在 TensorFlow.org 上查看 在 TensorFlow.org 上查看
|
 在 Google Colab 中运行 在 Google Colab 中运行
|
 在 GitHub 上查看源代码 在 GitHub 上查看源代码
|
 下载笔记本 下载笔记本
|
概述
GPU 和 TPU 可以大幅减少执行单个训练步骤所需的时间。要实现峰值性能,需要一个高效的输入管道,在当前步骤完成之前提供下一步骤的数据。 tf.data API 有助于构建灵活高效的输入管道。本文档演示了如何使用 tf.data API 构建高性能 TensorFlow 输入管道。
在继续之前,请查看 构建 TensorFlow 输入管道 指南,了解如何使用 tf.data API。
资源
设置
import tensorflow as tf
import time
2024-07-05 01:29:56.308143: E external/local_xla/xla/stream_executor/cuda/cuda_fft.cc:479] Unable to register cuFFT factory: Attempting to register factory for plugin cuFFT when one has already been registered 2024-07-05 01:29:56.333878: E external/local_xla/xla/stream_executor/cuda/cuda_dnn.cc:10575] Unable to register cuDNN factory: Attempting to register factory for plugin cuDNN when one has already been registered 2024-07-05 01:29:56.333913: E external/local_xla/xla/stream_executor/cuda/cuda_blas.cc:1442] Unable to register cuBLAS factory: Attempting to register factory for plugin cuBLAS when one has already been registered
在本指南中,您将遍历数据集并衡量性能。进行可重复的性能基准测试可能很困难。影响可重复性的因素包括
- 当前 CPU 负载
- 网络流量
- 缓存等复杂机制
为了获得可重复的基准测试,您将构建一个人工示例。
数据集
首先定义一个继承自 tf.data.Dataset 的名为 ArtificialDataset 的类。此数据集
- 生成
num_samples个样本(默认值为 3) - 在第一个项目之前休眠一段时间,以模拟打开文件
- 在生成每个项目之前休眠一段时间,以模拟从文件中读取数据
class ArtificialDataset(tf.data.Dataset):
def _generator(num_samples):
# Opening the file
time.sleep(0.03)
for sample_idx in range(num_samples):
# Reading data (line, record) from the file
time.sleep(0.015)
yield (sample_idx,)
def __new__(cls, num_samples=3):
return tf.data.Dataset.from_generator(
cls._generator,
output_signature = tf.TensorSpec(shape = (1,), dtype = tf.int64),
args=(num_samples,)
)
此数据集类似于 tf.data.Dataset.range,在每个样本的开头和中间添加固定延迟。
训练循环
接下来,编写一个虚拟训练循环,用于衡量遍历数据集所需的时间。训练时间是模拟的。
def benchmark(dataset, num_epochs=2):
start_time = time.perf_counter()
for epoch_num in range(num_epochs):
for sample in dataset:
# Performing a training step
time.sleep(0.01)
print("Execution time:", time.perf_counter() - start_time)
优化性能
为了展示如何优化性能,您将提高 ArtificialDataset 的性能。
朴素方法
从使用没有任何技巧的朴素管道开始,按原样遍历数据集。
benchmark(ArtificialDataset())
Execution time: 0.2957320680000066 2024-07-05 01:30:00.632263: W tensorflow/core/framework/local_rendezvous.cc:404] Local rendezvous is aborting with status: OUT_OF_RANGE: End of sequence 2024-07-05 01:30:00.774083: W tensorflow/core/framework/local_rendezvous.cc:404] Local rendezvous is aborting with status: OUT_OF_RANGE: End of sequence
在幕后,您的执行时间是这样分配的
该图显示,执行训练步骤涉及
- 如果文件尚未打开,则打开文件
- 从文件中获取数据条目
- 使用数据进行训练
然而,在像这里这样的朴素同步实现中,当您的管道正在获取数据时,您的模型处于空闲状态。反之,当您的模型正在训练时,输入管道处于空闲状态。因此,训练步骤时间是打开、读取和训练时间的总和。
