 在 TensorFlow.org 上查看 在 TensorFlow.org 上查看
|
 在 Google Colab 中运行 在 Google Colab 中运行
|
 在 GitHub 上查看源代码 在 GitHub 上查看源代码
|
 下载笔记本 下载笔记本
|
本教程演示了如何使用 Kaggle 竞赛中 PetFinder 数据集的简化版本(存储在 CSV 文件中)对结构化数据(如表格数据)进行分类。
您将使用 Keras 来定义模型,并使用 Keras 预处理层 作为桥梁,将 CSV 文件中的列映射到用于训练模型的特征。目标是预测宠物是否会被领养。
本教程包含以下完整代码:
- 使用 pandas 将 CSV 文件加载到 DataFrame 中。
- 使用
tf.data构建输入管道,对行进行批处理和随机排序。(有关更多详细信息,请访问 tf.data:构建 TensorFlow 输入管道。) - 使用 Keras 预处理层将 CSV 文件中的列映射到用于训练模型的特征。
- 使用 Keras 内置方法构建、训练和评估模型。
PetFinder.my 迷你数据集
PetFinder.my 迷你的 CSV 数据集文件包含数千行,每行描述一只宠物(狗或猫),每列描述一个属性,例如年龄、品种、颜色等等。
在下面的数据集摘要中,请注意大多数是数值列和分类列。在本教程中,您将只处理这两种特征类型,在数据预处理期间丢弃 Description(自由文本特征)和 AdoptionSpeed(分类特征)。
| 列 | 宠物描述 | 特征类型 | 数据类型 |
|---|---|---|---|
类型 |
动物类型 (Dog, Cat) |
分类 | 字符串 |
年龄 |
年龄 | 数值 | 整数 |
Breed1 |
主要品种 | 分类 | 字符串 |
Color1 |
颜色 1 | 分类 | 字符串 |
Color2 |
颜色 2 | 分类 | 字符串 |
MaturitySize |
成熟时的尺寸 | 分类 | 字符串 |
FurLength |
毛发长度 | 分类 | 字符串 |
Vaccinated |
宠物是否已接种疫苗 | 分类 | 字符串 |
Sterilized |
宠物是否已绝育 | 分类 | 字符串 |
Health |
健康状况 | 分类 | 字符串 |
Fee |
领养费 | 数值 | 整数 |
Description |
个人资料简介 | 文本 | 字符串 |
PhotoAmt |
上传的总照片数 | 数值 | 整数 |
AdoptionSpeed |
领养速度的分类 | 分类 | 整数 |
导入 TensorFlow 和其他库
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
import tensorflow as tf
from tensorflow.keras import layers
2024-01-12 02:20:50.190753: E external/local_xla/xla/stream_executor/cuda/cuda_dnn.cc:9261] Unable to register cuDNN factory: Attempting to register factory for plugin cuDNN when one has already been registered 2024-01-12 02:20:50.190796: E external/local_xla/xla/stream_executor/cuda/cuda_fft.cc:607] Unable to register cuFFT factory: Attempting to register factory for plugin cuFFT when one has already been registered 2024-01-12 02:20:50.192423: E external/local_xla/xla/stream_executor/cuda/cuda_blas.cc:1515] Unable to register cuBLAS factory: Attempting to register factory for plugin cuBLAS when one has already been registered
tf.__version__
'2.15.0'
加载数据集并将其读入 pandas DataFrame
pandas 是一个 Python 库,它包含许多用于加载和处理结构化数据的实用程序。使用 tf.keras.utils.get_file 下载并解压缩包含 PetFinder.my 迷你数据集的 CSV 文件,并使用 pandas.read_csv 将其加载到 DataFrame 中。
dataset_url = 'http://storage.googleapis.com/download.tensorflow.org/data/petfinder-mini.zip'
csv_file = 'datasets/petfinder-mini/petfinder-mini.csv'
tf.keras.utils.get_file('petfinder_mini.zip', dataset_url,
extract=True, cache_dir='.')
