 在 TensorFlow.org 上查看 在 TensorFlow.org 上查看
|
 在 Google Colab 中运行 在 Google Colab 中运行
|
 在 GitHub 上查看源代码 在 GitHub 上查看源代码
|
 下载笔记本 下载笔记本
|
本教程演示了如何构建和训练一个名为 pix2pix 的条件生成对抗网络 (cGAN),该网络学习从输入图像到输出图像的映射,如 Isola 等人 (2017) 在 使用条件对抗网络进行图像到图像的转换 中所述。pix2pix 不是特定于应用程序的 - 它可以应用于各种任务,包括从标签图合成照片、从黑白图像生成彩色照片、将 Google 地图照片转换为航拍图像,甚至将草图转换为照片。
在本示例中,您的网络将使用 CMP 外观数据库 生成建筑立面的图像,该数据库由 机器感知中心 在 捷克布拉格理工大学 提供。为了简短起见,您将使用 pix2pix 作者创建的 预处理副本。
在 pix2pix cGAN 中,您需要根据输入图像进行条件设置,并生成相应的输出图像。cGAN 最初是在 条件生成对抗网络 (Mirza 和 Osindero,2014) 中提出的。
您的网络架构将包含
- 一个基于 U-Net 架构的生成器。
- 一个由卷积 PatchGAN 分类器(在 pix2pix 论文 中提出)表示的判别器。
请注意,每个 epoch 在单个 V100 GPU 上大约需要 15 秒。
以下是 pix2pix cGAN 在 facades 数据集(80k 步)上训练 200 个 epoch 后生成的输出示例。


导入 TensorFlow 和其他库
import tensorflow as tf
import os
import pathlib
import time
import datetime
from matplotlib import pyplot as plt
from IPython import display
加载数据集
下载 CMP Facade Database 数据(30MB)。其他数据集以相同格式提供 此处。在 Colab 中,您可以从下拉菜单中选择其他数据集。请注意,其他一些数据集的大小要大得多(edges2handbags 的大小为 8GB)。
dataset_name = "facades"
_URL = f'http://efrosgans.eecs.berkeley.edu/pix2pix/datasets/{dataset_name}.tar.gz'
path_to_zip = tf.keras.utils.get_file(
fname=f"{dataset_name}.tar.gz",
origin=_URL,
extract=True)
path_to_zip = pathlib.Path(path_to_zip)
PATH = path_to_zip.parent/dataset_name
Downloading data from http://efrosgans.eecs.berkeley.edu/pix2pix/datasets/facades.tar.gz 30168306/30168306 ━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━ 11s 0us/step
list(PATH.parent.iterdir())
[PosixPath('/home/kbuilder/.keras/datasets/Red_sunflower'),
PosixPath('/home/kbuilder/.keras/datasets/fashion-mnist'),
PosixPath('/home/kbuilder/.keras/datasets/mnist.npz'),
PosixPath('/home/kbuilder/.keras/datasets/HIGGS.csv.gz'),
PosixPath('/home/kbuilder/.keras/datasets/facades.tar.gz'),
PosixPath('/home/kbuilder/.keras/datasets/facades'),
PosixPath('/home/kbuilder/.keras/datasets/flower_photos.tar'),
PosixPath('/home/kbuilder/.keras/datasets/flower_photos')]
每个原始图像的大小为 256 x 512,包含两个 256 x 256 图像
sample_image = tf.io.read_file(str(PATH / 'train/1.jpg'))
sample_image = tf.io.decode_jpeg(sample_image)
print(sample_image.shape)
(256, 512, 3)
plt.figure()
plt.imshow(sample_image)
<matplotlib.image.AxesImage at 0x7f2d3a277550>
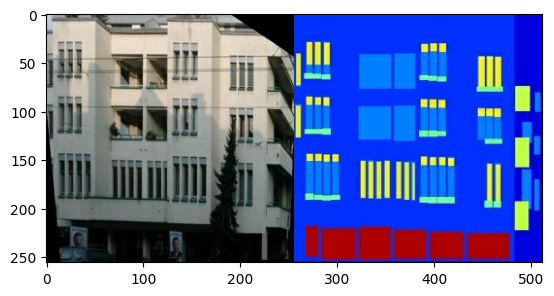
