 在 TensorFlow.org 上查看 在 TensorFlow.org 上查看
|
 在 Google Colab 中运行 在 Google Colab 中运行
|
 在 GitHub 上查看 在 GitHub 上查看
|
 下载笔记本 下载笔记本
|
本示例将使用 Orbit 训练库来微调 BERT 模型。
Orbit 是一个灵活、轻量级的库,旨在简化在 TensorFlow 中编写 自定义训练循环 的过程。Orbit 处理常见的模型训练任务,例如保存检查点、运行模型评估和设置摘要写入,同时让用户完全控制内部训练循环的实现。它与 tf.distribute 集成,并支持在不同设备类型(CPU、GPU 和 TPU)上运行。
大多数 tensorflow.org 上的示例使用自定义训练循环或 Keras 中的 model.fit()。如果您的模型很复杂,并且您的训练循环需要更高的灵活性、控制或自定义,那么 Orbit 是 model.fit 的一个很好的替代方案。此外,当存在多个使用相同自定义训练循环的不同模型架构时,使用 Orbit 可以简化代码。
本教程重点介绍如何设置和使用 Orbit,而不是 BERT、模型构建和数据处理的详细信息。有关这些主题的更深入的教程,请参考以下教程
- 微调 BERT - 详细介绍了这些子主题。
- 为 GLUE 在 TPU 上微调 BERT - 将代码推广到在任何 GLUE 子任务上运行任何 BERT 配置,并在 TPU 上运行。
安装 TensorFlow 模型包
安装并导入必要的包,然后配置训练模型所需的所有对象。
pip install -q opencv-pythonpip install tensorflow>=2.9.0 tf-models-official
tf-models-official 包包含 orbit 和 tensorflow_models 模块。
import tensorflow_models as tfm
import orbit
2023-10-17 11:55:57.421119: E tensorflow/compiler/xla/stream_executor/cuda/cuda_dnn.cc:9342] Unable to register cuDNN factory: Attempting to register factory for plugin cuDNN when one has already been registered 2023-10-17 11:55:57.421164: E tensorflow/compiler/xla/stream_executor/cuda/cuda_fft.cc:609] Unable to register cuFFT factory: Attempting to register factory for plugin cuFFT when one has already been registered 2023-10-17 11:55:57.421203: E tensorflow/compiler/xla/stream_executor/cuda/cuda_blas.cc:1518] Unable to register cuBLAS factory: Attempting to register factory for plugin cuBLAS when one has already been registered
训练设置
本教程不侧重于配置环境、构建模型和优化器以及加载数据。所有这些技术在 微调 BERT 和 使用 GLUE 微调 BERT 教程中都有更详细的介绍。
要查看本教程的训练设置,请展开本节的其余部分。
导入必要的包
从 Tensorflow 模型花园 导入 BERT 模型和数据集构建库。
import glob
import os
import pathlib
import tempfile
import time
import numpy as np
import tensorflow as tf
from official.nlp.data import sentence_prediction_dataloader
from official.nlp import optimization
配置分布式策略
虽然 tf.distribute 不会在单机或 GPU 上运行时帮助模型的运行时间,但它对于 TPU 来说是必要的。设置分布式策略允许您使用相同的代码,无论配置如何。
logical_device_names = [logical_device.name for logical_device in tf.config.list_logical_devices()]
if 'GPU' in ''.join(logical_device_names):
strategy = tf.distribute.MirroredStrategy()
elif 'TPU' in ''.join(logical_device_names):
resolver = tf.distribute.cluster_resolver.TPUClusterResolver(tpu='')
tf.config.experimental_connect_to_cluster(resolver)
tf.tpu.experimental.initialize_tpu_system(resolver)
strategy = tf.distribute.TPUStrategy(resolver)
else:
strategy = tf.distribute.OneDeviceStrategy(logical_device_names[0])
2023-10-17 11:56:02.076511: W tensorflow/core/common_runtime/gpu/gpu_device.cc:2211] Cannot dlopen some GPU libraries. Please make sure the missing libraries mentioned above are installed properly if you would like to use GPU. Follow the guide at https://tensorflowcn.cn/install/gpu for how to download and setup the required libraries for your platform. Skipping registering GPU devices...
