使用图形处理单元 (GPU) 运行机器学习 (ML) 模型可以显著提高模型的性能以及 ML 增强应用程序的用户体验。在 iOS 设备上,您可以使用 委托 启用对模型使用 GPU 加速执行。委托充当 TensorFlow Lite 的硬件驱动程序,使您能够在 GPU 处理器上运行模型代码。
本页面介绍如何在 iOS 应用程序中为 TensorFlow Lite 模型启用 GPU 加速。有关使用 TensorFlow Lite 的 GPU 委托的更多信息,包括最佳实践和高级技术,请参阅 GPU 委托 页面。
使用 Interpreter API 与 GPU 配合使用
TensorFlow Lite Interpreter API 提供了一组通用 API,用于构建机器学习应用程序。以下说明指导您将 GPU 支持添加到 iOS 应用程序。本指南假设您已经拥有一个 iOS 应用程序,该应用程序可以使用 TensorFlow Lite 成功执行 ML 模型。
修改 Podfile 以包含 GPU 支持
从 TensorFlow Lite 2.3.0 版本开始,GPU 委托已从 pod 中排除,以减小二进制文件大小。您可以通过为 TensorFlowLiteSwift pod 指定子规范来包含它们
pod 'TensorFlowLiteSwift/Metal', '~> 0.0.1-nightly',
或
pod 'TensorFlowLiteSwift', '~> 0.0.1-nightly', :subspecs => ['Metal']
如果您想使用 Objective-C(适用于 2.4.0 及更高版本)或 C API,也可以使用 TensorFlowLiteObjC 或 TensorFlowLiteC。
初始化和使用 GPU 委托
您可以使用多种编程语言将 GPU 委托与 TensorFlow Lite Interpreter API 配合使用。建议使用 Swift 和 Objective-C,但您也可以使用 C++ 和 C。如果您使用的是 2.4 之前的 TensorFlow Lite 版本,则必须使用 C。以下代码示例概述了如何在每种语言中使用委托。
import TensorFlowLite
// Load model ...
// Initialize TensorFlow Lite interpreter with the GPU delegate.
let delegate = MetalDelegate()
if let interpreter = try Interpreter(modelPath: modelPath,
delegates: [delegate]) {
// Run inference ...
}
// Import module when using CocoaPods with module support
@import TFLTensorFlowLite;
// Or import following headers manually
#import "tensorflow/lite/objc/apis/TFLMetalDelegate.h"
#import "tensorflow/lite/objc/apis/TFLTensorFlowLite.h"
// Initialize GPU delegate
TFLMetalDelegate* metalDelegate = [[TFLMetalDelegate alloc] init];
// Initialize interpreter with model path and GPU delegate
TFLInterpreterOptions* options = [[TFLInterpreterOptions alloc] init];
NSError* error = nil;
TFLInterpreter* interpreter = [[TFLInterpreter alloc]
initWithModelPath:modelPath
options:options
delegates:@[ metalDelegate ]
error:&error];
if (error != nil) { /* Error handling... */ }
if (![interpreter allocateTensorsWithError:&error]) { /* Error handling... */ }
if (error != nil) { /* Error handling... */ }
// Run inference ...
// Set up interpreter.
auto model = FlatBufferModel::BuildFromFile(model_path);
if (!model) return false;
tflite::ops::builtin::BuiltinOpResolver op_resolver;
std::unique_ptr<Interpreter> interpreter;
InterpreterBuilder(*model, op_resolver)(&interpreter);
// Prepare GPU delegate.
auto* delegate = TFLGpuDelegateCreate(/*default options=*/nullptr);
if (interpreter->ModifyGraphWithDelegate(delegate) != kTfLiteOk) return false;
// Run inference.
WriteToInputTensor(interpreter->typed_input_tensor<float>(0));
if (interpreter->Invoke() != kTfLiteOk) return false;
ReadFromOutputTensor(interpreter->typed_output_tensor<float>(0));
// Clean up.