您需要将真实的建筑立面图像与建筑标签图像分开——所有图像的大小都将为 256 x 256。
定义一个加载图像文件并输出两个图像张量的函数
def load(image_file):
# Read and decode an image file to a uint8 tensor
image = tf.io.read_file(image_file)
image = tf.io.decode_jpeg(image)
# Split each image tensor into two tensors:
# - one with a real building facade image
# - one with an architecture label image
w = tf.shape(image)[1]
w = w // 2
input_image = image[:, w:, :]
real_image = image[:, :w, :]
# Convert both images to float32 tensors
input_image = tf.cast(input_image, tf.float32)
real_image = tf.cast(real_image, tf.float32)
return input_image, real_image
绘制输入(建筑标签图像)和真实(建筑立面照片)图像的样本
inp, re = load(str(PATH / 'train/100.jpg'))
# Casting to int for matplotlib to display the images
plt.figure()
plt.imshow(inp / 255.0)
plt.figure()
plt.imshow(re / 255.0)
<matplotlib.image.AxesImage at 0x7f2d380249d0>
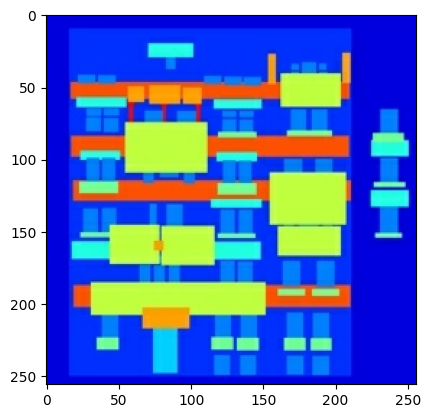
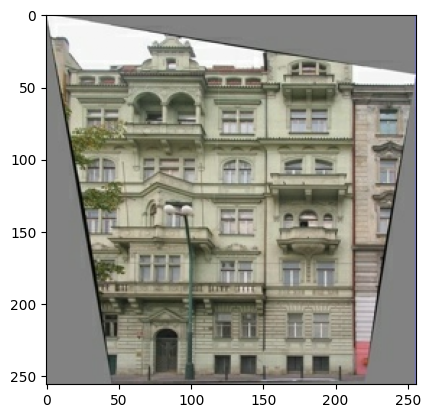
如 pix2pix 论文 中所述,您需要应用随机抖动和镜像来预处理训练集。
定义几个函数,这些函数
- 将每个
256 x 256图像调整为更大的高度和宽度——286 x 286。 - 随机将其裁剪回
256 x 256。 - 随机水平翻转图像,即从左到右(随机镜像)。
- 将图像归一化为
[-1, 1]范围。
# The facade training set consist of 400 images
BUFFER_SIZE = 400
# The batch size of 1 produced better results for the U-Net in the original pix2pix experiment
BATCH_SIZE = 1
# Each image is 256x256 in size
IMG_WIDTH = 256
IMG_HEIGHT = 256
def resize(input_image, real_image, height, width):
input_image = tf.image.resize(input_image, [height, width],
method=tf.image.ResizeMethod.NEAREST_NEIGHBOR)
real_image = tf.image.resize(real_image, [height, width],
method=tf.image.ResizeMethod.NEAREST_NEIGHBOR)
return input_image, real_image
def random_crop(input_image, real_image):
stacked_image = tf.stack([input_image, real_image], axis=0)
cropped_image = tf.image.random_crop(
stacked_image, size=[2, IMG_HEIGHT, IMG_WIDTH, 3])
return cropped_image[0], cropped_image[1]
# Normalizing the images to [-1, 1]
def normalize(input_image, real_image):
input_image = (input_image / 127.5) - 1
real_image = (real_image / 127.5) - 1
return input_image, real_image
@tf.function()
def random_jitter(input_image, real_image):
# Resizing to 286x286
input_image, real_image = resize(input_image, real_image, 286, 286)
# Random cropping back to 256x256
input_image, real_image = random_crop(input_image, real_image)
