 在 TensorFlow.org 上查看 在 TensorFlow.org 上查看
|
 在 Google Colab 中运行 在 Google Colab 中运行
|
 在 GitHub 上查看源代码 在 GitHub 上查看源代码
|
 下载笔记本 下载笔记本
|
在处理目标检测和 NLP 等机器学习应用程序时,有时需要处理张量的子部分(切片)。例如,如果您的模型架构包括路由,其中一层可能控制哪个训练示例被路由到下一层。在这种情况下,您可以使用张量切片操作来拆分张量并以正确的顺序将它们重新组合在一起。
在 NLP 应用程序中,您可以使用张量切片来执行训练期间的词语掩码。例如,您可以从句子列表中生成训练数据,方法是选择每个句子中要掩码的词语索引,将该词语作为标签取出,然后用掩码标记替换所选词语。
在本指南中,您将学习如何使用 TensorFlow API 来
- 从张量中提取切片
- 在张量的特定索引处插入数据
本指南假设您熟悉张量索引。在开始使用本指南之前,请阅读张量和TensorFlow NumPy指南中的索引部分。
设置
import tensorflow as tf
import numpy as np
提取张量切片
使用tf.slice执行类似 NumPy 的张量切片。
t1 = tf.constant([0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7])
print(tf.slice(t1,
begin=[1],
size=[3]))
或者,您可以使用更 Pythonic 的语法。请注意,张量切片在起始-结束范围内均匀分布。
print(t1[1:4])
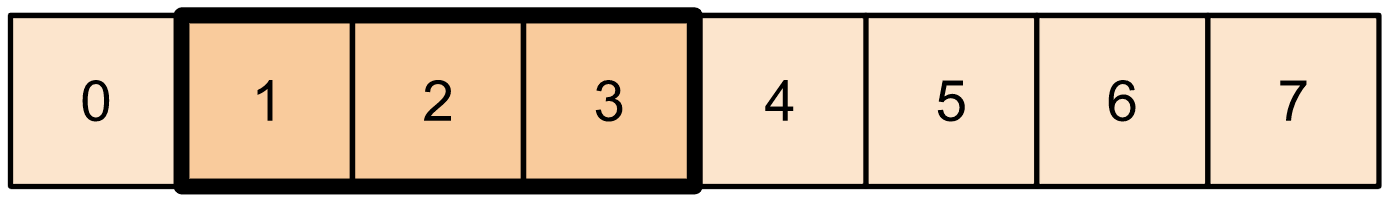
print(t1[-3:])