接下来的部分将在此输入管道基础上构建,说明设计高性能 TensorFlow 输入管道的最佳实践。
预取
预取会重叠训练步骤的预处理和模型执行。当模型正在执行训练步骤 s 时,输入管道正在读取步骤 s+1 的数据。这样做将步骤时间缩短为训练时间和提取数据所需时间的最大值(而不是总和)。
tf.data API 提供了 tf.data.Dataset.prefetch 变换。它可以用来将数据生成的时间与数据使用的时间解耦。特别是,该变换使用后台线程和内部缓冲区来预取来自输入数据集的元素,早于它们被请求的时间。要预取的元素数量应等于(或可能大于)单个训练步骤消耗的批次数量。您可以手动调整此值,也可以将其设置为 tf.data.AUTOTUNE,这将提示 tf.data 运行时在运行时动态调整该值。
请注意,预取变换在任何时候都提供好处,只要有机会重叠“生产者”的工作和“消费者”的工作。
benchmark(
ArtificialDataset()
.prefetch(tf.data.AUTOTUNE)
)
Execution time: 0.28615551899997627 2024-07-05 01:30:00.955879: W tensorflow/core/framework/local_rendezvous.cc:404] Local rendezvous is aborting with status: OUT_OF_RANGE: End of sequence 2024-07-05 01:30:01.096260: W tensorflow/core/framework/local_rendezvous.cc:404] Local rendezvous is aborting with status: OUT_OF_RANGE: End of sequence
现在,正如数据执行时间图所示,当训练步骤正在为样本 0 运行时,输入管道正在读取样本 1 的数据,依此类推。
并行化数据提取
在实际环境中,输入数据可能存储在远程位置(例如,在 Google Cloud Storage 或 HDFS 上)。当读取本地数据时效果良好的数据集管道在读取远程数据时可能会遇到 I/O 瓶颈,因为本地存储和远程存储之间存在以下差异
- 首次字节时间:从远程存储读取文件的第一个字节可能比从本地存储读取文件第一个字节所需的时间长得多。
- 读取吞吐量:虽然远程存储通常提供较大的聚合带宽,但读取单个文件可能只能利用一小部分带宽。
此外,一旦原始字节被加载到内存中,可能还需要反序列化和/或解密数据(例如 protobuf),这需要额外的计算。这种开销无论数据是存储在本地还是远程都存在,但在远程情况下,如果数据没有有效预取,则可能会更糟。
为了减轻各种数据提取开销的影响,tf.data.Dataset.interleave 变换可用于并行化数据加载步骤,交错其他数据集(例如数据文件读取器)的内容。要重叠的数据集数量可以通过 cycle_length 参数指定,而并行级别可以通过 num_parallel_calls 参数指定。与 prefetch 变换类似,interleave 变换支持 tf.data.AUTOTUNE,它将关于使用什么并行级别的决定委托给 tf.data 运行时。
顺序交错
tf.data.Dataset.interleave 变换的默认参数使其顺序地从两个数据集交错单个样本。
benchmark(
tf.data.Dataset.range(2)
.interleave(lambda _: ArtificialDataset())
)
2024-07-05 01:30:01.387067: W tensorflow/core/framework/local_rendezvous.cc:404] Local rendezvous is aborting with status: OUT_OF_RANGE: End of sequence Execution time: 0.4829045789999782 2024-07-05 01:30:01.625100: W tensorflow/core/framework/local_rendezvous.cc:404] Local rendezvous is aborting with status: OUT_OF_RANGE: End of sequence
此数据执行时间图允许展示 interleave 变换的行为,从两个可用的数据集中交替获取样本。但是,这里没有涉及性能改进。
并行交错
现在,使用 interleave 变换的 num_parallel_calls 参数。这将并行加载多个数据集,从而减少等待文件打开的时间。
benchmark(
tf.data.Dataset.range(2)
.interleave(
lambda _: ArtificialDataset(),
num_parallel_calls=tf.data.AUTOTUNE
)
)
Execution time: 0.3866158929999983 2024-07-05 01:30:01.865332: W tensorflow/core/framework/local_rendezvous.cc:404] Local rendezvous is aborting with status: OUT_OF_RANGE: End of sequence 2024-07-05 01:30:02.053387: W tensorflow/core/framework/local_rendezvous.cc:404] Local rendezvous is aborting with status: OUT_OF_RANGE: End of sequence
这一次,正如数据执行时间图所示,两个数据集的读取是并行的,从而减少了全局数据处理时间。
并行化数据变换