if tf.random.uniform(()) > 0.5:
# Random mirroring
input_image = tf.image.flip_left_right(input_image)
real_image = tf.image.flip_left_right(real_image)
return input_image, real_image
您可以检查一些预处理后的输出
plt.figure(figsize=(6, 6))
for i in range(4):
rj_inp, rj_re = random_jitter(inp, re)
plt.subplot(2, 2, i + 1)
plt.imshow(rj_inp / 255.0)
plt.axis('off')
plt.show()
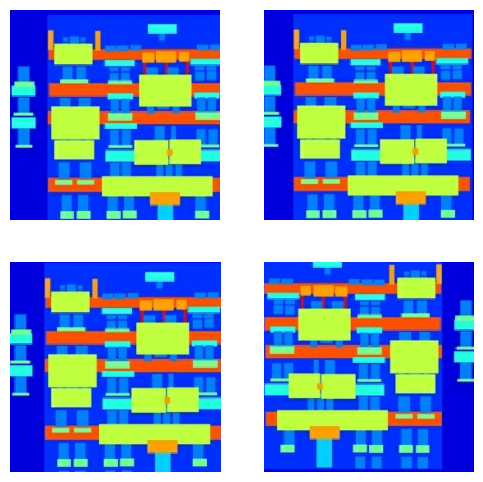
在检查了加载和预处理是否有效后,让我们定义几个辅助函数来加载和预处理训练集和测试集
def load_image_train(image_file):
input_image, real_image = load(image_file)
input_image, real_image = random_jitter(input_image, real_image)
input_image, real_image = normalize(input_image, real_image)
return input_image, real_image
def load_image_test(image_file):
input_image, real_image = load(image_file)
input_image, real_image = resize(input_image, real_image,
IMG_HEIGHT, IMG_WIDTH)
input_image, real_image = normalize(input_image, real_image)
return input_image, real_image
使用 tf.data 构建输入管道
train_dataset = tf.data.Dataset.list_files(str(PATH / 'train/*.jpg'))
train_dataset = train_dataset.map(load_image_train,
num_parallel_calls=tf.data.AUTOTUNE)
train_dataset = train_dataset.shuffle(BUFFER_SIZE)
train_dataset = train_dataset.batch(BATCH_SIZE)
try:
test_dataset = tf.data.Dataset.list_files(str(PATH / 'test/*.jpg'))
except tf.errors.InvalidArgumentError:
test_dataset = tf.data.Dataset.list_files(str(PATH / 'val/*.jpg'))
test_dataset = test_dataset.map(load_image_test)
test_dataset = test_dataset.batch(BATCH_SIZE)
构建生成器
pix2pix cGAN 的生成器是一个修改后的 U-Net。U-Net 由编码器(降采样器)和解码器(上采样器)组成。(您可以在 图像分割 教程和 U-Net 项目网站 上找到更多相关信息。)
- 编码器中的每个块为:卷积 -> 批量归一化 -> Leaky ReLU
- 解码器中的每个块为:转置卷积 -> 批量归一化 -> Dropout(应用于前 3 个块) -> ReLU
- 编码器和解码器之间存在跳跃连接(如 U-Net 中那样)。
定义降采样器(编码器)
OUTPUT_CHANNELS = 3
def downsample(filters, size, apply_batchnorm=True):
initializer = tf.random_normal_initializer(0., 0.02)
result = tf.keras.Sequential()
result.add(
tf.keras.layers.Conv2D(filters, size, strides=2, padding='same',
kernel_initializer=initializer, use_bias=False))
if apply_batchnorm:
result.add(tf.keras.layers.BatchNormalization())
result.add(tf.keras.layers.LeakyReLU())
return result
down_model = downsample(3, 4)
down_result = down_model(tf.expand_dims(inp, 0))
print (down_result.shape)
