResNet 中的每个卷积都被 (2+1)D 卷积替换。
# Define the dimensions of one frame in the set of frames created
HEIGHT = 224
WIDTH = 224
class Conv2Plus1D(keras.layers.Layer):
def __init__(self, filters, kernel_size, padding):
"""
A sequence of convolutional layers that first apply the convolution operation over the
spatial dimensions, and then the temporal dimension.
"""
super().__init__()
self.seq = keras.Sequential([
# Spatial decomposition
layers.Conv3D(filters=filters,
kernel_size=(1, kernel_size[1], kernel_size[2]),
padding=padding),
# Temporal decomposition
layers.Conv3D(filters=filters,
kernel_size=(kernel_size[0], 1, 1),
padding=padding)
])
def call(self, x):
return self.seq(x)
ResNet 模型由一系列残差块组成。残差块有两个分支。主分支执行计算,但梯度难以流过。残差分支绕过主计算,主要只是将输入添加到主分支的输出。梯度很容易流过这个分支。因此,从损失函数到残差块的任何主分支都会存在一条简单的路径。这避免了梯度消失问题。
使用以下类创建残差块的主分支。与标准 ResNet 结构不同,它使用自定义的 Conv2Plus1D 层,而不是 layers.Conv2D。
class ResidualMain(keras.layers.Layer):
"""
Residual block of the model with convolution, layer normalization, and the
activation function, ReLU.
"""
def __init__(self, filters, kernel_size):
super().__init__()
self.seq = keras.Sequential([
Conv2Plus1D(filters=filters,
kernel_size=kernel_size,
padding='same'),
layers.LayerNormalization(),
layers.ReLU(),
Conv2Plus1D(filters=filters,
kernel_size=kernel_size,
padding='same'),
layers.LayerNormalization()
])
def call(self, x):
return self.seq(x)
要将残差分支添加到主分支,它需要具有相同的大小。下面的 Project 层处理分支上通道数量发生变化的情况。特别是,添加了一系列密集连接层,然后进行归一化。
class Project(keras.layers.Layer):
"""
Project certain dimensions of the tensor as the data is passed through different
sized filters and downsampled.
"""
def __init__(self, units):
super().__init__()
self.seq = keras.Sequential([
layers.Dense(units),
layers.LayerNormalization()
])
def call(self, x):
return self.seq(x)
使用 add_residual_block 在模型的层之间引入跳跃连接。
def add_residual_block(input, filters, kernel_size):
"""
Add residual blocks to the model. If the last dimensions of the input data
and filter size does not match, project it such that last dimension matches.
"""
out = ResidualMain(filters,
kernel_size)(input)
res = input
# Using the Keras functional APIs, project the last dimension of the tensor to
# match the new filter size
if out.shape[-1] != input.shape[-1]:
res = Project(out.shape[-1])(res)
return layers.add([res, out])
调整视频大小对于执行数据的下采样是必要的。特别是,对视频帧进行下采样允许模型检查帧的特定部分,以检测可能特定于某个动作的模式。通过下采样,可以丢弃不必要的信息。此外,调整视频大小将允许进行降维,从而通过模型进行更快的处理。
class ResizeVideo(keras.layers.Layer):
def __init__(self, height, width):
super().__init__()
self.height = height
self.width = width
self.resizing_layer = layers.Resizing(self.height, self.width)
def call(self, video):
"""
Use the einops library to resize the tensor.
Args:
video: Tensor representation of the video, in the form of a set of frames.
Return:
A downsampled size of the video according to the new height and width it should be resized to.
"""