dataframe = pd.read_csv(csv_file)
Downloading data from http://storage.googleapis.com/download.tensorflow.org/data/petfinder-mini.zip 1668792/1668792 [==============================] - 0s 0us/step
通过检查 DataFrame 的前五行来检查数据集。
dataframe.head()
创建目标变量
Kaggle 的 PetFinder.my 领养预测竞赛 中的原始任务是预测宠物被领养的速度(例如,在第一周、第一个月、前三个月等等)。
在本教程中,您将通过将其转换为二元分类问题来简化任务,您只需要预测宠物是否被领养。
修改 AdoptionSpeed 列后,0 表示宠物未被领养,1 表示宠物被领养。
# In the original dataset, `'AdoptionSpeed'` of `4` indicates
# a pet was not adopted.
dataframe['target'] = np.where(dataframe['AdoptionSpeed']==4, 0, 1)
# Drop unused features.
dataframe = dataframe.drop(columns=['AdoptionSpeed', 'Description'])
将 DataFrame 分割成训练集、验证集和测试集
数据集位于单个 pandas DataFrame 中。使用例如 80:10:10 的比例将其分割成训练集、验证集和测试集。
train, val, test = np.split(dataframe.sample(frac=1), [int(0.8*len(dataframe)), int(0.9*len(dataframe))])
/tmpfs/src/tf_docs_env/lib/python3.9/site-packages/numpy/core/fromnumeric.py:59: FutureWarning: 'DataFrame.swapaxes' is deprecated and will be removed in a future version. Please use 'DataFrame.transpose' instead. return bound(*args, **kwds)
print(len(train), 'training examples')
print(len(val), 'validation examples')
print(len(test), 'test examples')
9229 training examples 1154 validation examples 1154 test examples
使用 tf.data 创建输入管道
接下来,创建一个实用程序函数,将每个训练集、验证集和测试集 DataFrame 转换为 tf.data.Dataset,然后对数据进行随机排序和批处理。
def df_to_dataset(dataframe, shuffle=True, batch_size=32):
df = dataframe.copy()
labels = df.pop('target')
df = {key: value.values[:,tf.newaxis] for key, value in dataframe.items()}
ds = tf.data.Dataset.from_tensor_slices((dict(df), labels))
if shuffle:
ds = ds.shuffle(buffer_size=len(dataframe))
ds = ds.batch(batch_size)
ds = ds.prefetch(batch_size)
return ds
现在,使用新创建的函数 (df_to_dataset) 通过对训练数据调用它来检查输入管道辅助函数返回的数据格式,并使用较小的批次大小来保持输出可读性。
batch_size = 5
train_ds = df_to_dataset(train, batch_size=batch_size)
[(train_features, label_batch)] = train_ds.take(1)
print('Every feature:', list(train_features.keys()))
print('A batch of ages:', train_features['Age'])
print('A batch of targets:', label_batch )
Every feature: ['Type', 'Age', 'Breed1', 'Gender', 'Color1', 'Color2', 'MaturitySize', 'FurLength', 'Vaccinated', 'Sterilized', 'Health', 'Fee', 'PhotoAmt', 'target'] A batch of ages: tf.Tensor( [[18] [48] [ 1] [38] [12]], shape=(5, 1), dtype=int64) A batch of targets: tf.Tensor([1 1 1 1 0], shape=(5,), dtype=int64)
正如输出所示,训练集返回一个字典,其中包含列名(来自 DataFrame),这些列名映射到来自行的列值。
应用 Keras 预处理层
Keras 预处理层允许您构建 Keras 原生的输入处理管道,这些管道可以用作非 Keras 工作流中的独立预处理代码,直接与 Keras 模型结合使用,并作为 Keras SavedModel 的一部分导出。
在本教程中,您将使用以下四个预处理层来演示如何执行预处理、结构化数据编码和特征工程。
tf.keras.layers.Normalization:对输入特征执行逐特征归一化。tf.keras.layers.CategoryEncoding:将整数分类特征转换为独热、多热或 tf-idf 稠密表示。tf.keras.layers.StringLookup:将字符串分类值转换为整数索引。tf.keras.layers.IntegerLookup:将整数分类值转换为整数索引。
您可以在 使用预处理层 指南中了解有关可用层的更多信息。
- 对于 PetFinder.my 迷你数据集的数值特征,您将使用
tf.keras.layers.Normalization层来标准化数据的分布。 - 对于分类特征,例如宠物
Type(Dog和Cat字符串),您将使用tf.keras.layers.CategoryEncoding将它们转换为多热编码的张量。
数值列
对于 PetFinder.my 迷你数据集中每个数值特征,您将使用 tf.keras.layers.Normalization 层来标准化数据的分布。
定义一个新的实用程序函数,该函数返回一个层,该层使用该 Keras 预处理层对数值特征应用逐特征归一化。
def get_normalization_layer(name, dataset):
