在 TensorFlow.org 上查看 在 TensorFlow.org 上查看
|
 在 Google Colab 中运行 在 Google Colab 中运行
|
 在 GitHub 上查看源代码 在 GitHub 上查看源代码
|
 下载笔记本 下载笔记本
|
概述
使用 **TensorBoard Embedding Projector**,您可以以图形方式表示高维嵌入。这有助于可视化、检查和理解您的嵌入层。
在本教程中,您将学习如何可视化这种类型的训练层。
设置
在本教程中,我们将使用 TensorBoard 来可视化为对电影评论数据进行分类而生成的嵌入层。
try:
# %tensorflow_version only exists in Colab.
%tensorflow_version 2.x
except Exception:
pass
%load_ext tensorboard
import os
import tensorflow as tf
import tensorflow_datasets as tfds
from tensorboard.plugins import projector
IMDB 数据
我们将使用一个包含 25,000 条 IMDB 电影评论的数据集,每条评论都有一个情感标签(正面/负面)。每条评论都经过预处理并编码为一系列词索引(整数)。为简单起见,单词按数据集中的总体频率进行索引,例如整数“3”编码所有评论中出现的第 3 个最常出现的单词。这允许快速过滤操作,例如:“只考虑前 10,000 个最常见的单词,但排除前 20 个最常见的单词”。
按照惯例,“0”不代表任何特定单词,而是用于编码任何未知单词。在本教程的后面,我们将从可视化中删除“0”的行。
(train_data, test_data), info = tfds.load(
"imdb_reviews/subwords8k",
split=(tfds.Split.TRAIN, tfds.Split.TEST),
with_info=True,
as_supervised=True,
)
encoder = info.features["text"].encoder
# Shuffle and pad the data.
train_batches = train_data.shuffle(1000).padded_batch(
10, padded_shapes=((None,), ())
)
test_batches = test_data.shuffle(1000).padded_batch(
10, padded_shapes=((None,), ())
)
train_batch, train_labels = next(iter(train_batches))
Keras 嵌入层
可以使用 Keras 嵌入层 为词汇表中的每个单词训练嵌入。每个单词(或在这种情况下是子词)将与一个 16 维向量(或嵌入)相关联,该向量将由模型训练。
请参阅 本教程,详细了解词嵌入。
# Create an embedding layer.
embedding_dim = 16
embedding = tf.keras.layers.Embedding(encoder.vocab_size, embedding_dim)
# Configure the embedding layer as part of a keras model.
model = tf.keras.Sequential(
[
embedding, # The embedding layer should be the first layer in a model.
tf.keras.layers.GlobalAveragePooling1D(),
tf.keras.layers.Dense(16, activation="relu"),
tf.keras.layers.Dense(1),
]
)
# Compile model.
model.compile(
optimizer="adam",
loss=tf.keras.losses.BinaryCrossentropy(from_logits=True),
metrics=["accuracy"],
)
# Train model for one epoch.
history = model.fit(
train_batches, epochs=1, validation_data=test_batches, validation_steps=20
)
2500/2500 [==============================] - 13s 5ms/step - loss: 0.5330 - accuracy: 0.6769 - val_loss: 0.4043 - val_accuracy: 0.7800
保存 TensorBoard 数据
TensorBoard 从 TensorFlow 项目的日志中读取张量和元数据。日志目录的路径由下面的 log_dir 指定。在本教程中,我们将使用 /logs/imdb-example/。
为了将数据加载到 Tensorboard,我们需要将训练检查点保存到该目录,以及允许可视化模型中特定感兴趣层的元数据。
# Set up a logs directory, so Tensorboard knows where to look for files.
log_dir='/logs/imdb-example/'
if not os.path.exists(log_dir):
os.makedirs(log_dir)
# Save Labels separately on a line-by-line manner.
with open(os.path.join(log_dir, 'metadata.tsv'), "w") as f:
for subwords in encoder.subwords:
f.write("{}\n".format(subwords))
# Fill in the rest of the labels with "unknown".
for unknown in range(1, encoder.vocab_size - len(encoder.subwords)):
f.write("unknown #{}\n".format(unknown))
# Save the weights we want to analyze as a variable. Note that the first
# value represents any unknown word, which is not in the metadata, here
# we will remove this value.
weights = tf.Variable(model.layers[0].get_weights()[0][1:])
# Create a checkpoint from embedding, the filename and key are the
# name of the tensor.
checkpoint = tf.train.Checkpoint(embedding=weights)
checkpoint.save(os.path.join(log_dir, "embedding.ckpt"))
# Set up config.
config = projector.ProjectorConfig()
embedding = config.embeddings.add()
# The name of the tensor will be suffixed by `/.ATTRIBUTES/VARIABLE_VALUE`.
embedding.tensor_name = "embedding/.ATTRIBUTES/VARIABLE_VALUE"
embedding.metadata_path = 'metadata.tsv'
projector.visualize_embeddings(log_dir, config)