(1, 128, 128, 3)
定义上采样器(解码器)
def upsample(filters, size, apply_dropout=False):
initializer = tf.random_normal_initializer(0., 0.02)
result = tf.keras.Sequential()
result.add(
tf.keras.layers.Conv2DTranspose(filters, size, strides=2,
padding='same',
kernel_initializer=initializer,
use_bias=False))
result.add(tf.keras.layers.BatchNormalization())
if apply_dropout:
result.add(tf.keras.layers.Dropout(0.5))
result.add(tf.keras.layers.ReLU())
return result
up_model = upsample(3, 4)
up_result = up_model(down_result)
print (up_result.shape)
(1, 256, 256, 3)
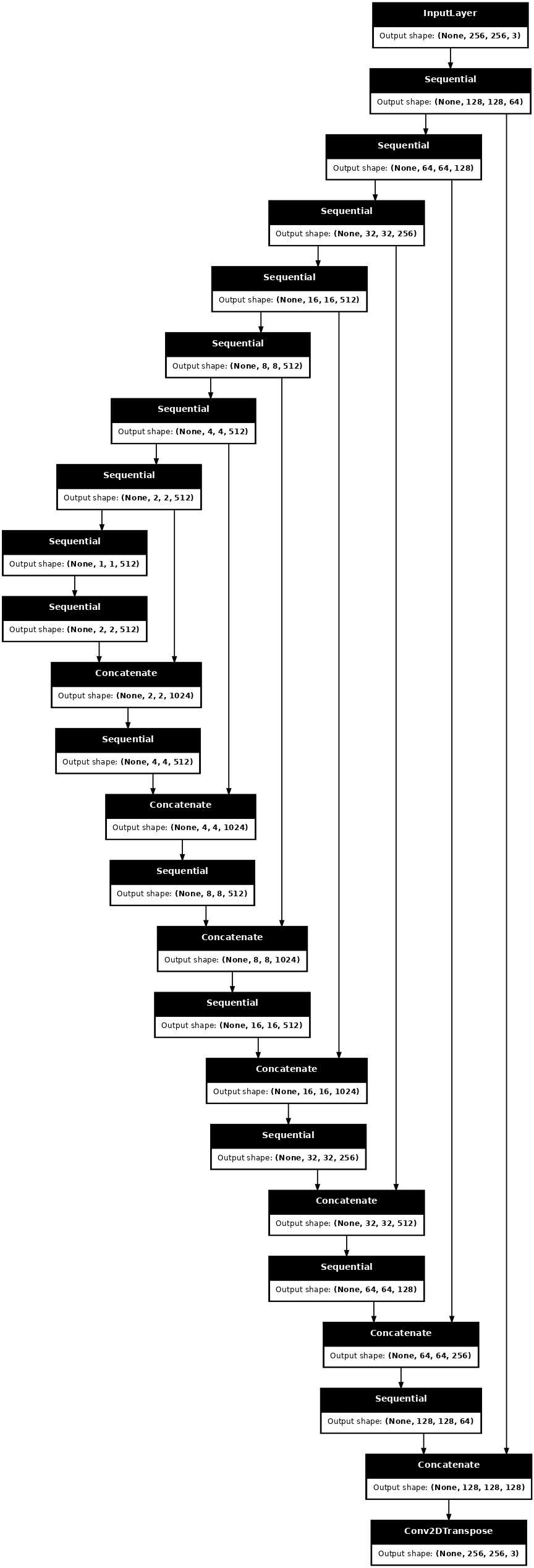
使用降采样器和上采样器定义生成器
def Generator():
inputs = tf.keras.layers.Input(shape=[256, 256, 3])
down_stack = [
downsample(64, 4, apply_batchnorm=False), # (batch_size, 128, 128, 64)
downsample(128, 4), # (batch_size, 64, 64, 128)
downsample(256, 4), # (batch_size, 32, 32, 256)
downsample(512, 4), # (batch_size, 16, 16, 512)
downsample(512, 4), # (batch_size, 8, 8, 512)
downsample(512, 4), # (batch_size, 4, 4, 512)
downsample(512, 4), # (batch_size, 2, 2, 512)
downsample(512, 4), # (batch_size, 1, 1, 512)
]
up_stack = [
upsample(512, 4, apply_dropout=True), # (batch_size, 2, 2, 1024)
upsample(512, 4, apply_dropout=True), # (batch_size, 4, 4, 1024)
upsample(512, 4, apply_dropout=True), # (batch_size, 8, 8, 1024)
upsample(512, 4), # (batch_size, 16, 16, 1024)
upsample(256, 4), # (batch_size, 32, 32, 512)
upsample(128, 4), # (batch_size, 64, 64, 256)
upsample(64, 4), # (batch_size, 128, 128, 128)
]
initializer = tf.random_normal_initializer(0., 0.02)
last = tf.keras.layers.Conv2DTranspose(OUTPUT_CHANNELS, 4,
strides=2,
padding='same',
kernel_initializer=initializer,
activation='tanh') # (batch_size, 256, 256, 3)
x = inputs
# Downsampling through the model
skips = []
for down in down_stack:
x = down(x)
skips.append(x)
skips = reversed(skips[:-1])
# Upsampling and establishing the skip connections
for up, skip in zip(up_stack, skips):
x = up(x)
x = tf.keras.layers.Concatenate()([x, skip])
x = last(x)
return tf.keras.Model(inputs=inputs, outputs=x)
可视化生成器模型架构
generator = Generator()
tf.keras.utils.plot_model(generator, show_shapes=True, dpi=64)
测试生成器
gen_output = generator(inp[tf.newaxis, ...], training=False)
plt.imshow(gen_output[0, ...])