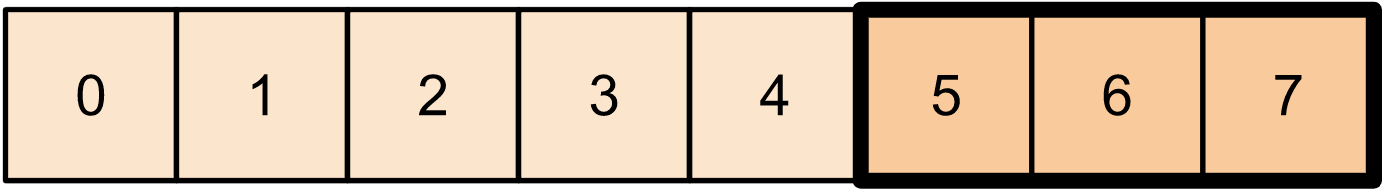
对于二维张量,您可以使用类似于以下内容:
t2 = tf.constant([[0, 1, 2, 3, 4],
[5, 6, 7, 8, 9],
[10, 11, 12, 13, 14],
[15, 16, 17, 18, 19]])
print(t2[:-1, 1:3])
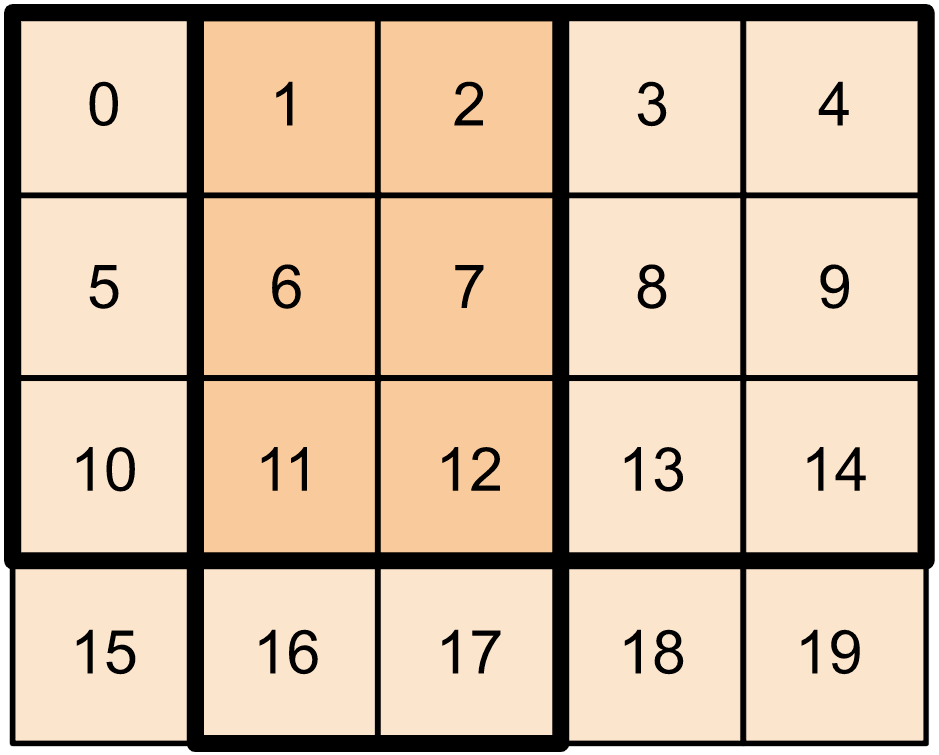
您也可以在更高维度的张量上使用 tf.slice。
t3 = tf.constant([[[1, 3, 5, 7],
[9, 11, 13, 15]],
[[17, 19, 21, 23],
[25, 27, 29, 31]]
])
print(tf.slice(t3,
begin=[1, 1, 0],
size=[1, 1, 2]))
您还可以使用 tf.strided_slice 通过“跨越”张量维度来提取张量的切片。
使用 tf.gather 从张量单个轴中提取特定索引。
print(tf.gather(t1,
indices=[0, 3, 6]))
# This is similar to doing
t1[::3]
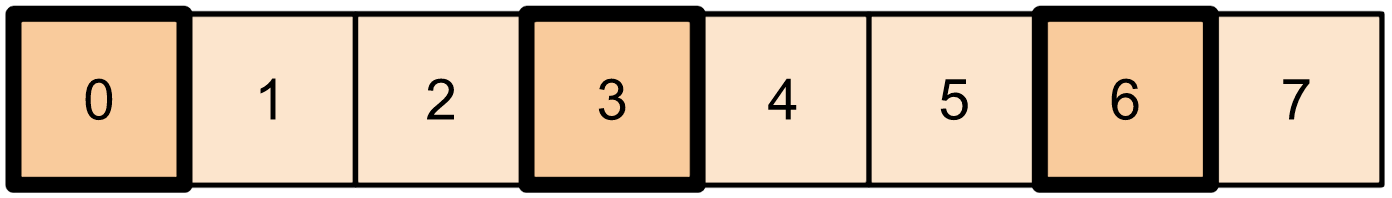
tf.gather 不需要索引均匀分布。
alphabet = tf.constant(list('abcdefghijklmnopqrstuvwxyz'))
print(tf.gather(alphabet,
indices=[2, 0, 19, 18]))
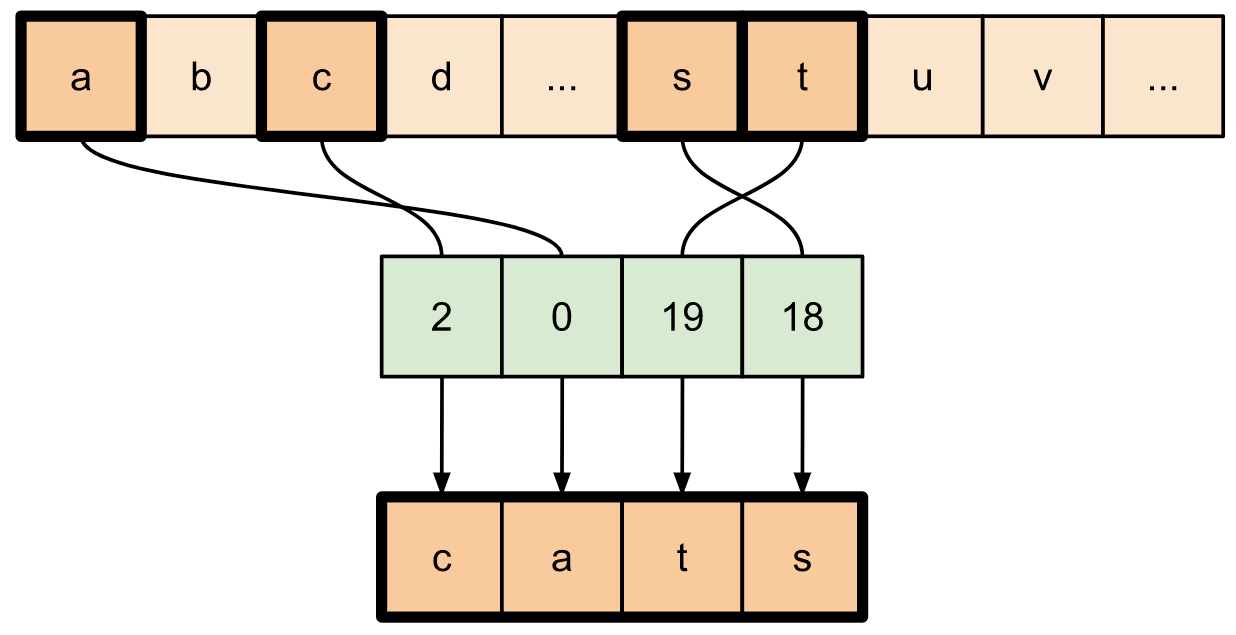
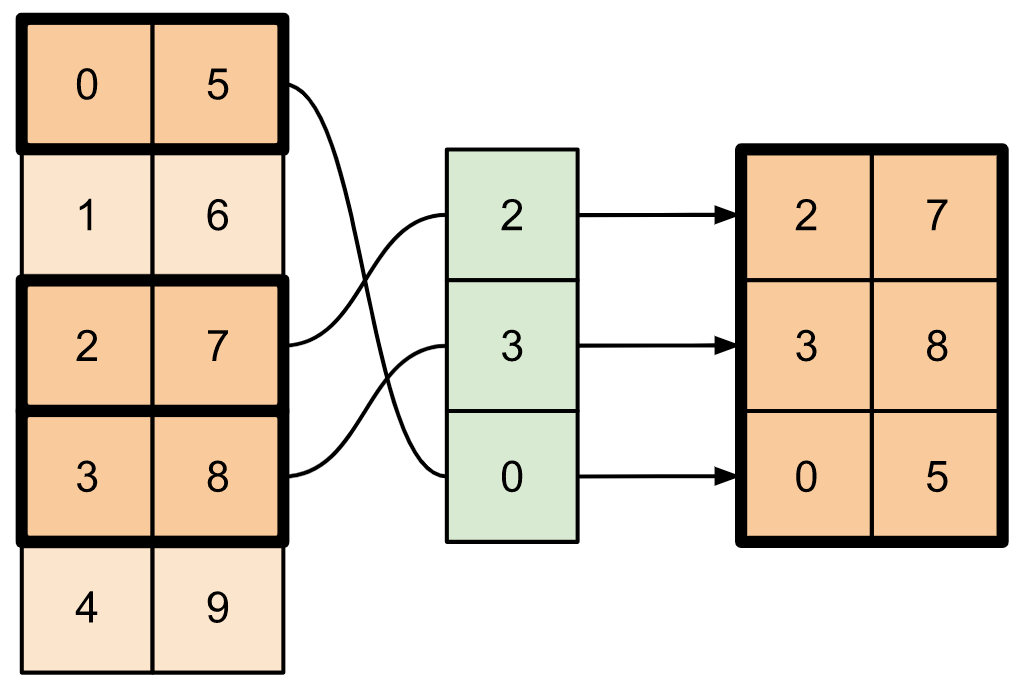
