 在 TensorFlow.org 上查看 在 TensorFlow.org 上查看
|
 在 Google Colab 中运行 在 Google Colab 中运行
|
 在 GitHub 上查看源代码 在 GitHub 上查看源代码
|
 下载笔记本 下载笔记本
|
本教程使用 Goodfellow 等人发表的论文 解释和利用对抗样本 中描述的快速梯度符号法 (FGSM) 攻击创建了一个对抗样本。这是最早也是最流行的欺骗神经网络的攻击之一。
什么是对抗样本?
对抗样本是专门设计的输入,旨在迷惑神经网络,导致对给定输入的错误分类。这些臭名昭著的输入对人眼来说是无法区分的,但会导致网络无法识别图像内容。这类攻击有多种类型,但这里重点关注快速梯度符号法攻击,这是一种**白盒攻击**,其目标是确保错误分类。白盒攻击是指攻击者可以完全访问被攻击的模型。

下面展示了一个著名的对抗样本示例,来自上述论文。从熊猫图像开始,攻击者向原始图像添加微小的扰动(失真),导致模型将该图像标记为长臂猿,并且置信度很高。添加这些扰动的过程将在下面解释。
快速梯度符号法
快速梯度符号法通过使用神经网络的梯度来创建对抗样本。对于输入图像,该方法使用损失函数相对于输入图像的梯度来创建一个新的图像,该图像最大化损失。这个新图像被称为对抗样本。这可以用以下表达式概括:
\[adv\_x = x + \epsilon*\text{sign}(\nabla_xJ(\theta, x, y))\]
其中:
- adv_x:对抗样本。
- x:原始输入图像。
- y:原始输入标签。
- \(\epsilon\):乘数,确保扰动很小。
- \(\theta\):模型参数。
- \(J\):损失函数。
这里一个有趣的特性是,梯度是相对于输入图像计算的。这是因为目标是创建一个最大化损失的图像。实现这一点的一种方法是找到图像中每个像素对损失值的贡献,并相应地添加扰动。这非常快,因为使用链式法则很容易找到每个输入像素对损失的贡献,并找到所需的梯度。因此,梯度是相对于图像计算的。此外,由于模型不再进行训练(因此梯度不是相对于可训练变量,即模型参数计算的),因此模型参数保持不变。唯一的目标是欺骗已经训练好的模型。
所以让我们尝试欺骗一个预训练模型。在本教程中,模型是MobileNetV2模型,在ImageNet上预训练。
import tensorflow as tf
import matplotlib as mpl
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
mpl.rcParams['figure.figsize'] = (8, 8)
mpl.rcParams['axes.grid'] = False
2023-11-16 03:39:24.939379: E external/local_xla/xla/stream_executor/cuda/cuda_dnn.cc:9261] Unable to register cuDNN factory: Attempting to register factory for plugin cuDNN when one has already been registered 2023-11-16 03:39:24.939428: E external/local_xla/xla/stream_executor/cuda/cuda_fft.cc:607] Unable to register cuFFT factory: Attempting to register factory for plugin cuFFT when one has already been registered 2023-11-16 03:39:24.941090: E external/local_xla/xla/stream_executor/cuda/cuda_blas.cc:1515] Unable to register cuBLAS factory: Attempting to register factory for plugin cuBLAS when one has already been registered
让我们加载预训练的 MobileNetV2 模型和 ImageNet 类别名称。
pretrained_model = tf.keras.applications.MobileNetV2(include_top=True,
weights='imagenet')
pretrained_model.trainable = False
# ImageNet labels
decode_predictions = tf.keras.applications.mobilenet_v2.decode_predictions
Downloading data from https://storage.googleapis.com/tensorflow/keras-applications/mobilenet_v2/mobilenet_v2_weights_tf_dim_ordering_tf_kernels_1.0_224.h5 14536120/14536120 [==============================] - 0s 0us/step
# Helper function to preprocess the image so that it can be inputted in MobileNetV2
def preprocess(image):
image = tf.cast(image, tf.float32)
image = tf.image.resize(image, (224, 224))
image = tf.keras.applications.mobilenet_v2.preprocess_input(image)
image = image[None, ...]