Clipping input data to the valid range for imshow with RGB data ([0..1] for floats or [0..255] for integers). <matplotlib.image.AxesImage at 0x7f2e4b7c56d0>
定义生成器损失
GAN 学习适应数据的损失,而 cGAN 学习结构化的损失,该损失会惩罚与网络输出和目标图像不同的可能结构,如 pix2pix 论文 中所述。
- 生成器损失是生成图像和一数组的 sigmoid 交叉熵损失。
- pix2pix 论文还提到了 L1 损失,它是生成图像与目标图像之间的 MAE(平均绝对误差)。
- 这使得生成图像在结构上与目标图像相似。
- 计算总生成器损失的公式为
gan_loss + LAMBDA * l1_loss,其中LAMBDA = 100。该值由论文作者决定。
LAMBDA = 100
loss_object = tf.keras.losses.BinaryCrossentropy(from_logits=True)
def generator_loss(disc_generated_output, gen_output, target):
gan_loss = loss_object(tf.ones_like(disc_generated_output), disc_generated_output)
# Mean absolute error
l1_loss = tf.reduce_mean(tf.abs(target - gen_output))
total_gen_loss = gan_loss + (LAMBDA * l1_loss)
return total_gen_loss, gan_loss, l1_loss
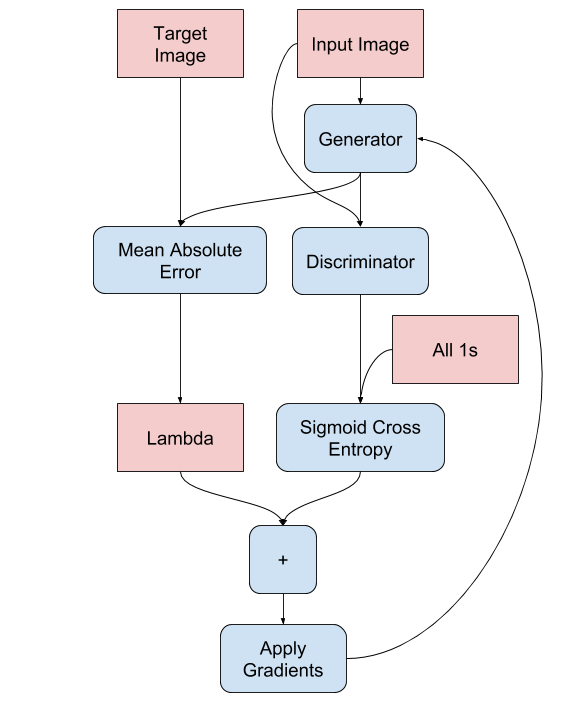
生成器的训练过程如下
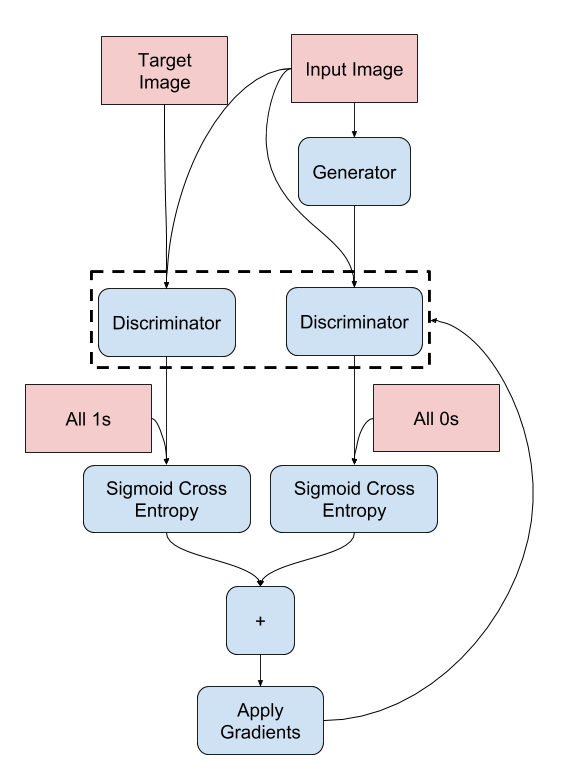
构建判别器
pix2pix cGAN 中的判别器是一个卷积 PatchGAN 分类器——它试图对每个图像块进行分类,判断它是真实的还是假的,如 pix2pix 论文 中所述。
- 判别器中的每个块为:卷积 -> 批量归一化 -> Leaky ReLU。
- 最后一层之后的输出形状为
(batch_size, 30, 30, 1)。 - 输出的每个
30 x 30图像块对输入图像的70 x 70部分进行分类。 - 判别器接收 2 个输入
- 输入图像和目标图像,它应该将其分类为真实图像。
- 输入图像和生成图像(生成器的输出),它应该将其分类为假图像。
- 使用
tf.concat([inp, tar], axis=-1)将这两个输入连接在一起。
让我们定义判别器
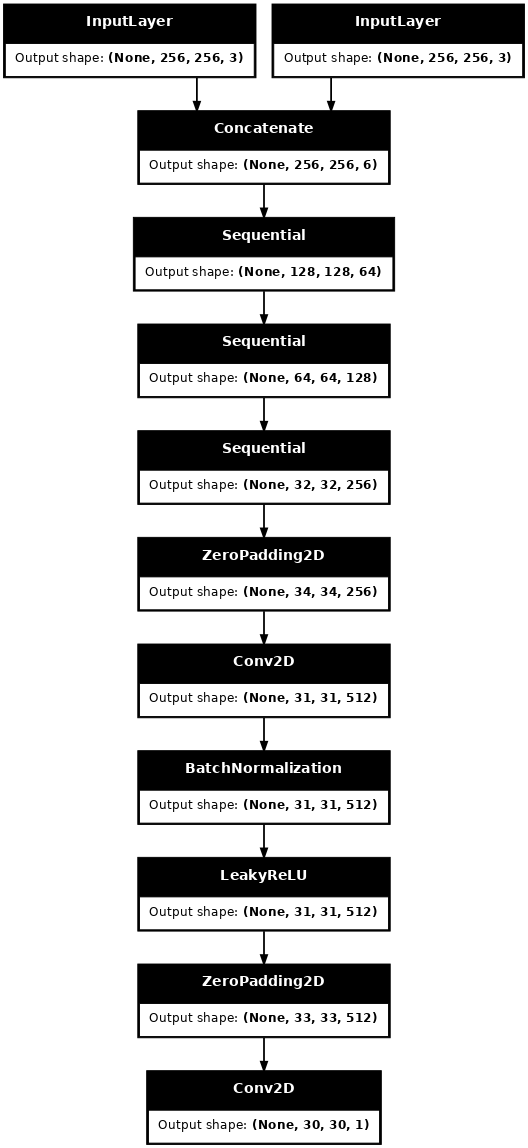
def Discriminator():
initializer = tf.random_normal_initializer(0., 0.02)
inp = tf.keras.layers.Input(shape=[256, 256, 3], name='input_image')
tar = tf.keras.layers.Input(shape=[256, 256, 3], name='target_image')
x = tf.keras.layers.concatenate([inp, tar]) # (batch_size, 256, 256, channels*2)
down1 = downsample(64, 4, False)(x) # (batch_size, 128, 128, 64)
down2 = downsample(128, 4)(down1) # (batch_size, 64, 64, 128)
down3 = downsample(256, 4)(down2) # (batch_size, 32, 32, 256)
zero_pad1 = tf.keras.layers.ZeroPadding2D()(down3) # (batch_size, 34, 34, 256)
conv = tf.keras.layers.Conv2D(512, 4, strides=1,
kernel_initializer=initializer,
use_bias=False)(zero_pad1) # (batch_size, 31, 31, 512)
batchnorm1 = tf.keras.layers.BatchNormalization()(conv)
leaky_relu = tf.keras.layers.LeakyReLU()(batchnorm1)
zero_pad2 = tf.keras.layers.ZeroPadding2D()(leaky_relu) # (batch_size, 33, 33, 512)