有关 TPU 设置的更多信息,请参阅 TPU 指南。
创建模型和优化器
max_seq_length = 128
learning_rate = 3e-5
num_train_epochs = 3
train_batch_size = 32
eval_batch_size = 64
train_data_size = 3668
steps_per_epoch = int(train_data_size / train_batch_size)
train_steps = steps_per_epoch * num_train_epochs
warmup_steps = int(train_steps * 0.1)
print("train batch size: ", train_batch_size)
print("train epochs: ", num_train_epochs)
print("steps_per_epoch: ", steps_per_epoch)
train batch size: 32 train epochs: 3 steps_per_epoch: 114
model_dir = pathlib.Path(tempfile.mkdtemp())
print(model_dir)
/tmpfs/tmp/tmpjbwlp79l
创建一个 BERT 分类器模型和一个简单的优化器。它们必须在 strategy.scope 内创建,以便变量可以分布。
with strategy.scope():
encoder_network = tfm.nlp.encoders.build_encoder(
tfm.nlp.encoders.EncoderConfig(type="bert"))
classifier_model = tfm.nlp.models.BertClassifier(
network=encoder_network, num_classes=2)
optimizer = optimization.create_optimizer(
init_lr=3e-5,
num_train_steps=steps_per_epoch * num_train_epochs,
num_warmup_steps=warmup_steps,
end_lr=0.0,
optimizer_type='adamw')
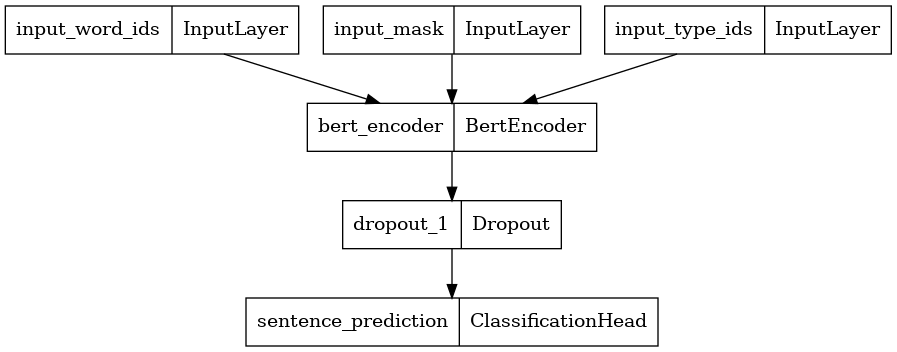
tf.keras.utils.plot_model(classifier_model)
从检查点初始化
bert_dir = 'gs://cloud-tpu-checkpoints/bert/v3/uncased_L-12_H-768_A-12/'
tf.io.gfile.listdir(bert_dir)
['bert_config.json', 'bert_model.ckpt.data-00000-of-00001', 'bert_model.ckpt.index', 'vocab.txt']
bert_checkpoint = bert_dir + 'bert_model.ckpt'
def init_from_ckpt_fn():
init_checkpoint = tf.train.Checkpoint(**classifier_model.checkpoint_items)
with strategy.scope():
(init_checkpoint
.read(bert_checkpoint)
.expect_partial()
.assert_existing_objects_matched())
with strategy.scope():
init_from_ckpt_fn()
要使用 Orbit,请创建一个 tf.train.CheckpointManager 对象。
checkpoint = tf.train.Checkpoint(model=classifier_model, optimizer=optimizer)
checkpoint_manager = tf.train.CheckpointManager(
checkpoint,
directory=model_dir,
max_to_keep=5,
step_counter=optimizer.iterations,
checkpoint_interval=steps_per_epoch,
init_fn=init_from_ckpt_fn)
创建分布式数据集
作为本教程的快捷方式,GLUE/MPRC 数据集 已被转换为一对 TFRecord 文件,其中包含序列化 tf.train.Example 协议缓冲区。
数据使用 此脚本 转换。
train_data_path = "gs://download.tensorflow.org/data/model_garden_colab/mrpc_train.tf_record"
eval_data_path = "gs://download.tensorflow.org/data/model_garden_colab/mrpc_eval.tf_record"
def _dataset_fn(input_file_pattern,
global_batch_size,
is_training,
input_context=None):
data_config = sentence_prediction_dataloader.SentencePredictionDataConfig(
input_path=input_file_pattern,
seq_length=max_seq_length,
global_batch_size=global_batch_size,
is_training=is_training)
return sentence_prediction_dataloader.SentencePredictionDataLoader(
data_config).load(input_context=input_context)
train_dataset = orbit.utils.make_distributed_dataset(
strategy, _dataset_fn, input_file_pattern=train_data_path,
global_batch_size=train_batch_size, is_training=True)
eval_dataset = orbit.utils.make_distributed_dataset(
strategy, _dataset_fn, input_file_pattern=eval_data_path,
global_batch_size=eval_batch_size, is_training=False)
创建损失函数
def loss_fn(labels, logits):
"""Classification loss."""