# Create a Normalization layer for the feature.
normalizer = layers.Normalization(axis=None)
# Prepare a Dataset that only yields the feature.
feature_ds = dataset.map(lambda x, y: x[name])
# Learn the statistics of the data.
normalizer.adapt(feature_ds)
return normalizer
接下来,通过对上传的总宠物照片特征调用它来测试新函数,以归一化 'PhotoAmt'。
photo_count_col = train_features['PhotoAmt']
layer = get_normalization_layer('PhotoAmt', train_ds)
layer(photo_count_col)
<tf.Tensor: shape=(5, 1), dtype=float32, numpy=
array([[0.12533209],
[0.12533209],
[1.079441 ],
[2.9876585 ],
[1.079441 ]], dtype=float32)>
分类列
数据集中宠物 Type 以字符串形式表示——Dog 和 Cat——在馈送到模型之前需要进行多热编码。Age 特征
定义另一个新的实用程序函数,该函数返回一个层,该层使用 tf.keras.layers.StringLookup、tf.keras.layers.IntegerLookup 和 tf.keras.CategoryEncoding 预处理层将词汇表中的值映射到整数索引并对特征进行多热编码。
def get_category_encoding_layer(name, dataset, dtype, max_tokens=None):
# Create a layer that turns strings into integer indices.
if dtype == 'string':
index = layers.StringLookup(max_tokens=max_tokens)
# Otherwise, create a layer that turns integer values into integer indices.
else:
index = layers.IntegerLookup(max_tokens=max_tokens)
# Prepare a `tf.data.Dataset` that only yields the feature.
feature_ds = dataset.map(lambda x, y: x[name])
# Learn the set of possible values and assign them a fixed integer index.
index.adapt(feature_ds)
# Encode the integer indices.
encoder = layers.CategoryEncoding(num_tokens=index.vocabulary_size())