last = tf.keras.layers.Conv2D(1, 4, strides=1,
kernel_initializer=initializer)(zero_pad2) # (batch_size, 30, 30, 1)
return tf.keras.Model(inputs=[inp, tar], outputs=last)
可视化判别器模型架构
discriminator = Discriminator()
tf.keras.utils.plot_model(discriminator, show_shapes=True, dpi=64)
测试判别器
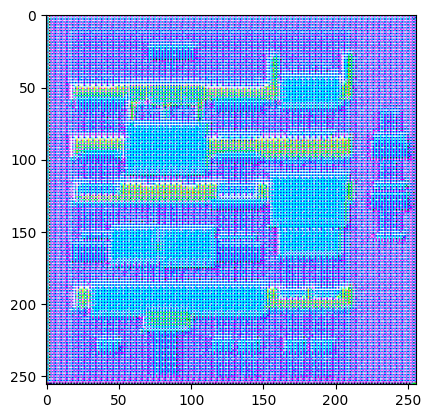
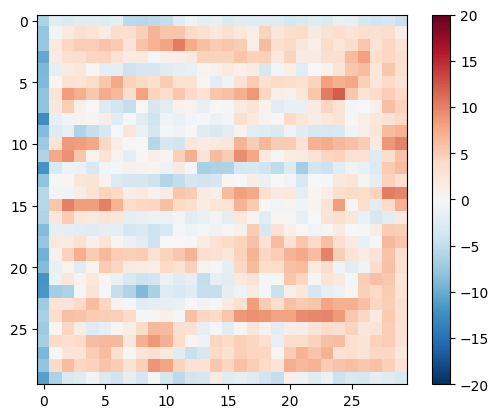
disc_out = discriminator([inp[tf.newaxis, ...], gen_output], training=False)
plt.imshow(disc_out[0, ..., -1], vmin=-20, vmax=20, cmap='RdBu_r')
plt.colorbar()
<matplotlib.colorbar.Colorbar at 0x7f2e4b77af10>
定义判别器损失
- 函数
discriminator_loss接收 2 个输入:真实图像和生成图像。 real_loss是真实图像和一数组(因为这些是真实图像)的 sigmoid 交叉熵损失。generated_loss是生成图像和一数组(因为这些是假图像)的 sigmoid 交叉熵损失。total_loss是real_loss和generated_loss的总和。
def discriminator_loss(disc_real_output, disc_generated_output):
real_loss = loss_object(tf.ones_like(disc_real_output), disc_real_output)
generated_loss = loss_object(tf.zeros_like(disc_generated_output), disc_generated_output)
total_disc_loss = real_loss + generated_loss
return total_disc_loss
判别器的训练过程如下所示。
要详细了解架构和超参数,您可以参考 pix2pix 论文。
定义优化器和检查点保存器
generator_optimizer = tf.keras.optimizers.Adam(2e-4, beta_1=0.5)
discriminator_optimizer = tf.keras.optimizers.Adam(2e-4, beta_1=0.5)
checkpoint_dir = './training_checkpoints'
checkpoint_prefix = os.path.join(checkpoint_dir, "ckpt")
checkpoint = tf.train.Checkpoint(generator_optimizer=generator_optimizer,
discriminator_optimizer=discriminator_optimizer,
generator=generator,
discriminator=discriminator)
生成图像
编写一个函数,在训练期间绘制一些图像。
- 将测试集中的图像传递给生成器。
- 然后,生成器将输入图像转换为输出。
- 最后一步是绘制预测结果,然后瞧!
def generate_images(model, test_input, tar):
prediction = model(test_input, training=True)
plt.figure(figsize=(15, 15))
display_list = [test_input[0], tar[0], prediction[0]]
title = ['Input Image', 'Ground Truth', 'Predicted Image']
for i in range(3):
plt.subplot(1, 3, i+1)
plt.title(title[i])
# Getting the pixel values in the [0, 1] range to plot.
plt.imshow(display_list[i] * 0.5 + 0.5)
plt.axis('off')
plt.show()
测试函数
for example_input, example_target in test_dataset.take(1):
generate_images(generator, example_input, example_target)