return image
# Helper function to extract labels from probability vector
def get_imagenet_label(probs):
return decode_predictions(probs, top=1)[0][0]
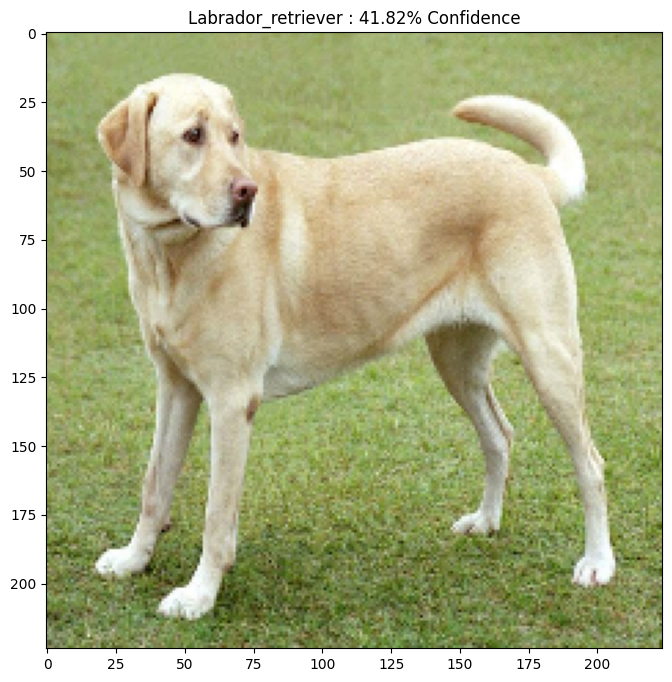
原始图像
让我们使用 Mirko 在 Wikimedia Common 上发布的拉布拉多犬的样本图像,并使用它创建对抗样本。第一步是对其进行预处理,以便可以将其作为输入提供给 MobileNetV2 模型。
image_path = tf.keras.utils.get_file('YellowLabradorLooking_new.jpg', 'https://storage.googleapis.com/download.tensorflow.org/example_images/YellowLabradorLooking_new.jpg')
image_raw = tf.io.read_file(image_path)
image = tf.image.decode_image(image_raw)
image = preprocess(image)
image_probs = pretrained_model.predict(image)
1/1 [==============================] - 2s 2s/step
让我们看一下图像。
plt.figure()
plt.imshow(image[0] * 0.5 + 0.5) # To change [-1, 1] to [0,1]
_, image_class, class_confidence = get_imagenet_label(image_probs)
plt.title('{} : {:.2f}% Confidence'.format(image_class, class_confidence*100))
plt.show()

创建对抗样本
实现快速梯度符号法
第一步是创建扰动,这些扰动将用于扭曲原始图像,从而产生对抗样本。如前所述,对于此任务,梯度是相对于图像计算的。
loss_object = tf.keras.losses.CategoricalCrossentropy()
def create_adversarial_pattern(input_image, input_label):
with tf.GradientTape() as tape:
tape.watch(input_image)
prediction = pretrained_model(input_image)
loss = loss_object(input_label, prediction)
# Get the gradients of the loss w.r.t to the input image.
gradient = tape.gradient(loss, input_image)
# Get the sign of the gradients to create the perturbation
signed_grad = tf.sign(gradient)