# b stands for batch size, t stands for time, h stands for height,
# w stands for width, and c stands for the number of channels.
old_shape = einops.parse_shape(video, 'b t h w c')
images = einops.rearrange(video, 'b t h w c -> (b t) h w c')
images = self.resizing_layer(images)
videos = einops.rearrange(
images, '(b t) h w c -> b t h w c',
t = old_shape['t'])
return videos
使用 Keras 函数式 API 来构建残差网络。
input_shape = (None, 10, HEIGHT, WIDTH, 3)
input = layers.Input(shape=(input_shape[1:]))
x = input
x = Conv2Plus1D(filters=16, kernel_size=(3, 7, 7), padding='same')(x)
x = layers.BatchNormalization()(x)
x = layers.ReLU()(x)
x = ResizeVideo(HEIGHT // 2, WIDTH // 2)(x)
# Block 1
x = add_residual_block(x, 16, (3, 3, 3))
x = ResizeVideo(HEIGHT // 4, WIDTH // 4)(x)
# Block 2
x = add_residual_block(x, 32, (3, 3, 3))
x = ResizeVideo(HEIGHT // 8, WIDTH // 8)(x)
# Block 3
x = add_residual_block(x, 64, (3, 3, 3))
x = ResizeVideo(HEIGHT // 16, WIDTH // 16)(x)
# Block 4
x = add_residual_block(x, 128, (3, 3, 3))
x = layers.GlobalAveragePooling3D()(x)
x = layers.Flatten()(x)
x = layers.Dense(10)(x)
model = keras.Model(input, x)
frames, label = next(iter(train_ds))
model.build(frames)
# Visualize the model
keras.utils.plot_model(model, expand_nested=True, dpi=60, show_shapes=True)
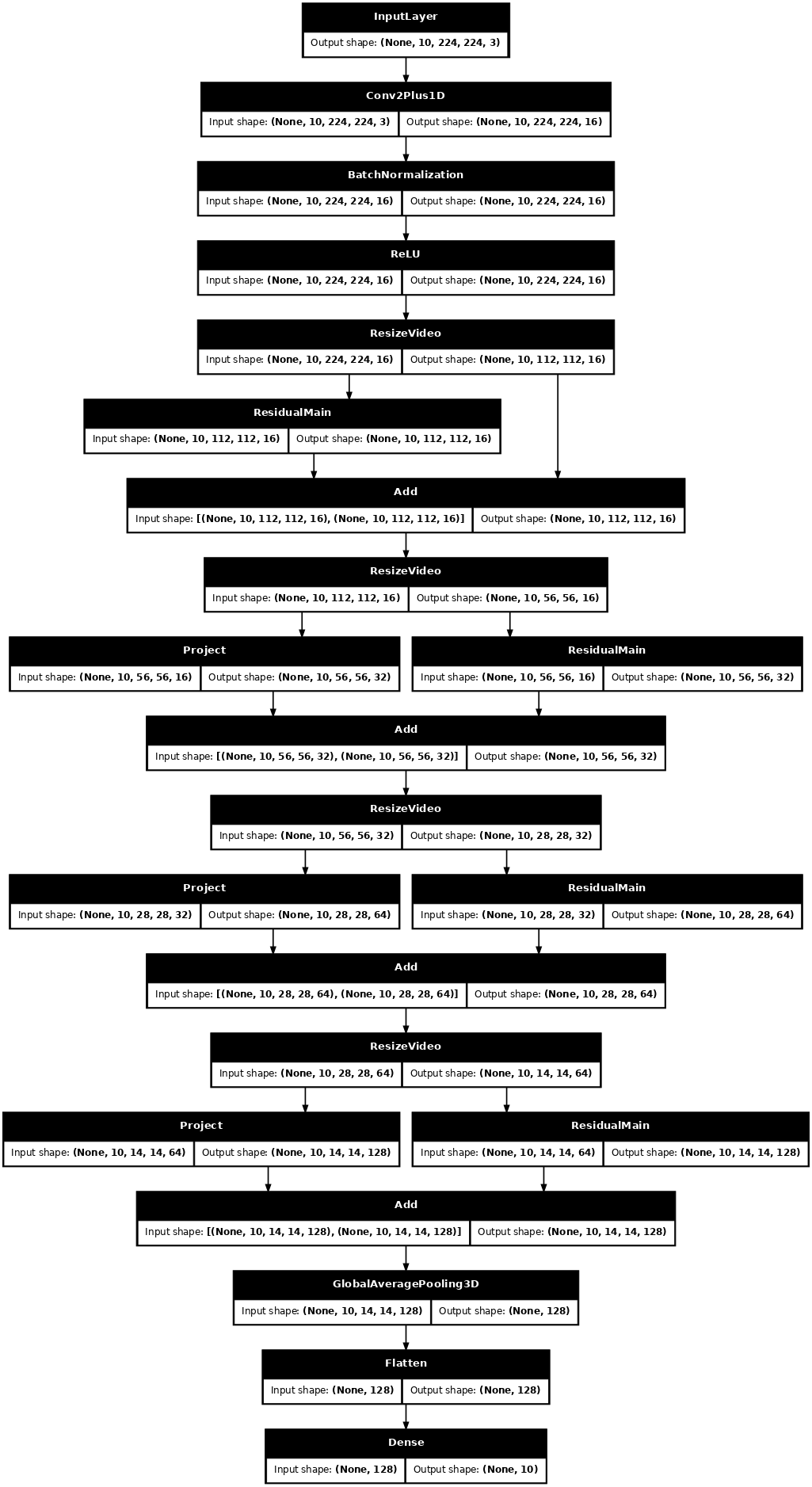
训练模型
在本教程中,选择 tf.keras.optimizers.Adam 优化器和 tf.keras.losses.SparseCategoricalCrossentropy 损失函数。使用 metrics 参数查看模型性能在每一步的准确性。
model.compile(loss = keras.losses.SparseCategoricalCrossentropy(from_logits=True),
optimizer = keras.optimizers.Adam(learning_rate = 0.0001),
metrics = ['accuracy'])
使用 Keras Model.fit 方法训练模型 50 个 epoch。
history = model.fit(x = train_ds,
epochs = 50,
validation_data = val_ds)
Epoch 1/50
WARNING: All log messages before absl::InitializeLog() is called are written to STDERR
I0000 00:00:1720846009.104625 108780 service.cc:146] XLA service 0x7fb998035a60 initialized for platform CUDA (this does not guarantee that XLA will be used). Devices:
I0000 00:00:1720846009.104656 108780 service.cc:154] StreamExecutor device (0): Tesla T4, Compute Capability 7.5
