 在 TensorFlow.org 上查看 在 TensorFlow.org 上查看
|
 在 Google Colab 中运行 在 Google Colab 中运行
|
 在 GitHub 上查看 在 GitHub 上查看
|
 下载笔记本 下载笔记本
|
 查看 TF Hub 模型 查看 TF Hub 模型
|
本教程使用深度学习将一张图像以另一张图像的风格进行合成(是否曾经希望自己能像毕加索或梵高一样作画?)。这被称为神经风格迁移,该技术在艺术风格的神经算法(Gatys 等人)中进行了概述。
要使用来自 TensorFlow Hub 的预训练模型简单应用风格迁移,请查看 任意风格的快速风格迁移 教程,该教程使用 任意图像风格化模型。有关使用 TensorFlow Lite 进行风格迁移的示例,请参阅 使用 TensorFlow Lite 进行艺术风格迁移。
神经风格迁移是一种优化技术,用于将两张图像(一张内容图像和一张风格参考图像(例如著名画家的作品))融合在一起,使输出图像看起来像内容图像,但“绘制”在风格参考图像的风格中。
这是通过优化输出图像来匹配内容图像的内容统计信息和风格参考图像的风格统计信息来实现的。这些统计信息是使用卷积网络从图像中提取的。
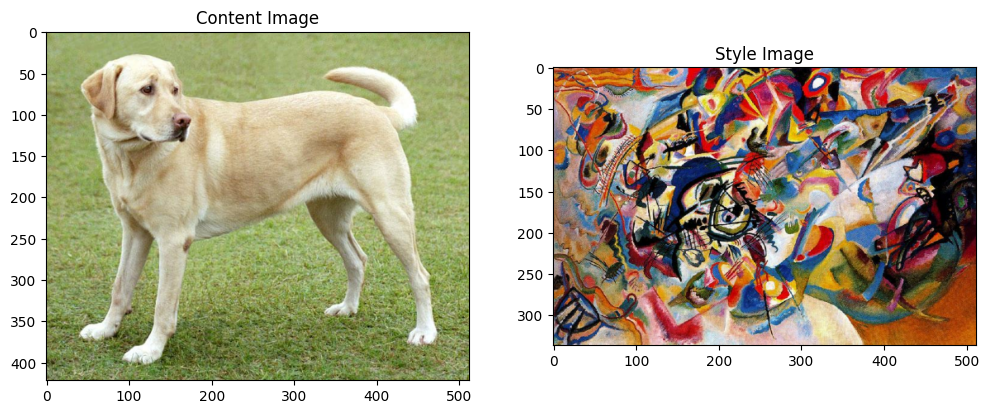
例如,让我们取一张这只狗的图像和瓦西里·康定斯基的《第七号构成》

黄色的拉布拉多犬,来自维基共享资源,作者 Elf。许可证 CC BY-SA 3.0

现在,如果康定斯基决定用这种风格专门画这只狗的图片,它会是什么样子?像这样吗?