2024-03-19 04:15:30.212279: W tensorflow/core/framework/local_rendezvous.cc:404] Local rendezvous is aborting with status: OUT_OF_RANGE: End of sequence
训练
- 对于每个示例输入,生成一个输出。
- 判别器接收
input_image和生成图像作为第一个输入。第二个输入是input_image和target_image。 - 接下来,计算生成器和判别器损失。
- 然后,计算损失相对于生成器和判别器变量(输入)的梯度,并将这些梯度应用于优化器。
- 最后,将损失记录到 TensorBoard。
log_dir="logs/"
summary_writer = tf.summary.create_file_writer(
log_dir + "fit/" + datetime.datetime.now().strftime("%Y%m%d-%H%M%S"))
@tf.function
def train_step(input_image, target, step):
with tf.GradientTape() as gen_tape, tf.GradientTape() as disc_tape:
gen_output = generator(input_image, training=True)
disc_real_output = discriminator([input_image, target], training=True)
disc_generated_output = discriminator([input_image, gen_output], training=True)
gen_total_loss, gen_gan_loss, gen_l1_loss = generator_loss(disc_generated_output, gen_output, target)
disc_loss = discriminator_loss(disc_real_output, disc_generated_output)
generator_gradients = gen_tape.gradient(gen_total_loss,
generator.trainable_variables)
discriminator_gradients = disc_tape.gradient(disc_loss,
discriminator.trainable_variables)
generator_optimizer.apply_gradients(zip(generator_gradients,
generator.trainable_variables))
discriminator_optimizer.apply_gradients(zip(discriminator_gradients,
discriminator.trainable_variables))
with summary_writer.as_default():
tf.summary.scalar('gen_total_loss', gen_total_loss, step=step//1000)
tf.summary.scalar('gen_gan_loss', gen_gan_loss, step=step//1000)
tf.summary.scalar('gen_l1_loss', gen_l1_loss, step=step//1000)
tf.summary.scalar('disc_loss', disc_loss, step=step//1000)
实际的训练循环。由于本教程可以在多个数据集上运行,并且数据集的大小差异很大,因此训练循环被设置为按步数而不是按 epoch 运行。
- 迭代步数。
- 每 10 步打印一个点 (
.)。 - 每 1k 步:清除显示并运行
generate_images以显示进度。 - 每 5k 步:保存一个检查点。
def fit(train_ds, test_ds, steps):
example_input, example_target = next(iter(test_ds.take(1)))
start = time.time()
for step, (input_image, target) in train_ds.repeat().take(steps).enumerate():
if (step) % 1000 == 0:
display.clear_output(wait=True)
if step != 0:
print(f'Time taken for 1000 steps: {time.time()-start:.2f} sec\n')
start = time.time()