I0000 00:00:1720846009.104661 108780 service.cc:154] StreamExecutor device (1): Tesla T4, Compute Capability 7.5
I0000 00:00:1720846009.104665 108780 service.cc:154] StreamExecutor device (2): Tesla T4, Compute Capability 7.5
I0000 00:00:1720846009.104668 108780 service.cc:154] StreamExecutor device (3): Tesla T4, Compute Capability 7.5
2024-07-13 04:46:56.420456: E external/local_xla/xla/service/slow_operation_alarm.cc:65] Trying algorithm eng0{} for conv (f32[16,3,1,7,7]{4,3,2,1,0}, u8[0]{0}) custom-call(f32[8,3,10,224,224]{4,3,2,1,0}, f32[8,16,10,224,224]{4,3,2,1,0}), window={size=1x7x7 pad=0_0x3_3x3_3}, dim_labels=bf012_oi012->bf012, custom_call_target="__cudnn$convBackwardFilter", backend_config={"operation_queue_id":"0","wait_on_operation_queues":[],"cudnn_conv_backend_config":{"conv_result_scale":1,"activation_mode":"kNone","side_input_scale":0,"leakyrelu_alpha":0},"force_earliest_schedule":false} is taking a while...
2024-07-13 04:46:56.587823: E external/local_xla/xla/service/slow_operation_alarm.cc:133] The operation took 1.167562786s
Trying algorithm eng0{} for conv (f32[16,3,1,7,7]{4,3,2,1,0}, u8[0]{0}) custom-call(f32[8,3,10,224,224]{4,3,2,1,0}, f32[8,16,10,224,224]{4,3,2,1,0}), window={size=1x7x7 pad=0_0x3_3x3_3}, dim_labels=bf012_oi012->bf012, custom_call_target="__cudnn$convBackwardFilter", backend_config={"operation_queue_id":"0","wait_on_operation_queues":[],"cudnn_conv_backend_config":{"conv_result_scale":1,"activation_mode":"kNone","side_input_scale":0,"leakyrelu_alpha":0},"force_earliest_schedule":false} is taking a while...
I0000 00:00:1720846028.403682 108780 device_compiler.h:188] Compiled cluster using XLA! This line is logged at most once for the lifetime of the process.
38/Unknown 82s 1s/step - accuracy: 0.1332 - loss: 2.6352
/usr/lib/python3.9/contextlib.py:137: UserWarning: Your input ran out of data; interrupting training. Make sure that your dataset or generator can generate at least `steps_per_epoch * epochs` batches. You may need to use the `.repeat()` function when building your dataset.