设置
导入和配置模块
import os
import tensorflow as tf
# Load compressed models from tensorflow_hub
os.environ['TFHUB_MODEL_LOAD_FORMAT'] = 'COMPRESSED'
import IPython.display as display
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import matplotlib as mpl
mpl.rcParams['figure.figsize'] = (12, 12)
mpl.rcParams['axes.grid'] = False
import numpy as np
import PIL.Image
import time
import functools
def tensor_to_image(tensor):
tensor = tensor*255
tensor = np.array(tensor, dtype=np.uint8)
if np.ndim(tensor)>3:
assert tensor.shape[0] == 1
tensor = tensor[0]
return PIL.Image.fromarray(tensor)
下载图像并选择风格图像和内容图像
content_path = tf.keras.utils.get_file('YellowLabradorLooking_new.jpg', 'https://storage.googleapis.com/download.tensorflow.org/example_images/YellowLabradorLooking_new.jpg')
style_path = tf.keras.utils.get_file('kandinsky5.jpg','https://storage.googleapis.com/download.tensorflow.org/example_images/Vassily_Kandinsky%2C_1913_-_Composition_7.jpg')
Downloading data from https://storage.googleapis.com/download.tensorflow.org/example_images/YellowLabradorLooking_new.jpg 83281/83281 ━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━ 0s 0us/step Downloading data from https://storage.googleapis.com/download.tensorflow.org/example_images/Vassily_Kandinsky%2C_1913_-_Composition_7.jpg 195196/195196 ━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━ 0s 0us/step
可视化输入
定义一个函数来加载图像,并将它的最大尺寸限制为 512 像素。
def load_img(path_to_img):
max_dim = 512
img = tf.io.read_file(path_to_img)
img = tf.image.decode_image(img, channels=3)
img = tf.image.convert_image_dtype(img, tf.float32)
shape = tf.cast(tf.shape(img)[:-1], tf.float32)
long_dim = max(shape)
scale = max_dim / long_dim
new_shape = tf.cast(shape * scale, tf.int32)
img = tf.image.resize(img, new_shape)
img = img[tf.newaxis, :]
return img
创建一个简单的函数来显示图像
def imshow(image, title=None):
if len(image.shape) > 3:
image = tf.squeeze(image, axis=0)
plt.imshow(image)
if title:
plt.title(title)
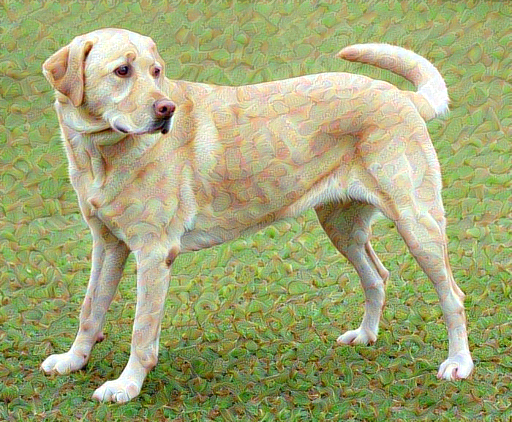
content_image = load_img(content_path)
style_image = load_img(style_path)
plt.subplot(1, 2, 1)
imshow(content_image, 'Content Image')
plt.subplot(1, 2, 2)
imshow(style_image, 'Style Image')
使用 TF-Hub 进行快速风格迁移
本教程演示了原始的风格迁移算法,该算法优化图像内容以适应特定风格。在深入了解细节之前,让我们看看 TensorFlow Hub 模型 是如何做到的
import tensorflow_hub as hub
hub_model = hub.load('https://tfhub.dev/google/magenta/arbitrary-image-stylization-v1-256/2')
stylized_image = hub_model(tf.constant(content_image), tf.constant(style_image))[0]
tensor_to_image(stylized_image)
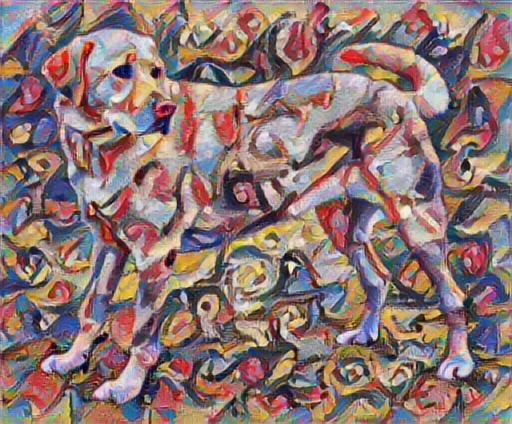
定义内容和风格表示