在准备数据时,可能需要预处理输入元素。为此,tf.data API 提供了 tf.data.Dataset.map 变换,它将用户定义的函数应用于输入数据集的每个元素。由于输入元素彼此独立,因此可以在多个 CPU 内核上并行化预处理。为了实现这一点,与 prefetch 和 interleave 变换类似,map 变换提供了 num_parallel_calls 参数来指定并行级别。
为 num_parallel_calls 参数选择最佳值取决于您的硬件、训练数据的特征(例如大小和形状)、映射函数的成本以及同时在 CPU 上进行的其他处理。一个简单的启发式方法是使用可用 CPU 内核的数量。但是,与 prefetch 和 interleave 变换一样,map 变换支持 tf.data.AUTOTUNE,它将关于使用什么并行级别的决定委托给 tf.data 运行时。
def mapped_function(s):
# Do some hard pre-processing
tf.py_function(lambda: time.sleep(0.03), [], ())
return s
顺序映射
首先使用 map 变换,不进行并行化,作为基线示例。
benchmark(
ArtificialDataset()
.map(mapped_function)
)
2024-07-05 01:30:02.372077: W tensorflow/core/framework/local_rendezvous.cc:404] Local rendezvous is aborting with status: OUT_OF_RANGE: End of sequence Execution time: 0.4950294169998415 2024-07-05 01:30:02.616726: W tensorflow/core/framework/local_rendezvous.cc:404] Local rendezvous is aborting with status: OUT_OF_RANGE: End of sequence
与 朴素方法 一样,这里,正如图所示,打开、读取、预处理(映射)和训练步骤所花费的时间在一个迭代中加在一起。
并行映射
现在,使用相同的预处理函数,但将其并行应用于多个样本。
benchmark(
ArtificialDataset()
.map(
mapped_function,
num_parallel_calls=tf.data.AUTOTUNE
)
)
Execution time: 0.3728290660001221 2024-07-05 01:30:02.841096: W tensorflow/core/framework/local_rendezvous.cc:404] Local rendezvous is aborting with status: OUT_OF_RANGE: End of sequence 2024-07-05 01:30:03.024465: W tensorflow/core/framework/local_rendezvous.cc:404] Local rendezvous is aborting with status: OUT_OF_RANGE: End of sequence
正如数据图所示,预处理步骤重叠,从而减少了单个迭代的总时间。
缓存
tf.data.Dataset.cache 变换可以缓存数据集,无论是在内存中还是在本地存储中。这将节省一些操作(例如文件打开和数据读取)在每个 epoch 中执行。
benchmark(
ArtificialDataset()
.map( # Apply time consuming operations before cache
mapped_function
).cache(
),
5
)
Execution time: 0.3902423539998381 2024-07-05 01:30:03.314025: W tensorflow/core/framework/local_rendezvous.cc:404] Local rendezvous is aborting with status: OUT_OF_RANGE: End of sequence 2024-07-05 01:30:03.348975: W tensorflow/core/framework/local_rendezvous.cc:404] Local rendezvous is aborting with status: OUT_OF_RANGE: End of sequence 2024-07-05 01:30:03.383824: W tensorflow/core/framework/local_rendezvous.cc:404] Local rendezvous is aborting with status: OUT_OF_RANGE: End of sequence 2024-07-05 01:30:03.418575: W tensorflow/core/framework/local_rendezvous.cc:404] Local rendezvous is aborting with status: OUT_OF_RANGE: End of sequence 2024-07-05 01:30:03.453486: W tensorflow/core/framework/local_rendezvous.cc:404] Local rendezvous is aborting with status: OUT_OF_RANGE: End of sequence
这里,数据执行时间图显示,当您缓存数据集时,cache 之前的变换(例如文件打开和数据读取)只在第一个 epoch 中执行。接下来的 epoch 将重用由 cache 变换缓存的数据。
如果传递给 map 变换的用户定义函数很昂贵,请在 map 变换之后应用 cache 变换,只要结果数据集仍然可以放入内存或本地存储中。如果用户定义的函数将存储数据集所需的空间增加到超过缓存容量,则可以在 cache 变换之后应用它,或者考虑在训练作业之前预处理您的数据以减少资源使用。