self.gen.throw(typ, value, traceback)
38/38 ━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━ 97s 2s/step - accuracy: 0.1328 - loss: 2.6308 - val_accuracy: 0.2000 - val_loss: 2.3839
Epoch 2/50
38/38 ━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━ 48s 1s/step - accuracy: 0.1803 - loss: 2.2322 - val_accuracy: 0.1200 - val_loss: 2.3050
Epoch 3/50
38/38 ━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━ 48s 1s/step - accuracy: 0.3031 - loss: 2.0525 - val_accuracy: 0.1600 - val_loss: 2.1330
Epoch 4/50
38/38 ━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━ 49s 1s/step - accuracy: 0.3243 - loss: 2.0293 - val_accuracy: 0.0900 - val_loss: 2.4266
Epoch 5/50
38/38 ━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━ 49s 1s/step - accuracy: 0.2847 - loss: 2.0217 - val_accuracy: 0.3000 - val_loss: 2.0872
Epoch 6/50
38/38 ━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━ 49s 1s/step - accuracy: 0.3383 - loss: 1.8919 - val_accuracy: 0.2100 - val_loss: 2.0846
Epoch 7/50
38/38 ━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━ 49s 1s/step - accuracy: 0.3150 - loss: 1.7813 - val_accuracy: 0.2400 - val_loss: 2.1339
Epoch 8/50
38/38 ━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━ 49s 1s/step - accuracy: 0.3919 - loss: 1.6938 - val_accuracy: 0.3300 - val_loss: 1.9234
Epoch 9/50
38/38 ━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━ 49s 1s/step - accuracy: 0.4240 - loss: 1.6314 - val_accuracy: 0.4000 - val_loss: 1.8705
Epoch 10/50
38/38 ━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━ 49s 1s/step - accuracy: 0.4294 - loss: 1.6563 - val_accuracy: 0.4200 - val_loss: 1.7679
Epoch 11/50
38/38 ━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━ 49s 1s/step - accuracy: 0.4686 - loss: 1.4776 - val_accuracy: 0.4500 - val_loss: 1.6136
Epoch 12/50
38/38 ━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━ 49s 1s/step - accuracy: 0.5025 - loss: 1.4471 - val_accuracy: 0.4600 - val_loss: 1.6525
Epoch 13/50
38/38 ━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━ 49s 1s/step - accuracy: 0.4857 - loss: 1.3609 - val_accuracy: 0.4100 - val_loss: 1.8119
Epoch 14/50
38/38 ━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━ 49s 1s/step - accuracy: 0.4720 - loss: 1.4036 - val_accuracy: 0.4800 - val_loss: 1.6955
Epoch 15/50
38/38 ━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━ 49s 1s/step - accuracy: 0.6068 - loss: 1.1491 - val_accuracy: 0.4700 - val_loss: 1.6980
Epoch 16/50
38/38 ━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━ 49s 1s/step - accuracy: 0.5794 - loss: 1.1960 - val_accuracy: 0.5300 - val_loss: 1.5192
Epoch 17/50
38/38 ━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━ 48s 1s/step - accuracy: 0.5967 - loss: 1.1523 - val_accuracy: 0.5900 - val_loss: 1.3474
Epoch 18/50
38/38 ━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━ 48s 1s/step - accuracy: 0.6513 - loss: 0.9858 - val_accuracy: 0.4800 - val_loss: 1.6132
Epoch 19/50
38/38 ━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━ 48s 1s/step - accuracy: 0.6359 - loss: 1.0695 - val_accuracy: 0.5800 - val_loss: 1.2987
Epoch 20/50
38/38 ━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━ 49s 1s/step - accuracy: 0.6223 - loss: 0.9976 - val_accuracy: 0.6300 - val_loss: 1.2035
Epoch 21/50
38/38 ━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━ 48s 1s/step - accuracy: 0.6802 - loss: 0.9198 - val_accuracy: 0.6300 - val_loss: 1.2715
Epoch 22/50
38/38 ━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━ 49s 1s/step - accuracy: 0.6602 - loss: 1.0153 - val_accuracy: 0.5900 - val_loss: 1.2321
Epoch 23/50
38/38 ━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━ 48s 1s/step - accuracy: 0.7773 - loss: 0.8142 - val_accuracy: 0.5500 - val_loss: 1.5163
Epoch 24/50
38/38 ━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━ 49s 1s/step - accuracy: 0.6530 - loss: 0.9162 - val_accuracy: 0.5700 - val_loss: 1.2871
Epoch 25/50
38/38 ━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━ 48s 1s/step - accuracy: 0.6627 - loss: 0.8742 - val_accuracy: 0.4200 - val_loss: 1.6656
Epoch 26/50