TFLGpuDelegateDelete(delegate);
#include "tensorflow/lite/c/c_api.h"
#include "tensorflow/lite/delegates/gpu/metal_delegate.h"
// Initialize model
TfLiteModel* model = TfLiteModelCreateFromFile(model_path);
// Initialize interpreter with GPU delegate
TfLiteInterpreterOptions* options = TfLiteInterpreterOptionsCreate();
TfLiteDelegate* delegate = TFLGPUDelegateCreate(nil); // default config
TfLiteInterpreterOptionsAddDelegate(options, metal_delegate);
TfLiteInterpreter* interpreter = TfLiteInterpreterCreate(model, options);
TfLiteInterpreterOptionsDelete(options);
TfLiteInterpreterAllocateTensors(interpreter);
NSMutableData *input_data = [NSMutableData dataWithLength:input_size * sizeof(float)];
NSMutableData *output_data = [NSMutableData dataWithLength:output_size * sizeof(float)];
TfLiteTensor* input = TfLiteInterpreterGetInputTensor(interpreter, 0);
const TfLiteTensor* output = TfLiteInterpreterGetOutputTensor(interpreter, 0);
// Run inference
TfLiteTensorCopyFromBuffer(input, inputData.bytes, inputData.length);
TfLiteInterpreterInvoke(interpreter);
TfLiteTensorCopyToBuffer(output, outputData.mutableBytes, outputData.length);
// Clean up
TfLiteInterpreterDelete(interpreter);
TFLGpuDelegateDelete(metal_delegate);
TfLiteModelDelete(model);
GPU API 语言使用说明
- 2.4.0 之前的 TensorFlow Lite 版本只能使用 C API 用于 Objective-C。
- C++ API 仅在使用 bazel 或自行构建 TensorFlow Lite 时可用。C++ API 不能与 CocoaPods 配合使用。
- 在使用 TensorFlow Lite 与 GPU 委托与 C++ 配合使用时,通过
TFLGpuDelegateCreate()函数获取 GPU 委托,然后将其传递给Interpreter::ModifyGraphWithDelegate(),而不是调用Interpreter::AllocateTensors()。
使用发布模式构建和测试
使用适当的 Metal API 加速器设置更改为发布构建,以获得更好的性能并进行最终测试。本节说明如何启用发布构建并配置 Metal 加速设置。
要更改为发布构建
- 通过选择产品 > 方案 > 编辑方案...,然后选择运行来编辑构建设置。
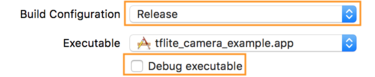
- 在信息选项卡上,将构建配置更改为发布,并取消选中调试可执行文件。
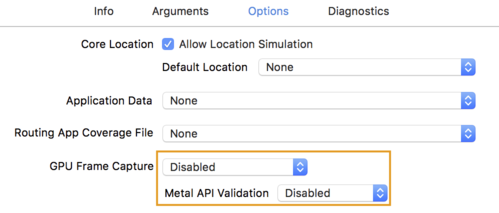
- 单击选项选项卡,并将GPU 帧捕获更改为禁用,并将Metal API 验证更改为禁用。
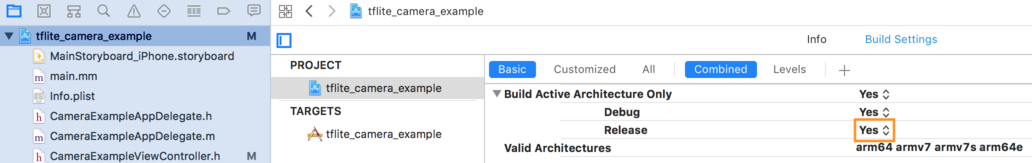
- 确保在 64 位架构上选择仅发布构建。在 **项目导航器 > tflite_camera_example > 项目 > your_project_name > 构建设置** 中,将 **仅构建活动架构 > 发布** 设置为 **是**。
高级 GPU 支持
本节介绍 iOS 上 GPU 代理的高级用法,包括代理选项、输入和输出缓冲区以及量化模型的使用。
iOS 的代理选项
GPU 代理的构造函数接受一个包含选项的 struct,这些选项在 Swift API、Objective-C API 和 C API 中定义。将 nullptr(C API)或空值(Objective-C 和 Swift API)传递给初始化程序将设置默认选项(这些选项在上面的基本用法示例中已说明)。
// THIS:
var options = MetalDelegate.Options()
options.isPrecisionLossAllowed = false
options.waitType = .passive
options.isQuantizationEnabled = true
let delegate = MetalDelegate(options: options)
// IS THE SAME AS THIS:
let delegate = MetalDelegate()
// THIS:
TFLMetalDelegateOptions* options = [[TFLMetalDelegateOptions alloc] init];
options.precisionLossAllowed = false;