矢量化映射
调用传递给 map 变换的用户定义函数会产生与调度和执行用户定义函数相关的开销。矢量化用户定义函数(即让它一次对一批输入进行操作),并在 map 变换之前应用 batch 变换。
为了说明这种最佳实践,您的合成数据集不适合。调度延迟约为 10 微秒(10e-6 秒),远小于 ArtificialDataset 中使用的数十毫秒,因此其影响很难看到。
对于此示例,使用基本 tf.data.Dataset.range 函数并将训练循环简化为最简单的形式。
fast_dataset = tf.data.Dataset.range(10000)
def fast_benchmark(dataset, num_epochs=2):
start_time = time.perf_counter()
for _ in tf.data.Dataset.range(num_epochs):
for _ in dataset:
pass
tf.print("Execution time:", time.perf_counter() - start_time)
def increment(x):
return x+1
标量映射
fast_benchmark(
fast_dataset
# Apply function one item at a time
.map(increment)
# Batch
.batch(256)
)
Execution time: 0.25260185999991336 2024-07-05 01:30:03.610517: W tensorflow/core/framework/local_rendezvous.cc:404] Local rendezvous is aborting with status: OUT_OF_RANGE: End of sequence 2024-07-05 01:30:03.744984: W tensorflow/core/framework/local_rendezvous.cc:404] Local rendezvous is aborting with status: OUT_OF_RANGE: End of sequence 2024-07-05 01:30:03.747348: W tensorflow/core/framework/local_rendezvous.cc:404] Local rendezvous is aborting with status: OUT_OF_RANGE: End of sequence
上面的图说明了使用标量映射方法正在发生的事情(样本更少)。它显示了映射函数是如何对每个样本应用的。虽然此函数非常快,但它有一些开销会影响时间性能。
矢量化映射
fast_benchmark(
fast_dataset
.batch(256)
# Apply function on a batch of items
# The tf.Tensor.__add__ method already handle batches
.map(increment)
)
2024-07-05 01:30:03.794190: W tensorflow/core/framework/local_rendezvous.cc:404] Local rendezvous is aborting with status: OUT_OF_RANGE: End of sequence Execution time: 0.05108185200015214 2024-07-05 01:30:03.815283: W tensorflow/core/framework/local_rendezvous.cc:404] Local rendezvous is aborting with status: OUT_OF_RANGE: End of sequence 2024-07-05 01:30:03.817405: W tensorflow/core/framework/local_rendezvous.cc:404] Local rendezvous is aborting with status: OUT_OF_RANGE: End of sequence
这一次,映射函数只调用一次,并应用于一批样本。正如数据执行时间图所示,虽然函数执行可能需要更多时间,但开销只出现一次,从而提高了整体时间性能。
减少内存占用
许多变换,包括 interleave、prefetch 和 shuffle,都会维护一个内部元素缓冲区。如果传递给 map 变换的用户定义函数更改了元素的大小,那么映射变换和缓冲元素的变换的顺序会影响内存使用情况。一般来说,选择导致内存占用更低的顺序,除非不同的顺序对性能有益。
缓存部分计算
建议在 map 变换之后缓存数据集,除非此变换使数据太大而无法放入内存。如果您的映射函数可以分成两部分:一个耗时的部分和一个占用内存的部分,则可以实现权衡。在这种情况下,您可以像下面这样链接您的变换
dataset.map(time_consuming_mapping).cache().map(memory_consuming_mapping)
这样,耗时的部分只在第一个 epoch 中执行,并且您避免使用过多的缓存空间。
最佳实践总结
以下是设计高性能 TensorFlow 输入管道的最佳实践总结
- 使用
prefetch变换 重叠生产者和消费者的工作 - 使用
interleave变换并行化数据读取变换 - 通过设置
num_parallel_calls参数并行化map变换 - 使用
cache变换 在第一个 epoch 中将数据缓存到内存中 - 矢量化传递给
map变换的用户定义函数 - 在应用
interleave、prefetch和shuffle变换时减少内存使用
复制图