使用模型的中间层来获取图像的内容和风格表示。从网络的输入层开始,前几个层激活表示低级特征,如边缘和纹理。随着你逐步遍历网络,最后几个层表示更高级别的特征——物体部件,如轮子或眼睛。在本例中,你使用的是 VGG19 网络架构,这是一个预训练的图像分类网络。这些中间层对于定义图像的内容和风格表示是必要的。对于输入图像,尝试在这些中间层匹配相应风格和内容目标表示。
加载一个 VGG19 并对我们的图像进行测试运行,以确保它被正确使用
x = tf.keras.applications.vgg19.preprocess_input(content_image*255)
x = tf.image.resize(x, (224, 224))
vgg = tf.keras.applications.VGG19(include_top=True, weights='imagenet')
prediction_probabilities = vgg(x)
prediction_probabilities.shape
Downloading data from https://storage.googleapis.com/tensorflow/keras-applications/vgg19/vgg19_weights_tf_dim_ordering_tf_kernels.h5 574710816/574710816 ━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━ 10s 0us/step TensorShape([1, 1000])
predicted_top_5 = tf.keras.applications.vgg19.decode_predictions(prediction_probabilities.numpy())[0]
[(class_name, prob) for (number, class_name, prob) in predicted_top_5]
Downloading data from https://storage.googleapis.com/download.tensorflow.org/data/imagenet_class_index.json
35363/35363 ━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━ 0s 0us/step
[('Labrador_retriever', 0.49317107),
('golden_retriever', 0.23665293),
('kuvasz', 0.03635751),
('Chesapeake_Bay_retriever', 0.024182767),
('Greater_Swiss_Mountain_dog', 0.018646102)]
现在加载一个 VGG19,不带分类头,并列出层名称
vgg = tf.keras.applications.VGG19(include_top=False, weights='imagenet')
print()
for layer in vgg.layers:
print(layer.name)
Downloading data from https://storage.googleapis.com/tensorflow/keras-applications/vgg19/vgg19_weights_tf_dim_ordering_tf_kernels_notop.h5 80134624/80134624 ━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━ 0s 0us/step input_layer_1 block1_conv1 block1_conv2 block1_pool block2_conv1 block2_conv2 block2_pool block3_conv1 block3_conv2 block3_conv3 block3_conv4 block3_pool block4_conv1 block4_conv2 block4_conv3 block4_conv4 block4_pool block5_conv1 block5_conv2 block5_conv3 block5_conv4 block5_pool
从网络中选择中间层来表示图像的风格和内容
content_layers = ['block5_conv2']
style_layers = ['block1_conv1',
'block2_conv1',
'block3_conv1',
'block4_conv1',
'block5_conv1']
num_content_layers = len(content_layers)
num_style_layers = len(style_layers)
风格和内容的中间层
那么,为什么我们预训练的图像分类网络中的这些中间输出能够让我们定义风格和内容表示呢?
从高层次上讲,为了让网络执行图像分类(这个网络已被训练执行此操作),它必须理解图像。这需要将原始图像作为输入像素,并构建一个内部表示,将原始图像像素转换为对图像中存在的特征的复杂理解。
这也是卷积神经网络能够很好地泛化的原因:它们能够捕获类(例如猫与狗)中的不变性和定义特征,这些特征与背景噪声和其他干扰无关。因此,在原始图像被馈送到模型和输出分类标签之间,模型充当一个复杂的特征提取器。通过访问模型的中间层,你能够描述输入图像的内容和风格。
构建模型
中的网络 tf.keras.applications 被设计为你可以使用 Keras 函数式 API 轻松提取中间层值。
要使用函数式 API 定义模型,请指定输入和输出
model = Model(inputs, outputs)
以下函数构建一个 VGG19 模型,该模型返回一个中间层输出列表
def vgg_layers(layer_names):
""" Creates a VGG model that returns a list of intermediate output values."""