# Apply multi-hot encoding to the indices. The lambda function captures the
# layer, so you can use them, or include them in the Keras Functional model later.
return lambda feature: encoder(index(feature))
通过对宠物 'Type' 特征调用 get_category_encoding_layer 函数来测试它,以将其转换为多热编码的张量。
test_type_col = train_features['Type']
test_type_layer = get_category_encoding_layer(name='Type',
dataset=train_ds,
dtype='string')
test_type_layer(test_type_col)
<tf.Tensor: shape=(5, 3), dtype=float32, numpy=
array([[0., 1., 0.],
[0., 1., 0.],
[0., 1., 0.],
[0., 1., 0.],
[0., 1., 0.]], dtype=float32)>
对宠物 'Age' 特征重复此过程。
test_age_col = train_features['Age']
test_age_layer = get_category_encoding_layer(name='Age',
dataset=train_ds,
dtype='int64',
max_tokens=5)
test_age_layer(test_age_col)
<tf.Tensor: shape=(5, 5), dtype=float32, numpy=
array([[1., 0., 0., 0., 0.],
[1., 0., 0., 0., 0.],
[0., 0., 0., 1., 0.],
[1., 0., 0., 0., 0.],
[1., 0., 0., 0., 0.]], dtype=float32)>
预处理选定的特征以训练模型
您已经学习了如何使用几种类型的 Keras 预处理层。接下来,您将
- 对 PetFinder.my 迷你数据集中的 13 个数值和分类特征应用之前定义的预处理实用程序函数。
- 将所有特征输入添加到一个列表中。
如开头所述,您将使用 PetFinder.my 迷你数据集的数值 ('PhotoAmt', 'Fee') 和分类 ('Age', 'Type', 'Color1', 'Color2', 'Gender', 'MaturitySize', 'FurLength', 'Vaccinated', 'Sterilized', 'Health', 'Breed1') 特征来训练模型。
之前,您使用较小的批次大小来演示输入管道。现在让我们创建一个新的输入管道,其批次大小为 256。
batch_size = 256
train_ds = df_to_dataset(train, batch_size=batch_size)
val_ds = df_to_dataset(val, shuffle=False, batch_size=batch_size)
test_ds = df_to_dataset(test, shuffle=False, batch_size=batch_size)
归一化数值特征(宠物照片数量和领养费),并将它们添加到一个名为 encoded_features 的输入列表中。
all_inputs = []
encoded_features = []
# Numerical features.
for header in ['PhotoAmt', 'Fee']:
numeric_col = tf.keras.Input(shape=(1,), name=header)
normalization_layer = get_normalization_layer(header, train_ds)
encoded_numeric_col = normalization_layer(numeric_col)
all_inputs.append(numeric_col)
encoded_features.append(encoded_numeric_col)
将数据集中整数分类值(宠物年龄)转换为整数索引,执行多热编码,并将生成的特征输入添加到 encoded_features 中。
age_col = tf.keras.Input(shape=(1,), name='Age', dtype='int64')
encoding_layer = get_category_encoding_layer(name='Age',
dataset=train_ds,
dtype='int64',
max_tokens=5)
encoded_age_col = encoding_layer(age_col)
all_inputs.append(age_col)
encoded_features.append(encoded_age_col)
对字符串分类值重复相同的步骤。
categorical_cols = ['Type', 'Color1', 'Color2', 'Gender', 'MaturitySize',
'FurLength', 'Vaccinated', 'Sterilized', 'Health', 'Breed1']
for header in categorical_cols:
categorical_col = tf.keras.Input(shape=(1,), name=header, dtype='string')
encoding_layer = get_category_encoding_layer(name=header,
dataset=train_ds,
dtype='string',
max_tokens=5)
encoded_categorical_col = encoding_layer(categorical_col)
all_inputs.append(categorical_col)
encoded_features.append(encoded_categorical_col)
创建、编译和训练模型
下一步是使用 Keras 函数式 API 创建一个模型。对于模型中的第一层,使用 tf.keras.layers.concatenate 将特征输入列表——encoded_features——合并为一个向量。
all_features = tf.keras.layers.concatenate(encoded_features)
x = tf.keras.layers.Dense(32, activation="relu")(all_features)
x = tf.keras.layers.Dropout(0.5)(x)
output = tf.keras.layers.Dense(1)(x)
model = tf.keras.Model(all_inputs, output)
使用 Keras 配置模型 Model.compile
model.compile(optimizer='adam',
loss=tf.keras.losses.BinaryCrossentropy(from_logits=True),
metrics=["accuracy"])