为了更深入地理解 tf.data.Dataset API,您可以使用自己的管道进行练习。以下是用于绘制本指南中图像的代码,它可以作为一个良好的起点,展示了一些解决常见问题的方法,例如
- 执行时间可重复性
- 映射函数的急切执行
interleave变换的可调用性
import itertools
from collections import defaultdict
import numpy as np
import matplotlib as mpl
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
数据集
类似于 ArtificialDataset,您可以构建一个数据集,返回每个步骤花费的时间。
class TimeMeasuredDataset(tf.data.Dataset):
# OUTPUT: (steps, timings, counters)
OUTPUT_TYPES = (tf.dtypes.string, tf.dtypes.float32, tf.dtypes.int32)
OUTPUT_SHAPES = ((2, 1), (2, 2), (2, 3))
_INSTANCES_COUNTER = itertools.count() # Number of datasets generated
_EPOCHS_COUNTER = defaultdict(itertools.count) # Number of epochs done for each dataset
def _generator(instance_idx, num_samples):
epoch_idx = next(TimeMeasuredDataset._EPOCHS_COUNTER[instance_idx])
# Opening the file
open_enter = time.perf_counter()
time.sleep(0.03)
open_elapsed = time.perf_counter() - open_enter
for sample_idx in range(num_samples):
# Reading data (line, record) from the file
read_enter = time.perf_counter()
time.sleep(0.015)
read_elapsed = time.perf_counter() - read_enter
yield (
[("Open",), ("Read",)],
[(open_enter, open_elapsed), (read_enter, read_elapsed)],
[(instance_idx, epoch_idx, -1), (instance_idx, epoch_idx, sample_idx)]
)
open_enter, open_elapsed = -1., -1. # Negative values will be filtered
def __new__(cls, num_samples=3):
return tf.data.Dataset.from_generator(
cls._generator,
output_types=cls.OUTPUT_TYPES,
output_shapes=cls.OUTPUT_SHAPES,
args=(next(cls._INSTANCES_COUNTER), num_samples)
)
此数据集提供形状为 [[2, 1], [2, 2], [2, 3]] 且类型为 [tf.dtypes.string, tf.dtypes.float32, tf.dtypes.int32] 的样本。每个样本都是
(
[("Open"), ("Read")],
[(t0, d), (t0, d)],
[(i, e, -1), (i, e, s)]
)
其中
Open和Read是步骤标识符t0是相应步骤开始时的时间戳d是在相应步骤中花费的时间i是实例索引e是纪元索引(数据集迭代的次数)s是样本索引
迭代循环
使迭代循环稍微复杂一些,以聚合所有计时。这将仅适用于生成如上所述样本的数据集。
def timelined_benchmark(dataset, num_epochs=2):
# Initialize accumulators
steps_acc = tf.zeros([0, 1], dtype=tf.dtypes.string)
times_acc = tf.zeros([0, 2], dtype=tf.dtypes.float32)
values_acc = tf.zeros([0, 3], dtype=tf.dtypes.int32)
start_time = time.perf_counter()
for epoch_num in range(num_epochs):
epoch_enter = time.perf_counter()
for (steps, times, values) in dataset:
# Record dataset preparation informations
steps_acc = tf.concat((steps_acc, steps), axis=0)
times_acc = tf.concat((times_acc, times), axis=0)
values_acc = tf.concat((values_acc, values), axis=0)
# Simulate training time
train_enter = time.perf_counter()
time.sleep(0.01)
train_elapsed = time.perf_counter() - train_enter
# Record training informations
steps_acc = tf.concat((steps_acc, [["Train"]]), axis=0)