要从张量的多个轴中提取切片,请使用 tf.gather_nd。当您想要收集矩阵的元素而不是仅仅收集其行或列时,这很有用。
t4 = tf.constant([[0, 5],
[1, 6],
[2, 7],
[3, 8],
[4, 9]])
print(tf.gather_nd(t4,
indices=[[2], [3], [0]]))
t5 = np.reshape(np.arange(18), [2, 3, 3])
print(tf.gather_nd(t5,
indices=[[0, 0, 0], [1, 2, 1]]))
# Return a list of two matrices
print(tf.gather_nd(t5,
indices=[[[0, 0], [0, 2]], [[1, 0], [1, 2]]]))
# Return one matrix
print(tf.gather_nd(t5,
indices=[[0, 0], [0, 2], [1, 0], [1, 2]]))
将数据插入张量
使用 tf.scatter_nd 将数据插入张量的特定切片/索引。请注意,您插入值的张量是零初始化的。
t6 = tf.constant([10])
indices = tf.constant([[1], [3], [5], [7], [9]])
data = tf.constant([2, 4, 6, 8, 10])
print(tf.scatter_nd(indices=indices,
updates=data,
shape=t6))
像 tf.scatter_nd 这样的需要零初始化张量的方法类似于稀疏张量初始化器。您可以使用 tf.gather_nd 和 tf.scatter_nd 来模拟稀疏张量操作的行为。