return signed_grad
生成的扰动也可以可视化。
# Get the input label of the image.
labrador_retriever_index = 208
label = tf.one_hot(labrador_retriever_index, image_probs.shape[-1])
label = tf.reshape(label, (1, image_probs.shape[-1]))
perturbations = create_adversarial_pattern(image, label)
plt.imshow(perturbations[0] * 0.5 + 0.5); # To change [-1, 1] to [0,1]
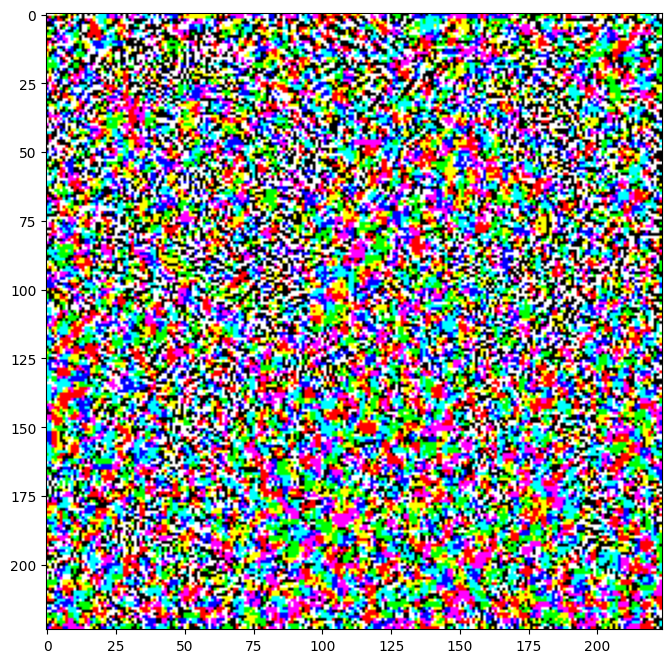
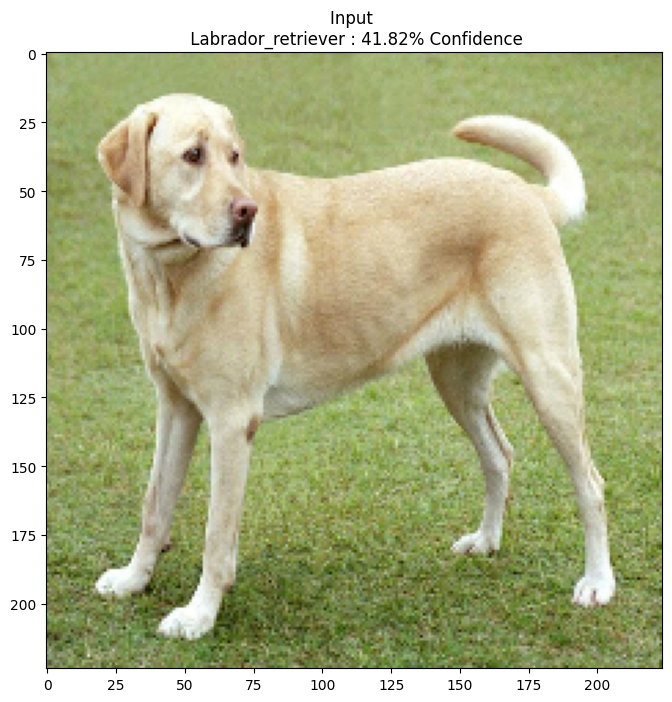
让我们尝试使用不同的 epsilon 值,并观察生成的图像。你会注意到,随着 epsilon 值的增加,欺骗网络变得更容易。然而,这是一种权衡,会导致扰动变得更容易识别。
def display_images(image, description):
_, label, confidence = get_imagenet_label(pretrained_model.predict(image))
plt.figure()
plt.imshow(image[0]*0.5+0.5)
plt.title('{} \n {} : {:.2f}% Confidence'.format(description,
label, confidence*100))
plt.show()
epsilons = [0, 0.01, 0.1, 0.15]