让我们可视化连接图
# Use `rankdir='LR'` to make the graph horizontal.
tf.keras.utils.plot_model(model, show_shapes=True, rankdir="LR")
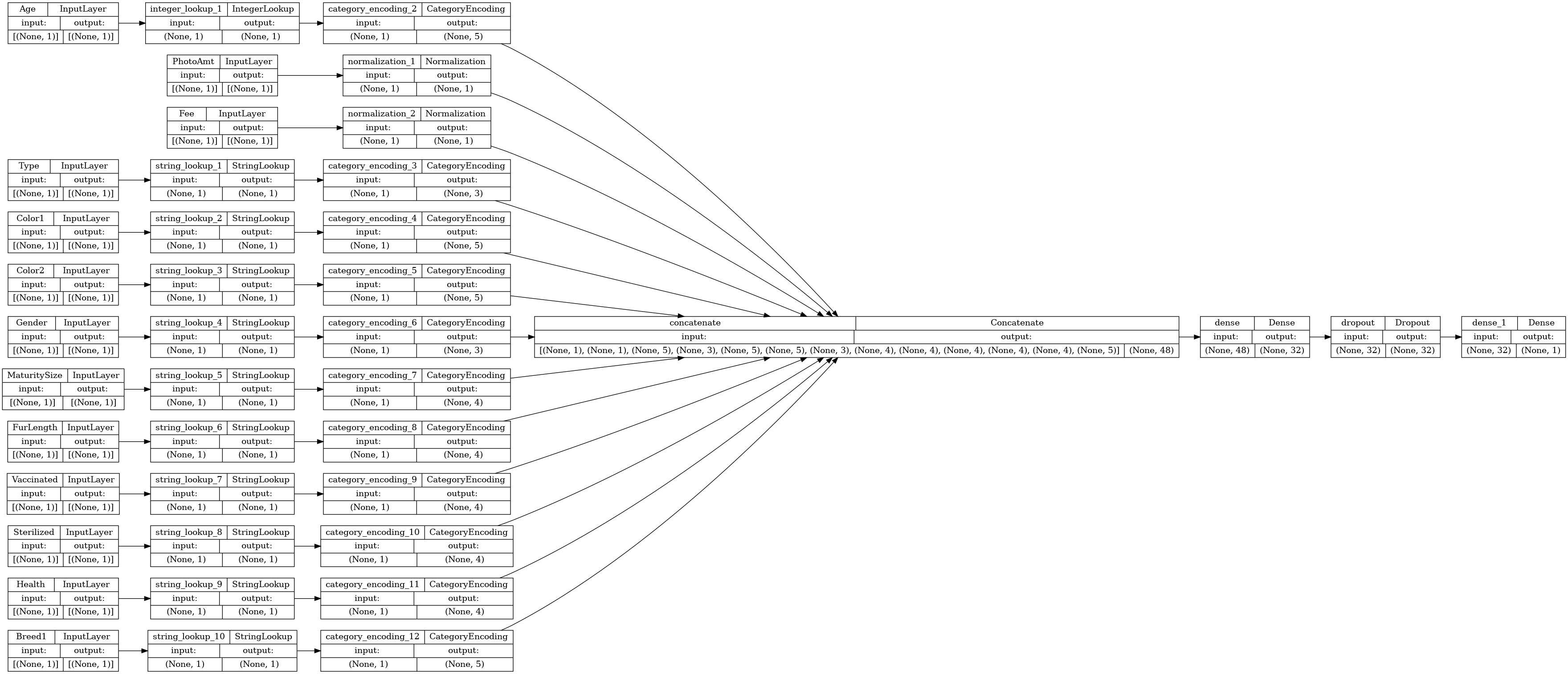
接下来,训练和测试模型
model.fit(train_ds, epochs=10, validation_data=val_ds)
Epoch 1/10 /tmpfs/src/tf_docs_env/lib/python3.9/site-packages/keras/src/engine/functional.py:642: UserWarning: Input dict contained keys ['target'] which did not match any model input. They will be ignored by the model. inputs = self._flatten_to_reference_inputs(inputs) WARNING: All log messages before absl::InitializeLog() is called are written to STDERR I0000 00:00:1705026069.800827 9903 device_compiler.h:186] Compiled cluster using XLA! This line is logged at most once for the lifetime of the process. 37/37 [==============================] - 4s 18ms/step - loss: 0.6416 - accuracy: 0.5808 - val_loss: 0.5700 - val_accuracy: 0.7253 Epoch 2/10 37/37 [==============================] - 0s 6ms/step - loss: 0.5878 - accuracy: 0.6641 - val_loss: 0.5470 - val_accuracy: 0.7314 Epoch 3/10 37/37 [==============================] - 0s 6ms/step - loss: 0.5700 - accuracy: 0.6863 - val_loss: 0.5353 - val_accuracy: 0.7409 Epoch 4/10 37/37 [==============================] - 0s 6ms/step - loss: 0.5525 - accuracy: 0.7009 - val_loss: 0.5267 - val_accuracy: 0.7392 Epoch 5/10 37/37 [==============================] - 0s 6ms/step - loss: 0.5438 - accuracy: 0.7070 - val_loss: 0.5219 - val_accuracy: 0.7400 Epoch 6/10 37/37 [==============================] - 0s 6ms/step - loss: 0.5379 - accuracy: 0.7120 - val_loss: 0.5179 - val_accuracy: 0.7374 Epoch 7/10 37/37 [==============================] - 0s 6ms/step - loss: 0.5381 - accuracy: 0.7150 - val_loss: 0.5157 - val_accuracy: 0.7392 Epoch 8/10 37/37 [==============================] - 0s 6ms/step - loss: 0.5352 - accuracy: 0.7216 - val_loss: 0.5140 - val_accuracy: 0.7383 Epoch 9/10 37/37 [==============================] - 0s 6ms/step - loss: 0.5299 - accuracy: 0.7230 - val_loss: 0.5120 - val_accuracy: 0.7418 Epoch 10/10 37/37 [==============================] - 0s 6ms/step - loss: 0.5283 - accuracy: 0.7293 - val_loss: 0.5112 - val_accuracy: 0.7435 <keras.src.callbacks.History at 0x7f858015b280>
loss, accuracy = model.evaluate(test_ds)
print("Accuracy", accuracy)
5/5 [==============================] - 0s 5ms/step - loss: 0.4979 - accuracy: 0.7591 Accuracy 0.7590987682342529
执行推理
您开发的模型现在可以对 CSV 文件中的行进行分类,前提是您已将预处理层包含在模型本身中。
现在您可以使用 Model.save 和 Model.load_model 保存和重新加载 Keras 模型,然后对新数据执行推理
model.save('my_pet_classifier.keras')
reloaded_model = tf.keras.models.load_model('my_pet_classifier.keras')
要获得新样本的预测,您可以简单地调用 Keras Model.predict 方法。您只需要做两件事
- 将标量包装到列表中,以便拥有批次维度(
Model仅处理数据批次,而不是单个样本)。 - 对每个特征调用
tf.convert_to_tensor。
sample = {
'Type': 'Cat',
'Age': 3,
'Breed1': 'Tabby',
'Gender': 'Male',
'Color1': 'Black',
'Color2': 'White',
'MaturitySize': 'Small',
'FurLength': 'Short',
'Vaccinated': 'No',
'Sterilized': 'No',
'Health': 'Healthy',
'Fee': 100,
'PhotoAmt': 2,
}
input_dict = {name: tf.convert_to_tensor([value]) for name, value in sample.items()}
predictions = reloaded_model.predict(input_dict)
prob = tf.nn.sigmoid(predictions[0])
print(
"This particular pet had a %.1f percent probability "
"of getting adopted." % (100 * prob)
)
1/1 [==============================] - 0s 412ms/step This particular pet had a 79.3 percent probability of getting adopted.
下一步
要详细了解如何对结构化数据进行分类,请尝试使用其他数据集。为了提高训练和测试模型时的准确性,请仔细考虑要包含在模型中的特征以及如何表示它们。
以下是一些数据集建议
- TensorFlow 数据集:MovieLens:来自电影推荐服务的电影评分集。
- TensorFlow 数据集:葡萄酒质量:与葡萄牙“Vinho Verde”葡萄酒的红葡萄酒和白葡萄酒变体相关的两个数据集。您也可以在 Kaggle 上找到红葡萄酒质量数据集。
- Kaggle:arXiv 数据集:来自 arXiv 的 170 万篇学术文章语料库,涵盖物理学、计算机科学、数学、统计学、电气工程、定量生物学和经济学。