labels = tf.squeeze(labels)
log_probs = tf.nn.log_softmax(logits, axis=-1)
one_hot_labels = tf.one_hot(
tf.cast(labels, dtype=tf.int32), depth=2, dtype=tf.float32)
per_example_loss = -tf.reduce_sum(
tf.cast(one_hot_labels, dtype=tf.float32) * log_probs, axis=-1)
return tf.reduce_mean(per_example_loss)
控制器、训练器和评估器
使用 Orbit 时,orbit.Controller 类驱动训练。控制器处理分布式策略、步骤计数、TensorBoard 摘要和检查点的详细信息。
要实现训练和评估,请传递一个 trainer 和 evaluator,它们是 orbit.AbstractTrainer 和 orbit.AbstractEvaluator 的子类实例。遵循 Orbit 的轻量级设计,这两个类具有最小的接口。
控制器通过调用 trainer.train(num_steps) 和 evaluator.evaluate(num_steps) 来驱动训练和评估。这些 train 和 evaluate 方法返回一个用于日志记录的结果字典。
训练被分成长度为 num_steps 的块。这由控制器的 steps_per_loop 参数设置。使用训练器和评估器抽象基类,num_steps 的含义完全由实现者决定。
一些常见示例包括
- 让块表示数据集纪元边界,就像默认的 Keras 设置一样。
- 使用它更有效地将一定数量的训练步骤调度到加速器,并使用单个
tf.function调用(如Model.compile的steps_per_execution参数)。 - 根据需要细分为更小的块。
StandardTrainer 和 StandardEvaluator
Orbit 提供了另外两个类,orbit.StandardTrainer 和 orbit.StandardEvaluator,为训练和评估循环提供更多结构。
使用 StandardTrainer,您只需要设置 train_loop_begin、train_step 和 train_loop_end。基类处理循环、数据集逻辑和 tf.function(根据其 orbit.StandardTrainerOptions 设置的选项)。这比 orbit.AbstractTrainer 更简单,后者要求您处理整个循环。StandardEvaluator 具有与 StandardTrainer 相似的结构和简化。
这实际上是 Keras 使用的 steps_per_execution 方法的实现。
将此与 Keras 进行对比,在 Keras 中,训练既被划分为纪元(对数据集的单次传递)又被划分为 steps_per_execution(在 Model.compile 中设置)。在 Keras 中,度量平均值通常在纪元内累积,并在纪元之间报告和重置。为了提高效率,steps_per_execution 仅控制每次调用的训练步骤数量。
在这个简单的情况下,steps_per_loop(在 StandardTrainer 中)将同时处理度量重置和每次调用的步骤数量。
使用这些基类时的最小设置是按如下方式实现方法
StandardTrainer.train_loop_begin- 重置您的训练度量。StandardTrainer.train_step- 应用单个梯度更新。StandardTrainer.train_loop_end- 报告您的训练度量。
和
StandardEvaluator.eval_begin- 重置您的评估度量。StandardEvaluator.eval_step- 运行单个评估步骤。StandardEvaluator.eval_reduce- 在此简单设置中不需要。StandardEvaluator.eval_end- 报告您的评估度量。
根据设置,基类可能会将 train_step 和 eval_step 代码包装在 tf.function 或 tf.while_loop 中,与标准 Python 相比,这有一些限制。
定义训练器类
在本节中,您将为该任务创建一个 orbit.StandardTrainer 的子类。
训练器需要访问训练数据、模型、优化器和分布式策略。将这些作为参数传递给初始化程序。
使用 tf.keras.metrics.Mean 定义一个单一的训练度量 training_loss。
def trainer_init(self,
train_dataset,
model,
optimizer,
strategy):
self.strategy = strategy
with self.strategy.scope():
self.model = model
self.optimizer = optimizer
self.global_step = self.optimizer.iterations
self.train_loss = tf.keras.metrics.Mean(
'training_loss', dtype=tf.float32)
orbit.StandardTrainer.__init__(self, train_dataset)
在开始运行训练循环之前,train_loop_begin 方法将重置 train_loss 度量。
def train_loop_begin(self):
self.train_loss.reset_states()
train_step 是一个简单的损失计算和梯度更新,由分布式策略运行。这是通过将梯度步骤定义为嵌套函数 (step_fn) 来实现的。
该方法接收 tf.distribute.DistributedIterator 来处理 分布式输入。该方法使用 Strategy.run 来执行 step_fn 并从分布式迭代器中馈送它。
def train_step(self, iterator):
def step_fn(inputs):
labels = inputs.pop("label_ids")
with tf.GradientTape() as tape:
model_outputs = self.model(inputs, training=True)