descriptions = [('Epsilon = {:0.3f}'.format(eps) if eps else 'Input')
for eps in epsilons]
for i, eps in enumerate(epsilons):
adv_x = image + eps*perturbations
adv_x = tf.clip_by_value(adv_x, -1, 1)
display_images(adv_x, descriptions[i])
1/1 [==============================] - 0s 46ms/step

1/1 [==============================] - 0s 45ms/step
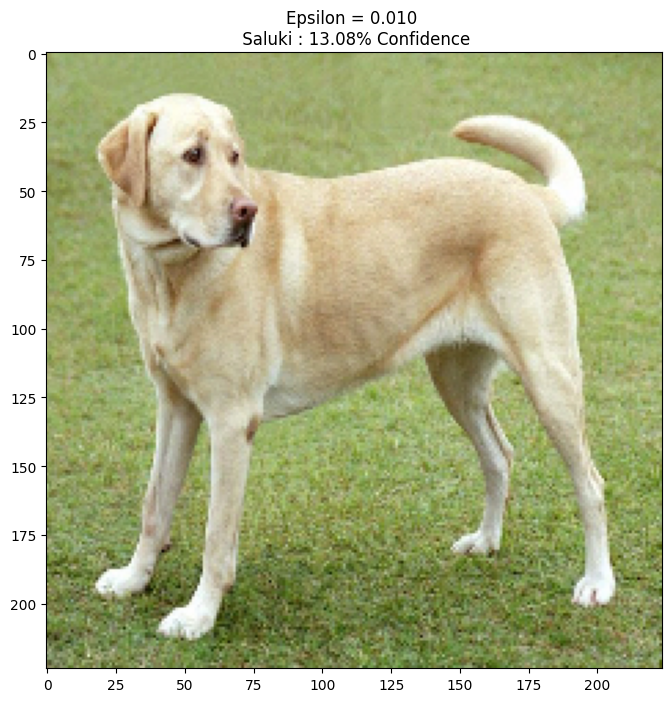
1/1 [==============================] - 0s 45ms/step
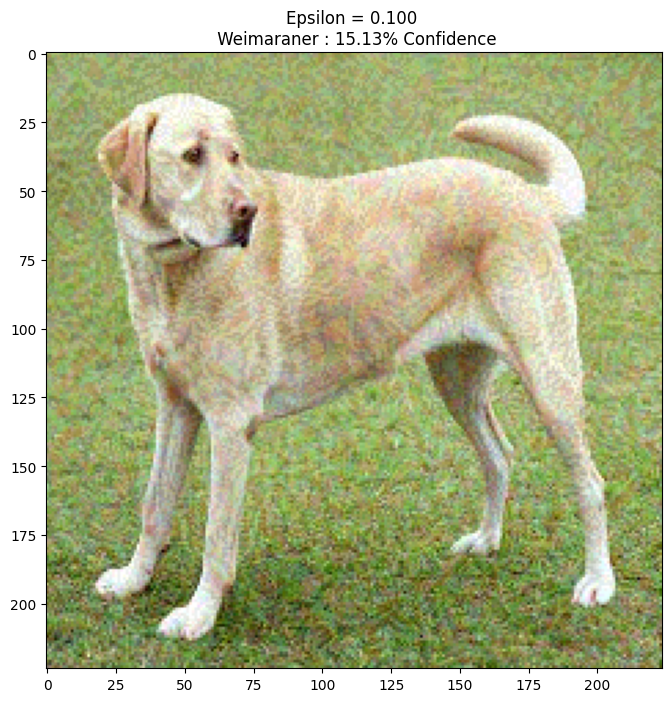
1/1 [==============================] - 0s 46ms/step
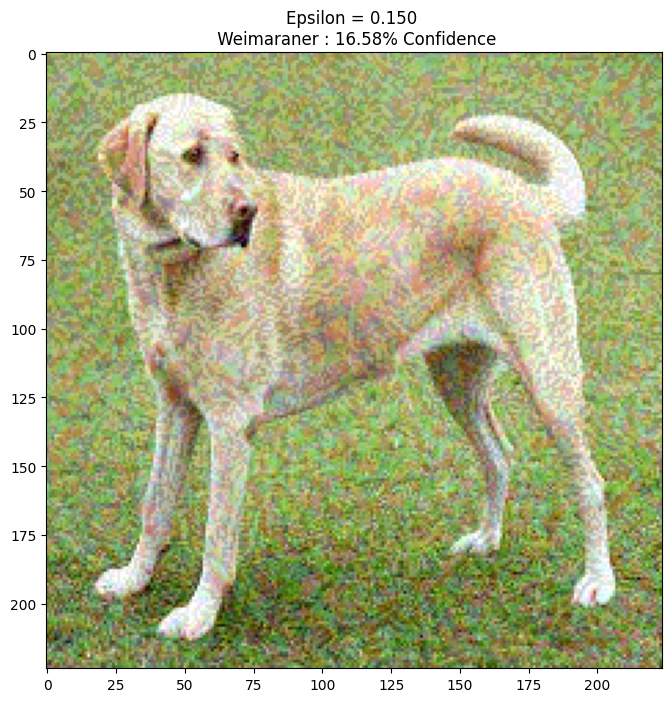
下一步
现在你已经了解了对抗攻击,尝试在不同的数据集和不同的架构上进行尝试。你也可以创建和训练自己的模型,然后尝试使用相同的方法欺骗它。你也可以尝试观察预测置信度随着 epsilon 变化而变化的情况。
虽然在本教程中展示的攻击很强大,但这只是对抗攻击研究的开始,此后出现了许多论文创建了更强大的攻击。除了对抗攻击之外,研究还导致了防御的创建,旨在创建鲁棒的机器学习模型。你可以查看这篇调查论文,以获取对抗攻击和防御的全面列表。
要查看更多对抗攻击和防御的实现,你可能想查看对抗样本库CleverHans。