generate_images(generator, example_input, example_target)
print(f"Step: {step//1000}k")
train_step(input_image, target, step)
# Training step
if (step+1) % 10 == 0:
print('.', end='', flush=True)
# Save (checkpoint) the model every 5k steps
if (step + 1) % 5000 == 0:
checkpoint.save(file_prefix=checkpoint_prefix)
此训练循环保存日志,您可以在 TensorBoard 中查看这些日志以监控训练进度。
如果您在本地机器上工作,您将启动一个单独的 TensorBoard 进程。在笔记本中工作时,在开始训练之前启动查看器,以便使用 TensorBoard 进行监控。
启动 TensorBoard 查看器(抱歉,这不会在 tensorflow.org 上显示)
%load_ext tensorboard
%tensorboard --logdir {log_dir}
您可以在 此笔记本的先前运行结果 上查看 TensorBoard.dev。
最后,运行训练循环
fit(train_dataset, test_dataset, steps=40000)
Time taken for 1000 steps: 115.74 sec

Step: 39k .................................................................................................... 2024-03-19 05:33:08.148154: W tensorflow/core/framework/local_rendezvous.cc:404] Local rendezvous is aborting with status: OUT_OF_RANGE: End of sequence
与简单的分类或回归模型相比,在训练 GAN(或像 pix2pix 这样的 cGAN)时,解释日志更加微妙。需要注意的事项
- 检查生成器和判别器模型都没有“获胜”。如果
gen_gan_loss或disc_loss变得非常低,则表明该模型正在支配另一个模型,并且您没有成功训练组合模型。 - 值
log(2) = 0.69是这些损失的一个很好的参考点,因为它表示困惑度为 2——判别器平均来说对两个选项同样不确定。 - 对于
disc_loss,低于0.69的值意味着判别器在真实图像和生成图像的组合集上比随机效果更好。 - 对于
gen_gan_loss,低于0.69的值意味着生成器在欺骗判别器方面比随机效果更好。 - 随着训练的进行,
gen_l1_loss应该下降。
恢复最新的检查点并测试网络
ls {checkpoint_dir}
checkpoint ckpt-5.data-00000-of-00001 ckpt-1.data-00000-of-00001 ckpt-5.index ckpt-1.index ckpt-6.data-00000-of-00001 ckpt-2.data-00000-of-00001 ckpt-6.index ckpt-2.index ckpt-7.data-00000-of-00001 ckpt-3.data-00000-of-00001 ckpt-7.index ckpt-3.index ckpt-8.data-00000-of-00001 ckpt-4.data-00000-of-00001 ckpt-8.index ckpt-4.index
# Restoring the latest checkpoint in checkpoint_dir
checkpoint.restore(tf.train.latest_checkpoint(checkpoint_dir))
<tensorflow.python.checkpoint.checkpoint.CheckpointLoadStatus at 0x7f2cec068ee0>
使用测试集生成一些图像
# Run the trained model on a few examples from the test set
for inp, tar in test_dataset.take(5):
generate_images(generator, inp, tar)





2024-03-19 05:33:11.669305: W tensorflow/core/framework/local_rendezvous.cc:404] Local rendezvous is aborting with status: OUT_OF_RANGE: End of sequence