38/38 ━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━ 49s 1s/step - accuracy: 0.6631 - loss: 0.8911 - val_accuracy: 0.5900 - val_loss: 1.1907
Epoch 27/50
38/38 ━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━ 49s 1s/step - accuracy: 0.7602 - loss: 0.7582 - val_accuracy: 0.6100 - val_loss: 1.2898
Epoch 28/50
38/38 ━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━ 48s 1s/step - accuracy: 0.7274 - loss: 0.8415 - val_accuracy: 0.5800 - val_loss: 1.2001
Epoch 29/50
38/38 ━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━ 49s 1s/step - accuracy: 0.7253 - loss: 0.7822 - val_accuracy: 0.6000 - val_loss: 1.1509
Epoch 30/50
38/38 ━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━ 48s 1s/step - accuracy: 0.7125 - loss: 0.7782 - val_accuracy: 0.6000 - val_loss: 1.0901
Epoch 31/50
38/38 ━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━ 49s 1s/step - accuracy: 0.6901 - loss: 0.8069 - val_accuracy: 0.6500 - val_loss: 1.1331
Epoch 32/50
38/38 ━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━ 49s 1s/step - accuracy: 0.7523 - loss: 0.7385 - val_accuracy: 0.6600 - val_loss: 1.1494
Epoch 33/50
38/38 ━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━ 49s 1s/step - accuracy: 0.7696 - loss: 0.6941 - val_accuracy: 0.6500 - val_loss: 1.1755
Epoch 34/50
38/38 ━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━ 49s 1s/step - accuracy: 0.7705 - loss: 0.6984 - val_accuracy: 0.5900 - val_loss: 1.1887
Epoch 35/50
38/38 ━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━ 48s 1s/step - accuracy: 0.7599 - loss: 0.6262 - val_accuracy: 0.5600 - val_loss: 1.1636
Epoch 36/50
38/38 ━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━ 49s 1s/step - accuracy: 0.7671 - loss: 0.7025 - val_accuracy: 0.6400 - val_loss: 1.0452
Epoch 37/50
38/38 ━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━ 48s 1s/step - accuracy: 0.7253 - loss: 0.7062 - val_accuracy: 0.5900 - val_loss: 1.3652
Epoch 38/50
38/38 ━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━ 48s 1s/step - accuracy: 0.7406 - loss: 0.7318 - val_accuracy: 0.6100 - val_loss: 1.1119
Epoch 39/50
38/38 ━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━ 49s 1s/step - accuracy: 0.8319 - loss: 0.5269 - val_accuracy: 0.6700 - val_loss: 1.1210
Epoch 40/50
38/38 ━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━ 49s 1s/step - accuracy: 0.8297 - loss: 0.5084 - val_accuracy: 0.6300 - val_loss: 1.1432
Epoch 41/50
38/38 ━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━ 48s 1s/step - accuracy: 0.7810 - loss: 0.6155 - val_accuracy: 0.4400 - val_loss: 2.0229
Epoch 42/50
38/38 ━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━ 48s 1s/step - accuracy: 0.7794 - loss: 0.7254 - val_accuracy: 0.5500 - val_loss: 1.3363
Epoch 43/50
38/38 ━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━ 49s 1s/step - accuracy: 0.7729 - loss: 0.6237 - val_accuracy: 0.5100 - val_loss: 1.4360
Epoch 44/50
38/38 ━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━ 49s 1s/step - accuracy: 0.8165 - loss: 0.5819 - val_accuracy: 0.6000 - val_loss: 1.1835
Epoch 45/50
38/38 ━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━ 49s 1s/step - accuracy: 0.8340 - loss: 0.5026 - val_accuracy: 0.6400 - val_loss: 1.1179
Epoch 46/50
38/38 ━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━ 48s 1s/step - accuracy: 0.8695 - loss: 0.4977 - val_accuracy: 0.6100 - val_loss: 1.0725
Epoch 47/50
38/38 ━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━ 48s 1s/step - accuracy: 0.8564 - loss: 0.4611 - val_accuracy: 0.6600 - val_loss: 1.1611
Epoch 48/50
38/38 ━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━ 49s 1s/step - accuracy: 0.8388 - loss: 0.5222 - val_accuracy: 0.5900 - val_loss: 1.2520
Epoch 49/50
38/38 ━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━ 48s 1s/step - accuracy: 0.8233 - loss: 0.5380 - val_accuracy: 0.6400 - val_loss: 1.0974
Epoch 50/50
38/38 ━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━ 48s 1s/step - accuracy: 0.8523 - loss: 0.4805 - val_accuracy: 0.6300 - val_loss: 1.1175
可视化结果
创建训练集和验证集上损失和准确性的图。
def plot_history(history):
"""
Plotting training and validation learning curves.