times_acc = tf.concat((times_acc, [(train_enter, train_elapsed)]), axis=0)
values_acc = tf.concat((values_acc, [values[-1]]), axis=0)
epoch_elapsed = time.perf_counter() - epoch_enter
# Record epoch informations
steps_acc = tf.concat((steps_acc, [["Epoch"]]), axis=0)
times_acc = tf.concat((times_acc, [(epoch_enter, epoch_elapsed)]), axis=0)
values_acc = tf.concat((values_acc, [[-1, epoch_num, -1]]), axis=0)
time.sleep(0.001)
tf.print("Execution time:", time.perf_counter() - start_time)
return {"steps": steps_acc, "times": times_acc, "values": values_acc}
绘图方法
最后,定义一个函数,该函数能够根据 timelined_benchmark 函数返回的值绘制时间线。
def draw_timeline(timeline, title, width=0.5, annotate=False, save=False):
# Remove invalid entries (negative times, or empty steps) from the timelines
invalid_mask = np.logical_and(timeline['times'] > 0, timeline['steps'] != b'')[:,0]
steps = timeline['steps'][invalid_mask].numpy()
times = timeline['times'][invalid_mask].numpy()
values = timeline['values'][invalid_mask].numpy()
# Get a set of different steps, ordered by the first time they are encountered
step_ids, indices = np.stack(np.unique(steps, return_index=True))
step_ids = step_ids[np.argsort(indices)]
# Shift the starting time to 0 and compute the maximal time value
min_time = times[:,0].min()
times[:,0] = (times[:,0] - min_time)
end = max(width, (times[:,0]+times[:,1]).max() + 0.01)
cmap = mpl.cm.get_cmap("plasma")
plt.close()
fig, axs = plt.subplots(len(step_ids), sharex=True, gridspec_kw={'hspace': 0})
fig.suptitle(title)
fig.set_size_inches(17.0, len(step_ids))
plt.xlim(-0.01, end)
for i, step in enumerate(step_ids):
step_name = step.decode()
ax = axs[i]
ax.set_ylabel(step_name)
ax.set_ylim(0, 1)
ax.set_yticks([])
ax.set_xlabel("time (s)")
ax.set_xticklabels([])
ax.grid(which="both", axis="x", color="k", linestyle=":")
# Get timings and annotation for the given step
entries_mask = np.squeeze(steps==step)
serie = np.unique(times[entries_mask], axis=0)
annotations = values[entries_mask]
ax.broken_barh(serie, (0, 1), color=cmap(i / len(step_ids)), linewidth=1, alpha=0.66)
if annotate:
for j, (start, width) in enumerate(serie):
annotation = "\n".join([f"{l}: {v}" for l,v in zip(("i", "e", "s"), annotations[j])])
ax.text(start + 0.001 + (0.001 * (j % 2)), 0.55 - (0.1 * (j % 2)), annotation,
horizontalalignment='left', verticalalignment='center')
if save:
plt.savefig(title.lower().translate(str.maketrans(" ", "_")) + ".svg")
使用映射函数的包装器
要在急切上下文中运行映射函数,您必须将它们包装在 tf.py_function 调用中。
def map_decorator(func):
def wrapper(steps, times, values):
# Use a tf.py_function to prevent auto-graph from compiling the method
return tf.py_function(