# Load our model. Load pretrained VGG, trained on ImageNet data
vgg = tf.keras.applications.VGG19(include_top=False, weights='imagenet')
vgg.trainable = False
outputs = [vgg.get_layer(name).output for name in layer_names]
model = tf.keras.Model([vgg.input], outputs)
return model
并创建模型
style_extractor = vgg_layers(style_layers)
style_outputs = style_extractor(style_image*255)
#Look at the statistics of each layer's output
for name, output in zip(style_layers, style_outputs):
print(name)
print(" shape: ", output.numpy().shape)
print(" min: ", output.numpy().min())
print(" max: ", output.numpy().max())
print(" mean: ", output.numpy().mean())
print()
block1_conv1 shape: (1, 336, 512, 64) min: 0.0 max: 835.5256 mean: 33.97525 block2_conv1 shape: (1, 168, 256, 128) min: 0.0 max: 4625.8857 mean: 199.82687 block3_conv1 shape: (1, 84, 128, 256) min: 0.0 max: 8789.239 mean: 230.78099 block4_conv1 shape: (1, 42, 64, 512) min: 0.0 max: 21566.135 mean: 791.24005 block5_conv1 shape: (1, 21, 32, 512) min: 0.0 max: 3189.2542 mean: 59.179478
计算风格
图像的内容由中间特征图的值表示。
事实证明,图像的风格可以用不同特征图之间的均值和相关性来描述。通过对每个位置的特征向量与其自身进行外积,并在所有位置上对该外积进行平均,来计算包含此信息的 Gram 矩阵。可以针对特定层计算此 Gram 矩阵,如下所示
\[G^l_{cd} = \frac{\sum_{ij} F^l_{ijc}(x)F^l_{ijd}(x)}{IJ}\]
这可以使用 tf.linalg.einsum 函数简洁地实现
def gram_matrix(input_tensor):
result = tf.linalg.einsum('bijc,bijd->bcd', input_tensor, input_tensor)
input_shape = tf.shape(input_tensor)
num_locations = tf.cast(input_shape[1]*input_shape[2], tf.float32)
return result/(num_locations)
提取风格和内容
构建一个返回风格和内容张量的模型。
class StyleContentModel(tf.keras.models.Model):
def __init__(self, style_layers, content_layers):
super(StyleContentModel, self).__init__()
self.vgg = vgg_layers(style_layers + content_layers)
self.style_layers = style_layers
self.content_layers = content_layers
self.num_style_layers = len(style_layers)
self.vgg.trainable = False
def call(self, inputs):
"Expects float input in [0,1]"
inputs = inputs*255.0
preprocessed_input = tf.keras.applications.vgg19.preprocess_input(inputs)
outputs = self.vgg(preprocessed_input)