Args:
history: model history with all the metric measures
"""
fig, (ax1, ax2) = plt.subplots(2)
fig.set_size_inches(18.5, 10.5)
# Plot loss
ax1.set_title('Loss')
ax1.plot(history.history['loss'], label = 'train')
ax1.plot(history.history['val_loss'], label = 'test')
ax1.set_ylabel('Loss')
# Determine upper bound of y-axis
max_loss = max(history.history['loss'] + history.history['val_loss'])
ax1.set_ylim([0, np.ceil(max_loss)])
ax1.set_xlabel('Epoch')
ax1.legend(['Train', 'Validation'])
# Plot accuracy
ax2.set_title('Accuracy')
ax2.plot(history.history['accuracy'], label = 'train')
ax2.plot(history.history['val_accuracy'], label = 'test')
ax2.set_ylabel('Accuracy')
ax2.set_ylim([0, 1])
ax2.set_xlabel('Epoch')
ax2.legend(['Train', 'Validation'])
plt.show()
plot_history(history)
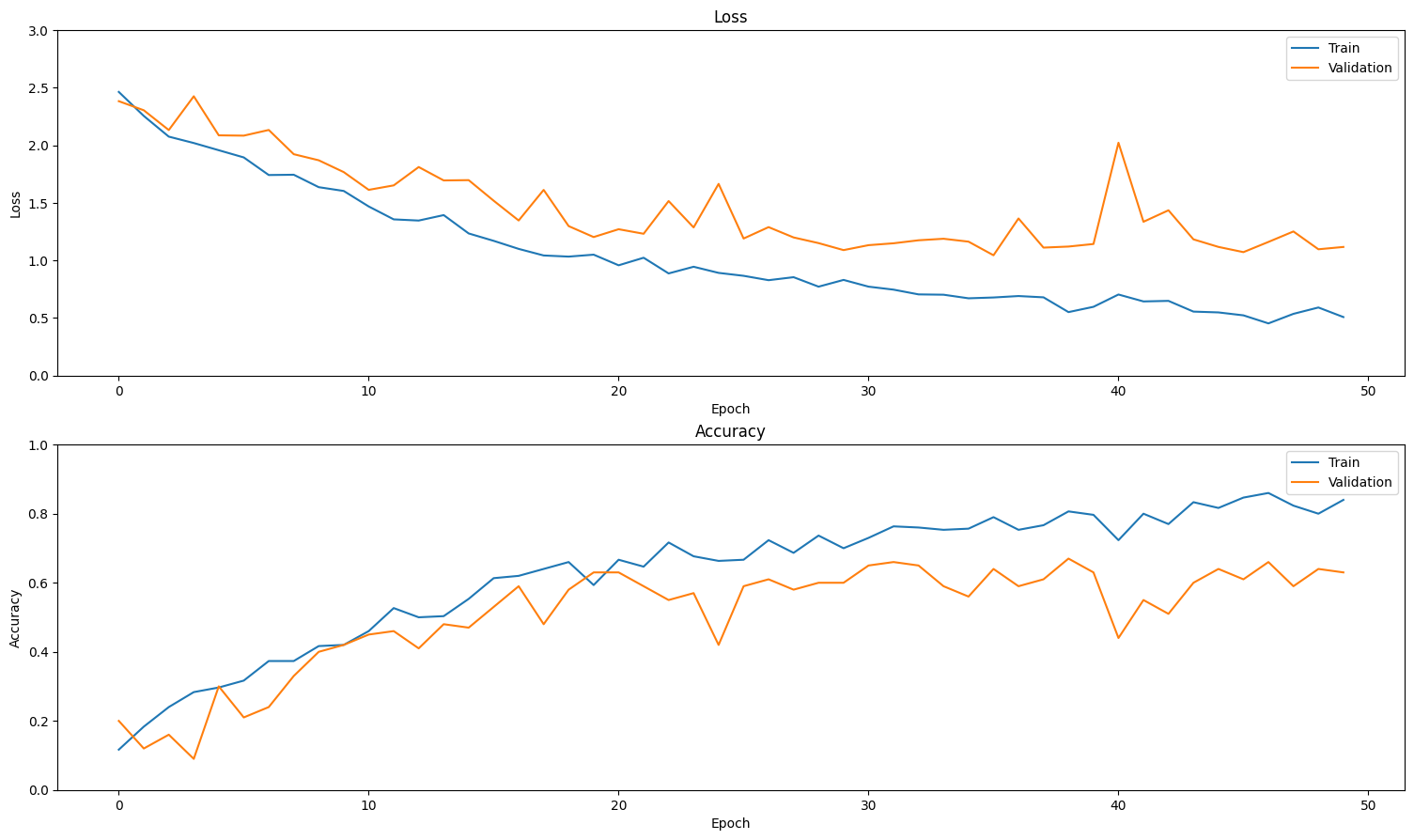
评估模型
使用 Keras Model.evaluate 获取测试数据集上的损失和准确性。
model.evaluate(test_ds, return_dict=True)
13/13 ━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━ 11s 844ms/step - accuracy: 0.4477 - loss: 1.2893
{'accuracy': 0.5099999904632568, 'loss': 1.2706645727157593}
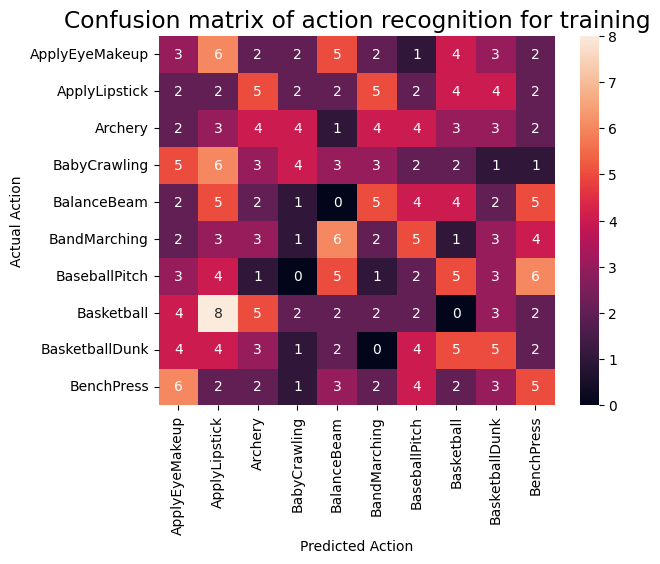
要进一步可视化模型性能,请使用 混淆矩阵。混淆矩阵允许您评估分类模型的性能,而不仅仅是准确性。为了构建此多类分类问题的混淆矩阵,请获取测试集中的实际值和预测值。
def get_actual_predicted_labels(dataset):
"""
Create a list of actual ground truth values and the predictions from the model.
Args:
dataset: An iterable data structure, such as a TensorFlow Dataset, with features and labels.
Return:
Ground truth and predicted values for a particular dataset.
"""