考虑一个使用这两种方法结合起来构建稀疏张量的示例。
# Gather values from one tensor by specifying indices
new_indices = tf.constant([[0, 2], [2, 1], [3, 3]])
t7 = tf.gather_nd(t2, indices=new_indices)
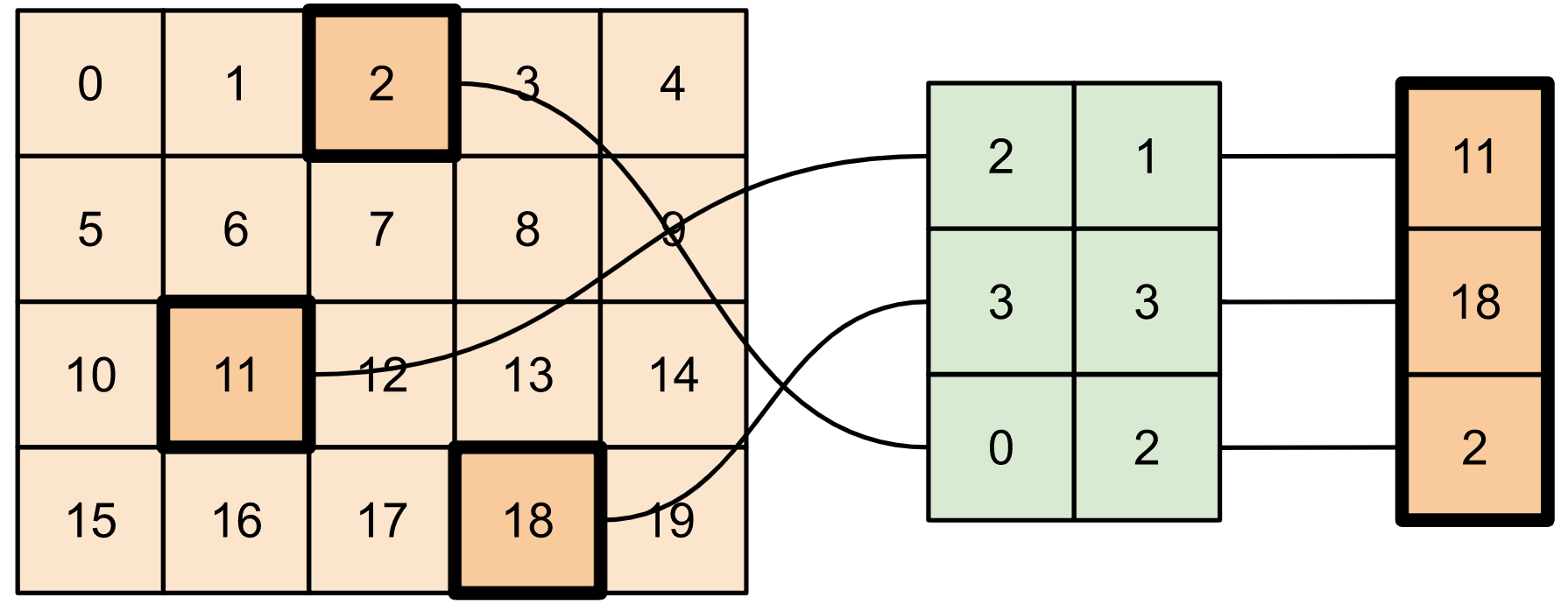
# Add these values into a new tensor
t8 = tf.scatter_nd(indices=new_indices, updates=t7, shape=tf.constant([4, 5]))
print(t8)
这类似于
t9 = tf.SparseTensor(indices=[[0, 2], [2, 1], [3, 3]],
values=[2, 11, 18],
dense_shape=[4, 5])
print(t9)
# Convert the sparse tensor into a dense tensor
t10 = tf.sparse.to_dense(t9)
print(t10)
要将数据插入具有预先存在值的张量,请使用 tf.tensor_scatter_nd_add。
t11 = tf.constant([[2, 7, 0],
[9, 0, 1],
[0, 3, 8]])
# Convert the tensor into a magic square by inserting numbers at appropriate indices
t12 = tf.tensor_scatter_nd_add(t11,
indices=[[0, 2], [1, 1], [2, 0]],