style_outputs, content_outputs = (outputs[:self.num_style_layers],
outputs[self.num_style_layers:])
style_outputs = [gram_matrix(style_output)
for style_output in style_outputs]
content_dict = {content_name: value
for content_name, value
in zip(self.content_layers, content_outputs)}
style_dict = {style_name: value
for style_name, value
in zip(self.style_layers, style_outputs)}
return {'content': content_dict, 'style': style_dict}
当对图像调用此模型时,它将返回 style_layers 的 Gram 矩阵(风格)和 content_layers 的内容
extractor = StyleContentModel(style_layers, content_layers)
results = extractor(tf.constant(content_image))
print('Styles:')
for name, output in sorted(results['style'].items()):
print(" ", name)
print(" shape: ", output.numpy().shape)
print(" min: ", output.numpy().min())
print(" max: ", output.numpy().max())
print(" mean: ", output.numpy().mean())
print()
print("Contents:")
for name, output in sorted(results['content'].items()):
print(" ", name)
print(" shape: ", output.numpy().shape)
print(" min: ", output.numpy().min())
print(" max: ", output.numpy().max())
print(" mean: ", output.numpy().mean())
Styles:
block1_conv1
shape: (1, 64, 64)
min: 0.005522845
max: 28014.555
mean: 263.79022
block2_conv1
shape: (1, 128, 128)
min: 0.0
max: 61479.484
mean: 9100.949
block3_conv1
shape: (1, 256, 256)
min: 0.0
max: 545623.44
mean: 7660.976
block4_conv1
shape: (1, 512, 512)
min: 0.0
max: 4320502.0
mean: 134288.84
block5_conv1
shape: (1, 512, 512)
min: 0.0
max: 110005.37
mean: 1487.0378
Contents:
block5_conv2
shape: (1, 26, 32, 512)
min: 0.0
max: 2410.8796
mean: 13.764149
运行梯度下降
有了这个风格和内容提取器,你现在可以实现风格迁移算法。通过计算图像输出相对于每个目标的均方误差来做到这一点,然后取这些损失的加权和。
设置你的风格和内容目标值
style_targets = extractor(style_image)['style']
content_targets = extractor(content_image)['content']
定义一个 tf.Variable 来包含要优化的图像。为了快速完成此操作,用内容图像对其进行初始化(tf.Variable 必须与内容图像具有相同的形状)
image = tf.Variable(content_image)
由于这是一个浮点图像,因此定义一个函数来将像素值保持在 0 和 1 之间
def clip_0_1(image):
return tf.clip_by_value(image, clip_value_min=0.0, clip_value_max=1.0)