actual = [labels for _, labels in dataset.unbatch()]
predicted = model.predict(dataset)
actual = tf.stack(actual, axis=0)
predicted = tf.concat(predicted, axis=0)
predicted = tf.argmax(predicted, axis=1)
return actual, predicted
def plot_confusion_matrix(actual, predicted, labels, ds_type):
cm = tf.math.confusion_matrix(actual, predicted)
ax = sns.heatmap(cm, annot=True, fmt='g')
sns.set(rc={'figure.figsize':(12, 12)})
sns.set(font_scale=1.4)
ax.set_title('Confusion matrix of action recognition for ' + ds_type)
ax.set_xlabel('Predicted Action')
ax.set_ylabel('Actual Action')
plt.xticks(rotation=90)
plt.yticks(rotation=0)
ax.xaxis.set_ticklabels(labels)
ax.yaxis.set_ticklabels(labels)
fg = FrameGenerator(subset_paths['train'], n_frames, training=True)
labels = list(fg.class_ids_for_name.keys())
actual, predicted = get_actual_predicted_labels(train_ds)
plot_confusion_matrix(actual, predicted, labels, 'training')
38/38 ━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━ 35s 877ms/step
actual, predicted = get_actual_predicted_labels(test_ds)
plot_confusion_matrix(actual, predicted, labels, 'test')
13/13 ━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━ 11s 831ms/step /usr/lib/python3.9/contextlib.py:137: UserWarning: Your input ran out of data; interrupting training. Make sure that your dataset or generator can generate at least `steps_per_epoch * epochs` batches. You may need to use the `.repeat()` function when building your dataset. self.gen.throw(typ, value, traceback)