options.waitType = TFLMetalDelegateThreadWaitTypePassive;
options.quantizationEnabled = true;
TFLMetalDelegate* delegate = [[TFLMetalDelegate alloc] initWithOptions:options];
// IS THE SAME AS THIS:
TFLMetalDelegate* delegate = [[TFLMetalDelegate alloc] init];
// THIS:
const TFLGpuDelegateOptions options = {
.allow_precision_loss = false,
.wait_type = TFLGpuDelegateWaitType::TFLGpuDelegateWaitTypePassive,
.enable_quantization = true,
};
TfLiteDelegate* delegate = TFLGpuDelegateCreate(options);
// IS THE SAME AS THIS:
TfLiteDelegate* delegate = TFLGpuDelegateCreate(nullptr);
使用 C++ API 的输入/输出缓冲区
GPU 上的计算要求数据对 GPU 可用。此要求通常意味着您必须执行内存复制。如果可能,您应该避免让数据跨越 CPU/GPU 内存边界,因为这可能需要大量时间。通常,这种跨越是不可避免的,但在某些特殊情况下,可以省略其中一个。
如果网络的输入是已加载到 GPU 内存中的图像(例如,包含相机馈送的 GPU 纹理),它可以保留在 GPU 内存中,而无需进入 CPU 内存。类似地,如果网络的输出是可渲染图像的形式,例如 图像风格迁移 操作,您可以直接在屏幕上显示结果。
为了获得最佳性能,TensorFlow Lite 使用户能够直接从 TensorFlow 硬件缓冲区读取和写入,并绕过可避免的内存复制。
假设图像输入位于 GPU 内存中,您必须首先将其转换为 Metal 的 MTLBuffer 对象。您可以使用 TFLGpuDelegateBindMetalBufferToTensor() 函数将 TfLiteTensor 与用户准备好的 MTLBuffer 关联。请注意,此函数**必须**在 Interpreter::ModifyGraphWithDelegate() 之后调用。此外,推理输出默认情况下会从 GPU 内存复制到 CPU 内存。您可以在初始化期间调用 Interpreter::SetAllowBufferHandleOutput(true) 来关闭此行为。
#include "tensorflow/lite/delegates/gpu/metal_delegate.h"
#include "tensorflow/lite/delegates/gpu/metal_delegate_internal.h"
// ...
// Prepare GPU delegate.
auto* delegate = TFLGpuDelegateCreate(nullptr);
if (interpreter->ModifyGraphWithDelegate(delegate) != kTfLiteOk) return false;
interpreter->SetAllowBufferHandleOutput(true); // disable default gpu->cpu copy
if (!TFLGpuDelegateBindMetalBufferToTensor(
delegate, interpreter->inputs()[0], user_provided_input_buffer)) {
return false;
}
if (!TFLGpuDelegateBindMetalBufferToTensor(
delegate, interpreter->outputs()[0], user_provided_output_buffer)) {
return false;
}
// Run inference.
if (interpreter->Invoke() != kTfLiteOk) return false;
关闭默认行为后,将推理输出从 GPU 内存复制到 CPU 内存需要对每个输出张量显式调用 Interpreter::EnsureTensorDataIsReadable()。此方法也适用于量化模型,但您仍然需要使用**大小为 float32 的缓冲区,其中包含 float32 数据**,因为该缓冲区绑定到内部去量化缓冲区。
量化模型
iOS GPU 代理库**默认支持量化模型**。您无需进行任何代码更改即可将量化模型与 GPU 代理一起使用。下一节将解释如何禁用量化支持以进行测试或实验目的。
禁用量化模型支持
以下代码显示了如何**禁用**对量化模型的支持。
var options = MetalDelegate.Options()
options.isQuantizationEnabled = false
let delegate = MetalDelegate(options: options)
TFLMetalDelegateOptions* options = [[TFLMetalDelegateOptions alloc] init];
options.quantizationEnabled = false;
TFLGpuDelegateOptions options = TFLGpuDelegateOptionsDefault();
options.enable_quantization = false;
TfLiteDelegate* delegate = TFLGpuDelegateCreate(options);
有关使用 GPU 加速运行量化模型的更多信息,请参阅 GPU 代理 概述。