创建一个优化器。论文推荐 LBFGS,但 Adam 也效果不错
opt = tf.keras.optimizers.Adam(learning_rate=0.02, beta_1=0.99, epsilon=1e-1)
为了优化这一点,使用两个损失的加权组合来获得总损失
style_weight=1e-2
content_weight=1e4
def style_content_loss(outputs):
style_outputs = outputs['style']
content_outputs = outputs['content']
style_loss = tf.add_n([tf.reduce_mean((style_outputs[name]-style_targets[name])**2)
for name in style_outputs.keys()])
style_loss *= style_weight / num_style_layers
content_loss = tf.add_n([tf.reduce_mean((content_outputs[name]-content_targets[name])**2)
for name in content_outputs.keys()])
content_loss *= content_weight / num_content_layers
loss = style_loss + content_loss
return loss
使用 tf.GradientTape 来更新图像。
@tf.function()
def train_step(image):
with tf.GradientTape() as tape:
outputs = extractor(image)
loss = style_content_loss(outputs)
grad = tape.gradient(loss, image)
opt.apply_gradients([(grad, image)])
image.assign(clip_0_1(image))
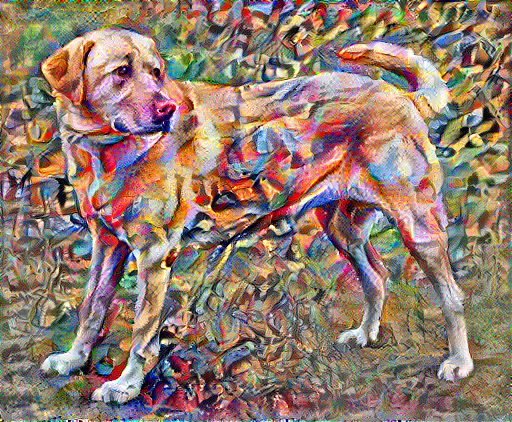
现在运行几个步骤进行测试
train_step(image)
train_step(image)
train_step(image)
tensor_to_image(image)

由于它正在工作,因此执行更长时间的优化
import time
start = time.time()
epochs = 10
steps_per_epoch = 100
step = 0
for n in range(epochs):
for m in range(steps_per_epoch):
step += 1
train_step(image)
print(".", end='', flush=True)
display.clear_output(wait=True)
display.display(tensor_to_image(image))
print("Train step: {}".format(step))
end = time.time()
print("Total time: {:.1f}".format(end-start))

Train step: 1000 Total time: 79.0
总变异损失
这种基本实现的一个缺点是它会产生很多高频伪影。使用图像高频分量的显式正则化项来减少这些伪影。在风格迁移中,这通常被称为总变异损失
def high_pass_x_y(image):
x_var = image[:, :, 1:, :] - image[:, :, :-1, :]
y_var = image[:, 1:, :, :] - image[:, :-1, :, :]
return x_var, y_var
x_deltas, y_deltas = high_pass_x_y(content_image)
plt.figure(figsize=(14, 10))
plt.subplot(2, 2, 1)
imshow(clip_0_1(2*y_deltas+0.5), "Horizontal Deltas: Original")
plt.subplot(2, 2, 2)
imshow(clip_0_1(2*x_deltas+0.5), "Vertical Deltas: Original")
x_deltas, y_deltas = high_pass_x_y(image)
plt.subplot(2, 2, 3)
imshow(clip_0_1(2*y_deltas+0.5), "Horizontal Deltas: Styled")