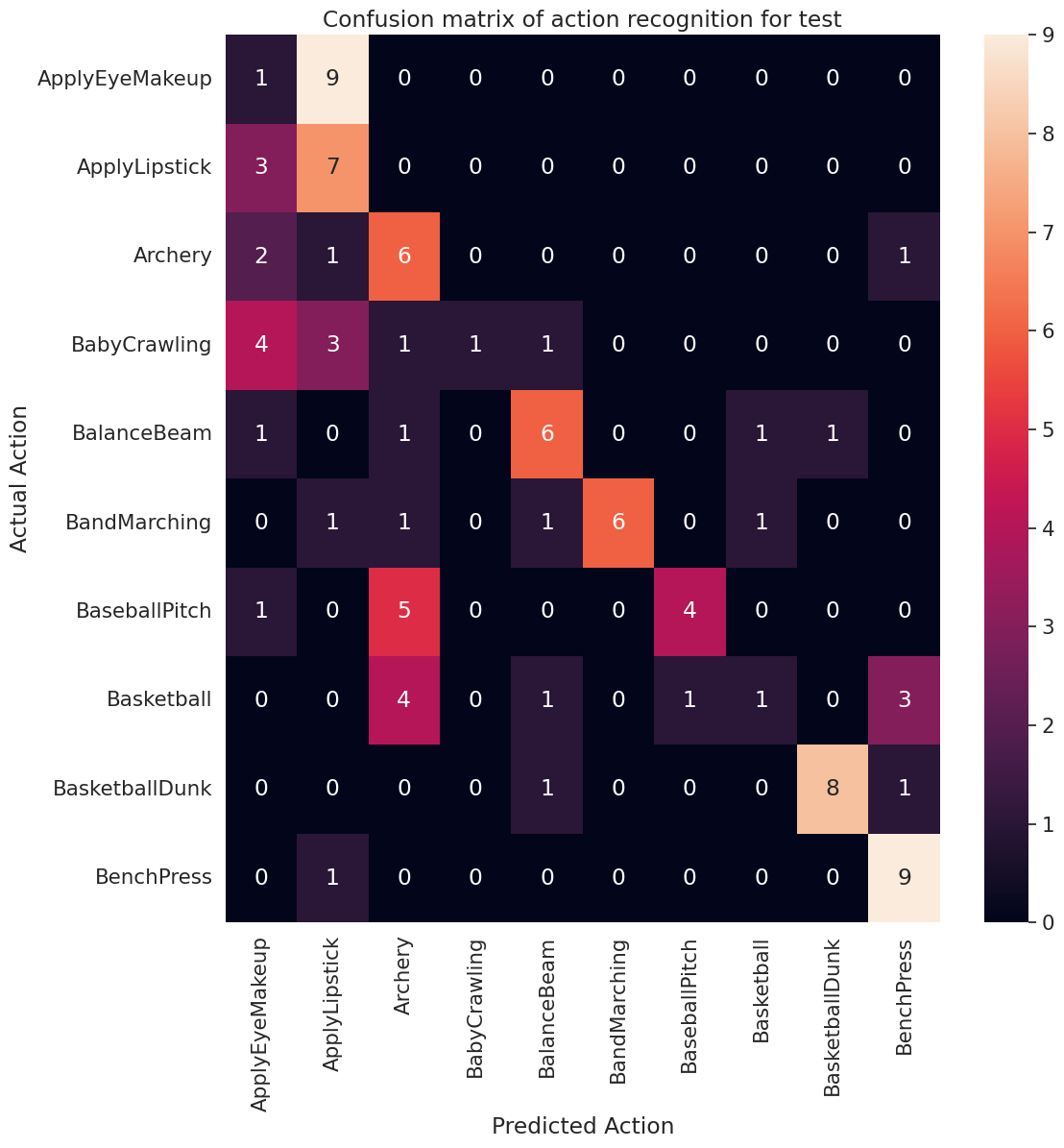
还可以使用混淆矩阵计算每个类的精确度和召回率值。
def calculate_classification_metrics(y_actual, y_pred, labels):
"""
Calculate the precision and recall of a classification model using the ground truth and
predicted values.
Args:
y_actual: Ground truth labels.
y_pred: Predicted labels.
labels: List of classification labels.
Return:
Precision and recall measures.
"""
cm = tf.math.confusion_matrix(y_actual, y_pred)
tp = np.diag(cm) # Diagonal represents true positives
precision = dict()
recall = dict()
for i in range(len(labels)):
col = cm[:, i]
fp = np.sum(col) - tp[i] # Sum of column minus true positive is false negative
row = cm[i, :]
fn = np.sum(row) - tp[i] # Sum of row minus true positive, is false negative
precision[labels[i]] = tp[i] / (tp[i] + fp) # Precision
recall[labels[i]] = tp[i] / (tp[i] + fn) # Recall
return precision, recall
precision, recall = calculate_classification_metrics(actual, predicted, labels) # Test dataset
precision
{'ApplyEyeMakeup': 0.08333333333333333,
'ApplyLipstick': 0.3181818181818182,
'Archery': 0.3333333333333333,
'BabyCrawling': 1.0,
'BalanceBeam': 0.6,
'BandMarching': 1.0,
'BaseballPitch': 0.8,
'Basketball': 0.3333333333333333,
'BasketballDunk': 0.8888888888888888,
'BenchPress': 0.6428571428571429}
recall
{'ApplyEyeMakeup': 0.1,
'ApplyLipstick': 0.7,
'Archery': 0.6,
'BabyCrawling': 0.1,
'BalanceBeam': 0.6,
'BandMarching': 0.6,
'BaseballPitch': 0.4,
'Basketball': 0.1,
'BasketballDunk': 0.8,
'BenchPress': 0.9}
下一步
要了解有关在 TensorFlow 中使用视频数据的更多信息,请查看以下教程