# Raw loss is used for reporting in metrics/logs.
raw_loss = loss_fn(labels, model_outputs)
# Scales down the loss for gradients to be invariant from replicas.
loss = raw_loss / self.strategy.num_replicas_in_sync
grads = tape.gradient(loss, self.model.trainable_variables)
optimizer.apply_gradients(zip(grads, self.model.trainable_variables))
# For reporting, the metric takes the mean of losses.
self.train_loss.update_state(raw_loss)
self.strategy.run(step_fn, args=(next(iterator),))
orbit.StandardTrainer 处理 @tf.function 和循环。
在完成 num_steps 次训练后,StandardTrainer 调用 train_loop_end。该函数返回度量结果
def train_loop_end(self):
return {
self.train_loss.name: self.train_loss.result(),
}
使用这些方法构建 orbit.StandardTrainer 的子类。
class BertClassifierTrainer(orbit.StandardTrainer):
__init__ = trainer_init
train_loop_begin = train_loop_begin
train_step = train_step
train_loop_end = train_loop_end
定义评估器类
对于此任务,评估器更简单。它需要访问评估数据集、模型和策略。在保存对这些对象的引用后,构造函数只需要创建度量。
def evaluator_init(self,
eval_dataset,
model,
strategy):
self.strategy = strategy
with self.strategy.scope():
self.model = model
self.eval_loss = tf.keras.metrics.Mean(
'evaluation_loss', dtype=tf.float32)
self.eval_accuracy = tf.keras.metrics.SparseCategoricalAccuracy(
name='accuracy', dtype=tf.float32)
orbit.StandardEvaluator.__init__(self, eval_dataset)
与训练器类似,eval_begin 和 eval_end 方法只需要在循环之前重置度量,然后在循环之后报告结果。
def eval_begin(self):
self.eval_accuracy.reset_states()
self.eval_loss.reset_states()
def eval_end(self):
return {
self.eval_accuracy.name: self.eval_accuracy.result(),
self.eval_loss.name: self.eval_loss.result(),
}
eval_step 方法的工作方式类似于 train_step。内部 step_fn 定义了计算损失和准确率以及更新度量的实际工作。外部 eval_step 接收 tf.distribute.DistributedIterator 作为输入,并使用 Strategy.run 启动对 step_fn 的分布式执行,并从分布式迭代器中馈送它。
def eval_step(self, iterator):
def step_fn(inputs):
labels = inputs.pop("label_ids")
model_outputs = self.model(inputs, training=True)
loss = loss_fn(labels, model_outputs)
self.eval_loss.update_state(loss)
self.eval_accuracy.update_state(labels, model_outputs)
self.strategy.run(step_fn, args=(next(iterator),))
使用这些方法构建 orbit.StandardEvaluator 的子类。
class BertClassifierEvaluator(orbit.StandardEvaluator):
__init__ = evaluator_init
eval_begin = eval_begin
eval_end = eval_end
eval_step = eval_step
端到端训练和评估
要运行训练和评估,只需创建训练器、评估器和 orbit.Controller 实例。然后调用 Controller.train_and_evaluate 方法。
trainer = BertClassifierTrainer(
train_dataset, classifier_model, optimizer, strategy)
evaluator = BertClassifierEvaluator(
eval_dataset, classifier_model, strategy)
controller = orbit.Controller(
trainer=trainer,
evaluator=evaluator,
global_step=trainer.global_step,
steps_per_loop=20,
checkpoint_manager=checkpoint_manager)
result = controller.train_and_evaluate(
train_steps=steps_per_epoch * num_train_epochs,
eval_steps=-1,
eval_interval=steps_per_epoch)
restoring or initializing model...