plt.subplot(2, 2, 4)
imshow(clip_0_1(2*x_deltas+0.5), "Vertical Deltas: Styled")
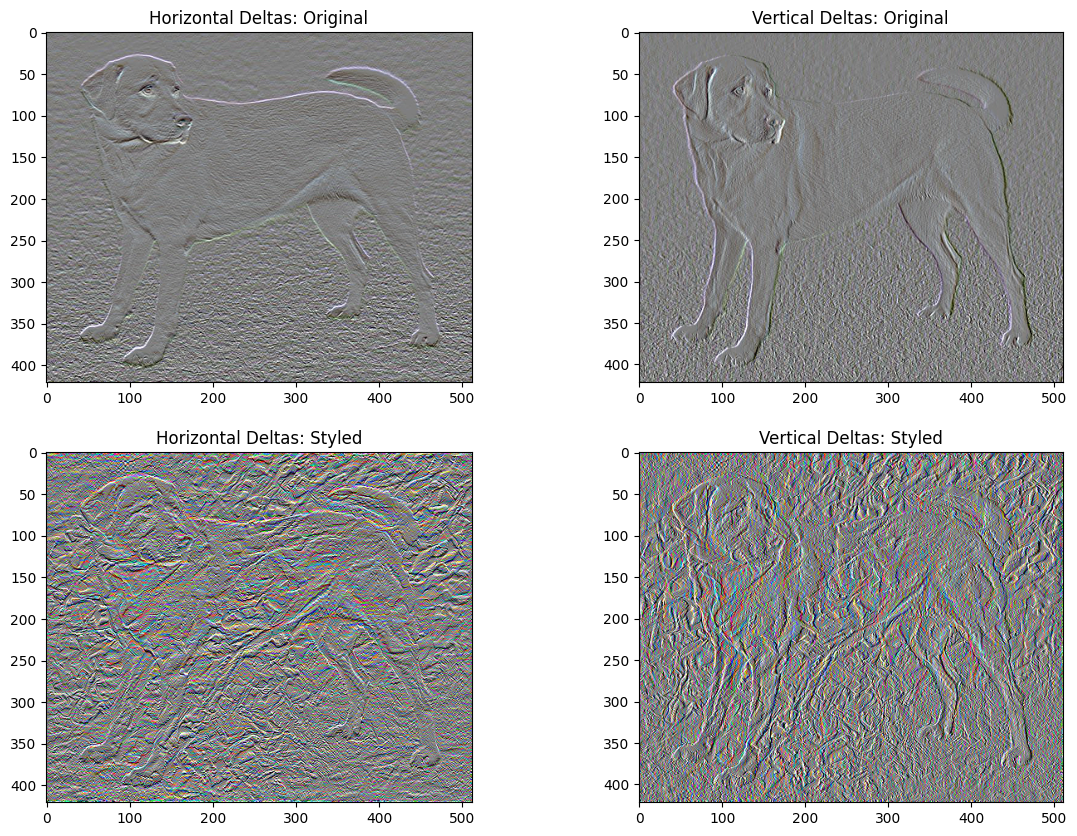
这显示了高频分量是如何增加的。
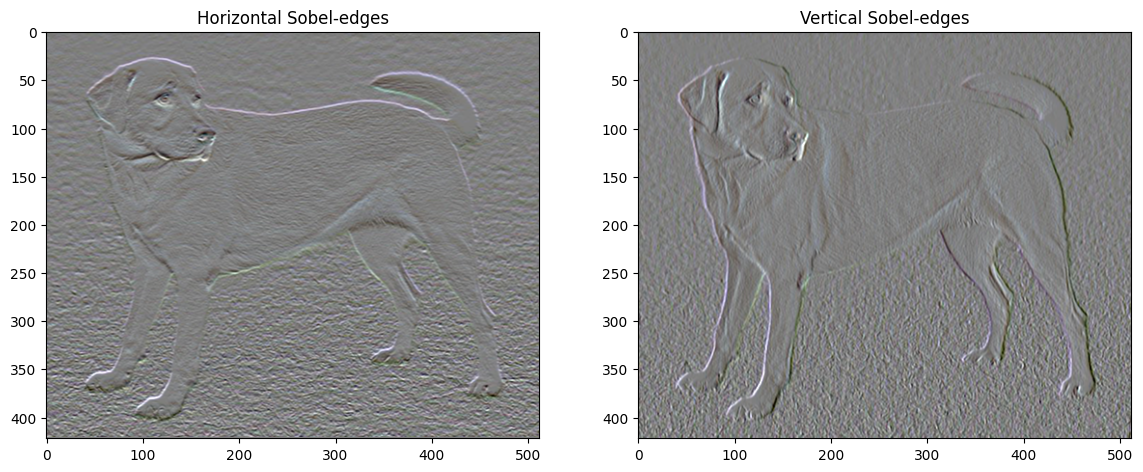
此外,这个高频分量基本上是一个边缘检测器。例如,你可以从 Sobel 边缘检测器获得类似的输出
plt.figure(figsize=(14, 10))
sobel = tf.image.sobel_edges(content_image)
plt.subplot(1, 2, 1)
imshow(clip_0_1(sobel[..., 0]/4+0.5), "Horizontal Sobel-edges")
plt.subplot(1, 2, 2)
imshow(clip_0_1(sobel[..., 1]/4+0.5), "Vertical Sobel-edges")
与此相关的正则化损失是值的平方和
def total_variation_loss(image):
x_deltas, y_deltas = high_pass_x_y(image)
return tf.reduce_sum(tf.abs(x_deltas)) + tf.reduce_sum(tf.abs(y_deltas))
total_variation_loss(image).numpy()
149171.38
这演示了它的作用。但是,你无需自己实现它,TensorFlow 包含一个标准实现
tf.image.total_variation(image).numpy()
array([149171.38], dtype=float32)
重新运行优化
为 total_variation_loss 选择一个权重
total_variation_weight=30
现在将其包含在 train_step 函数中
@tf.function()
def train_step(image):
with tf.GradientTape() as tape:
outputs = extractor(image)
loss = style_content_loss(outputs)
loss += total_variation_weight*tf.image.total_variation(image)
grad = tape.gradient(loss, image)
opt.apply_gradients([(grad, image)])
image.assign(clip_0_1(image))
重新初始化图像变量和优化器
opt = tf.keras.optimizers.Adam(learning_rate=0.02, beta_1=0.99, epsilon=1e-1)
image = tf.Variable(content_image)
并运行优化
import time
start = time.time()
epochs = 10
steps_per_epoch = 100
step = 0
for n in range(epochs):
for m in range(steps_per_epoch):
step += 1
train_step(image)
print(".", end='', flush=True)
display.clear_output(wait=True)
display.display(tensor_to_image(image))
print("Train step: {}".format(step))
end = time.time()
print("Total time: {:.1f}".format(end-start))
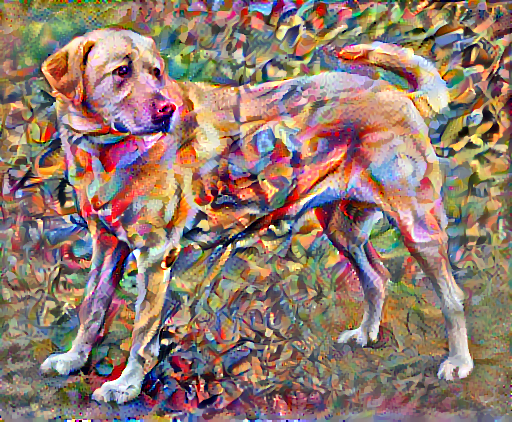

Train step: 1000 Total time: 83.0
最后,保存结果
file_name = 'stylized-image.png'
tensor_to_image(image).save(file_name)
try:
from google.colab import files
files.download(file_name)
except (ImportError, AttributeError):
pass
了解更多
本教程演示了原始的风格迁移算法。要简单应用风格迁移,请查看此 教程,以了解有关如何使用来自 TensorFlow Hub 的任意图像风格迁移模型的更多信息。