func,
inp=(steps, times, values),
Tout=(steps.dtype, times.dtype, values.dtype)
)
return wrapper
管道比较
_batch_map_num_items = 50
def dataset_generator_fun(*args):
return TimeMeasuredDataset(num_samples=_batch_map_num_items)
朴素
@map_decorator
def naive_map(steps, times, values):
map_enter = time.perf_counter()
time.sleep(0.001) # Time consuming step
time.sleep(0.0001) # Memory consuming step
map_elapsed = time.perf_counter() - map_enter
return (
tf.concat((steps, [["Map"]]), axis=0),
tf.concat((times, [[map_enter, map_elapsed]]), axis=0),
tf.concat((values, [values[-1]]), axis=0)
)
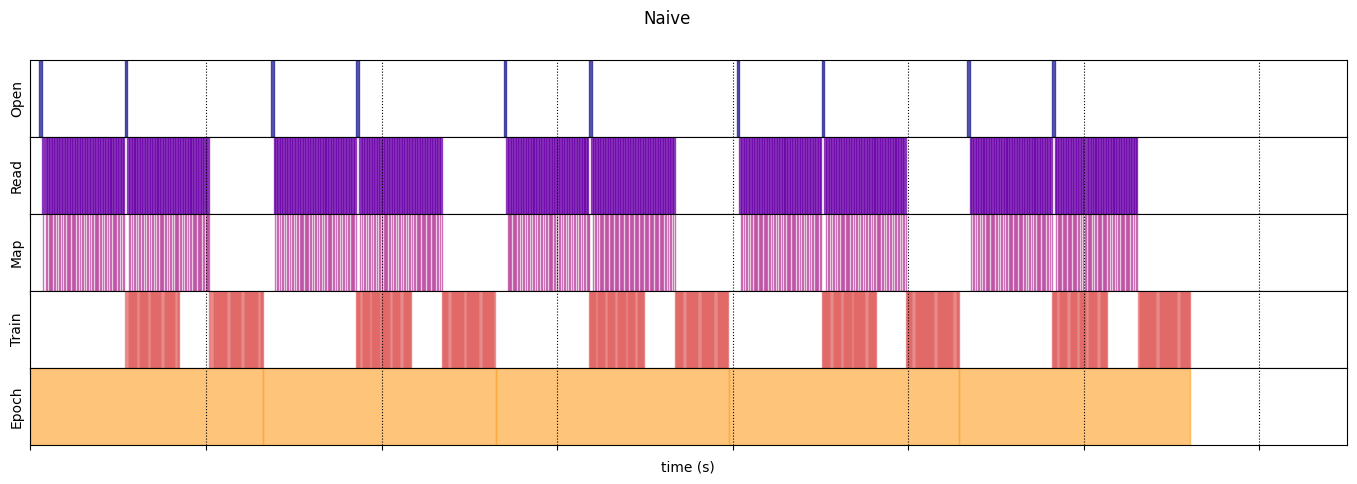
naive_timeline = timelined_benchmark(
tf.data.Dataset.range(2)
.flat_map(dataset_generator_fun)
.map(naive_map)
.batch(_batch_map_num_items, drop_remainder=True)
.unbatch(),
5
)
WARNING:tensorflow:From /tmpfs/tmp/ipykernel_18520/64197174.py:32: calling DatasetV2.from_generator (from tensorflow.python.data.ops.dataset_ops) with output_types is deprecated and will be removed in a future version. Instructions for updating: Use output_signature instead WARNING:tensorflow:From /tmpfs/tmp/ipykernel_18520/64197174.py:32: calling DatasetV2.from_generator (from tensorflow.python.data.ops.dataset_ops) with output_shapes is deprecated and will be removed in a future version. Instructions for updating: Use output_signature instead 2024-07-05 01:30:06.899542: W tensorflow/core/framework/local_rendezvous.cc:404] Local rendezvous is aborting with status: OUT_OF_RANGE: End of sequence 2024-07-05 01:30:09.551322: W tensorflow/core/framework/local_rendezvous.cc:404] Local rendezvous is aborting with status: OUT_OF_RANGE: End of sequence 2024-07-05 01:30:12.203750: W tensorflow/core/framework/local_rendezvous.cc:404] Local rendezvous is aborting with status: OUT_OF_RANGE: End of sequence 2024-07-05 01:30:14.829173: W tensorflow/core/framework/local_rendezvous.cc:404] Local rendezvous is aborting with status: OUT_OF_RANGE: End of sequence Execution time: 13.217723363000005 2024-07-05 01:30:17.465496: W tensorflow/core/framework/local_rendezvous.cc:404] Local rendezvous is aborting with status: OUT_OF_RANGE: End of sequence
优化
@map_decorator
def time_consuming_map(steps, times, values):
map_enter = time.perf_counter()
time.sleep(0.001 * values.shape[0]) # Time consuming step
map_elapsed = time.perf_counter() - map_enter
return (
tf.concat((steps, tf.tile([[["1st map"]]], [steps.shape[0], 1, 1])), axis=1),
tf.concat((times, tf.tile([[[map_enter, map_elapsed]]], [times.shape[0], 1, 1])), axis=1),
tf.concat((values, tf.tile([[values[:][-1][0]]], [values.shape[0], 1, 1])), axis=1)