INFO:tensorflow:Customized initialization is done through the passed `init_fn`.
INFO:tensorflow:Customized initialization is done through the passed `init_fn`.
train | step: 0 | training until step 114...
2023-10-17 11:56:16.208773: W tensorflow/core/framework/dataset.cc:959] Input of GeneratorDatasetOp::Dataset will not be optimized because the dataset does not implement the AsGraphDefInternal() method needed to apply optimizations.
train | step: 20 | steps/sec: 0.2 | output: {'training_loss': 0.776852}
saved checkpoint to /tmpfs/tmp/tmpjbwlp79l/ckpt-20.
train | step: 40 | steps/sec: 0.2 | output: {'training_loss': 0.71298754}
train | step: 60 | steps/sec: 0.2 | output: {'training_loss': 0.6112895}
train | step: 80 | steps/sec: 0.2 | output: {'training_loss': 0.57813513}
train | step: 100 | steps/sec: 0.2 | output: {'training_loss': 0.56901103}
train | step: 114 | steps/sec: 0.2 | output: {'training_loss': 0.5472072}
eval | step: 114 | running complete evaluation...
2023-10-17 12:04:29.320401: W tensorflow/core/framework/dataset.cc:959] Input of GeneratorDatasetOp::Dataset will not be optimized because the dataset does not implement the AsGraphDefInternal() method needed to apply optimizations.
eval | step: 114 | eval time: 20.0 sec | output: {'accuracy': 0.7630208, 'evaluation_loss': 0.52163863}
train | step: 114 | training until step 228...
train | step: 134 | steps/sec: 0.2 | output: {'training_loss': 0.51722306}
saved checkpoint to /tmpfs/tmp/tmpjbwlp79l/ckpt-134.
train | step: 154 | steps/sec: 0.2 | output: {'training_loss': 0.524362}
train | step: 174 | steps/sec: 0.2 | output: {'training_loss': 0.39253792}
train | step: 194 | steps/sec: 0.2 | output: {'training_loss': 0.35146618}
train | step: 214 | steps/sec: 0.2 | output: {'training_loss': 0.3962813}
train | step: 228 | steps/sec: 0.2 | output: {'training_loss': 0.27635574}
eval | step: 228 | running complete evaluation...
2023-10-17 12:12:42.261016: W tensorflow/core/framework/dataset.cc:959] Input of GeneratorDatasetOp::Dataset will not be optimized because the dataset does not implement the AsGraphDefInternal() method needed to apply optimizations.
eval | step: 228 | eval time: 18.7 sec | output: {'accuracy': 0.8020833, 'evaluation_loss': 0.4823281}
train | step: 228 | training until step 342...
train | step: 248 | steps/sec: 0.2 | output: {'training_loss': 0.33371425}
saved checkpoint to /tmpfs/tmp/tmpjbwlp79l/ckpt-248.
train | step: 268 | steps/sec: 0.2 | output: {'training_loss': 0.32890704}
train | step: 288 | steps/sec: 0.2 | output: {'training_loss': 0.21134928}
train | step: 308 | steps/sec: 0.2 | output: {'training_loss': 0.21237397}
train | step: 328 | steps/sec: 0.2 | output: {'training_loss': 0.2372253}
train | step: 342 | steps/sec: 0.2 | output: {'training_loss': 0.18402448}
eval | step: 342 | running complete evaluation...
2023-10-17 12:20:51.500609: W tensorflow/core/framework/dataset.cc:959] Input of GeneratorDatasetOp::Dataset will not be optimized because the dataset does not implement the AsGraphDefInternal() method needed to apply optimizations.
eval | step: 342 | eval time: 18.5 sec | output: {'accuracy': 0.8098958, 'evaluation_loss': 0.4728314}
saved checkpoint to /tmpfs/tmp/tmpjbwlp79l/ckpt-342.