updates=[6, 5, 4])
print(t12)
类似地,使用 tf.tensor_scatter_nd_sub 从具有预先存在值的张量中减去值。
# Convert the tensor into an identity matrix
t13 = tf.tensor_scatter_nd_sub(t11,
indices=[[0, 0], [0, 1], [1, 0], [1, 1], [1, 2], [2, 1], [2, 2]],
updates=[1, 7, 9, -1, 1, 3, 7])
print(t13)
使用 tf.tensor_scatter_nd_min 将一个张量的逐元素最小值复制到另一个张量。
t14 = tf.constant([[-2, -7, 0],
[-9, 0, 1],
[0, -3, -8]])
t15 = tf.tensor_scatter_nd_min(t14,
indices=[[0, 2], [1, 1], [2, 0]],
updates=[-6, -5, -4])
print(t15)
类似地,使用 tf.tensor_scatter_nd_max 将一个张量的逐元素最大值复制到另一个张量。
t16 = tf.tensor_scatter_nd_max(t14,
indices=[[0, 2], [1, 1], [2, 0]],
updates=[6, 5, 4])
print(t16)
进一步阅读和资源
在本指南中,您学习了如何使用 TensorFlow 提供的张量切片操作来更精细地控制张量中的元素。
查看 TensorFlow NumPy 提供的切片操作,例如
tf.experimental.numpy.take_along_axis和tf.experimental.numpy.take。