)
@map_decorator
def memory_consuming_map(steps, times, values):
map_enter = time.perf_counter()
time.sleep(0.0001 * values.shape[0]) # Memory consuming step
map_elapsed = time.perf_counter() - map_enter
# Use tf.tile to handle batch dimension
return (
tf.concat((steps, tf.tile([[["2nd map"]]], [steps.shape[0], 1, 1])), axis=1),
tf.concat((times, tf.tile([[[map_enter, map_elapsed]]], [times.shape[0], 1, 1])), axis=1),
tf.concat((values, tf.tile([[values[:][-1][0]]], [values.shape[0], 1, 1])), axis=1)
)
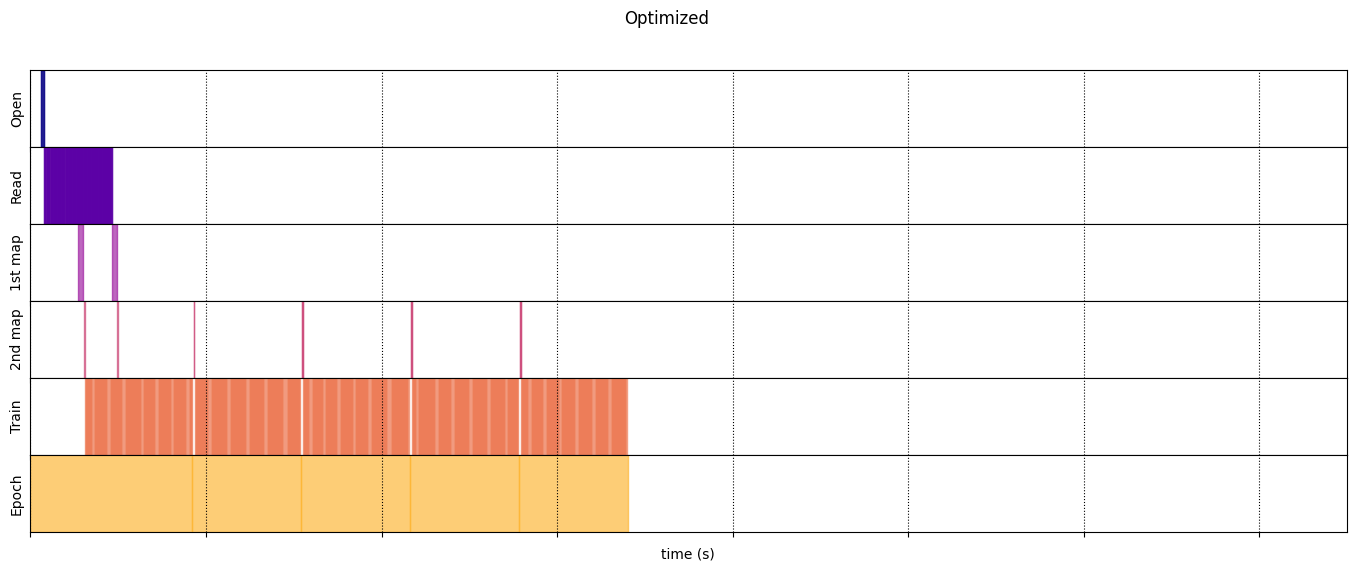
optimized_timeline = timelined_benchmark(
tf.data.Dataset.range(2)
.interleave( # Parallelize data reading
dataset_generator_fun,
num_parallel_calls=tf.data.AUTOTUNE
)
.batch( # Vectorize your mapped function
_batch_map_num_items,
drop_remainder=True)
.map( # Parallelize map transformation
time_consuming_map,
num_parallel_calls=tf.data.AUTOTUNE
)
.cache() # Cache data
.map( # Reduce memory usage
memory_consuming_map,
num_parallel_calls=tf.data.AUTOTUNE
)
.prefetch( # Overlap producer and consumer works
tf.data.AUTOTUNE
)
.unbatch(),
5
)
2024-07-05 01:30:19.383587: W tensorflow/core/framework/local_rendezvous.cc:404] Local rendezvous is aborting with status: OUT_OF_RANGE: End of sequence 2024-07-05 01:30:20.620389: W tensorflow/core/framework/local_rendezvous.cc:404] Local rendezvous is aborting with status: OUT_OF_RANGE: End of sequence 2024-07-05 01:30:21.864781: W tensorflow/core/framework/local_rendezvous.cc:404] Local rendezvous is aborting with status: OUT_OF_RANGE: End of sequence 2024-07-05 01:30:23.104293: W tensorflow/core/framework/local_rendezvous.cc:404] Local rendezvous is aborting with status: OUT_OF_RANGE: End of sequence Execution time: 6.807020873000056 2024-07-05 01:30:24.348445: W tensorflow/core/framework/local_rendezvous.cc:404] Local rendezvous is aborting with status: OUT_OF_RANGE: End of sequence
draw_timeline(naive_timeline, "Naive", 15)
/tmpfs/tmp/ipykernel_18520/2966908191.py:17: MatplotlibDeprecationWarning: The get_cmap function was deprecated in Matplotlib 3.7 and will be removed in 3.11. Use ``matplotlib.colormaps[name]`` or ``matplotlib.colormaps.get_cmap()`` or ``pyplot.get_cmap()`` instead.
cmap = mpl.cm.get_cmap("plasma")
draw_timeline(optimized_timeline, "Optimized", 15)
/tmpfs/tmp/ipykernel_18520/2966908191.py:17: MatplotlibDeprecationWarning: The get_cmap function was deprecated in Matplotlib 3.7 and will be removed in 3.11. Use ``matplotlib.colormaps[name]`` or ``matplotlib.colormaps.get_cmap()`` or ``pyplot.get_cmap()`` instead.
cmap = mpl.cm.get_cmap("plasma")