# Now run tensorboard against on log data we just saved.
%tensorboard --logdir /logs/imdb-example/
分析
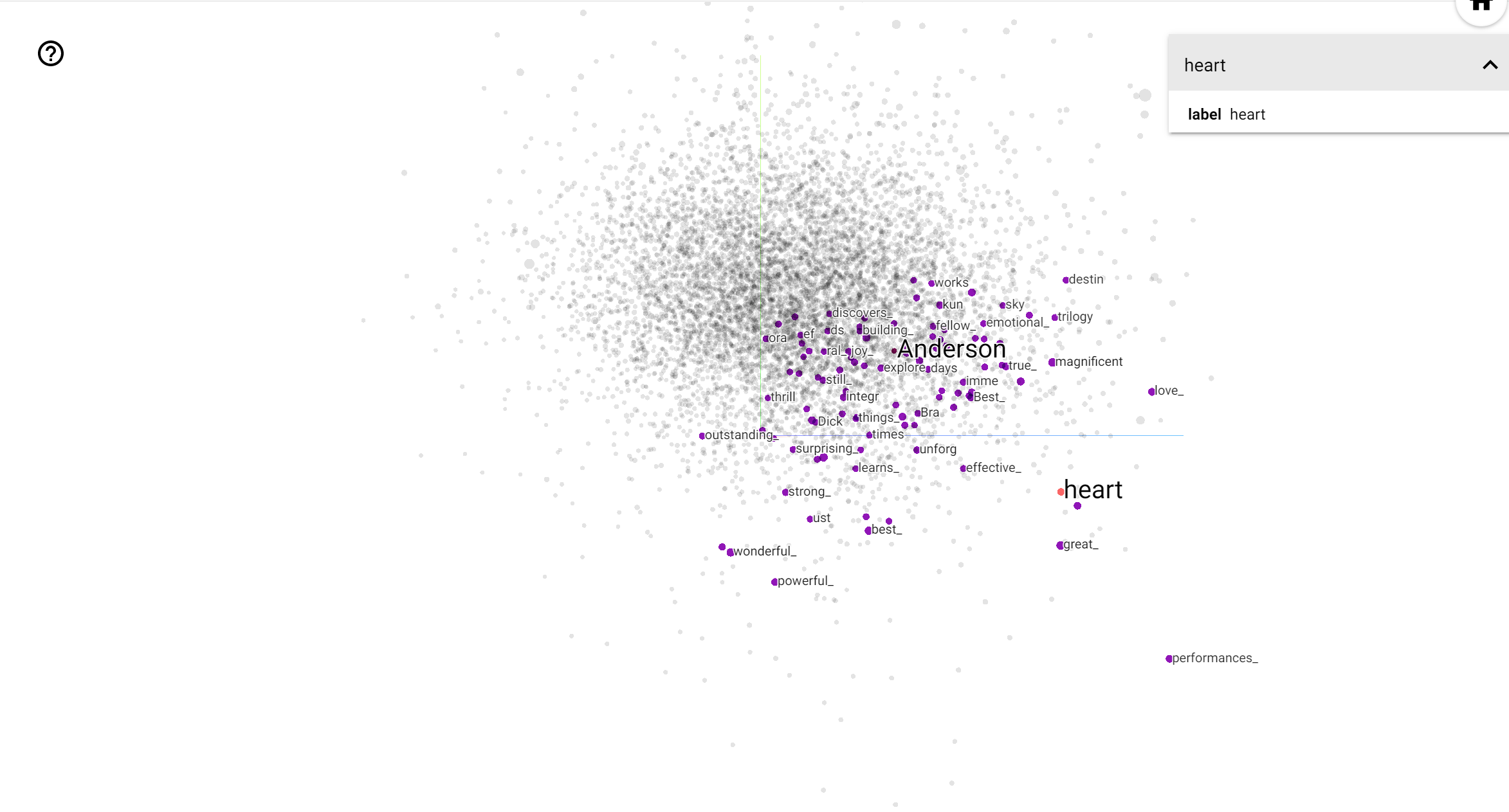
TensorBoard Projector 是一个用于解释和可视化嵌入的强大工具。仪表板允许用户搜索特定术语,并突出显示在嵌入(低维)空间中彼此相邻的单词。从这个例子中,我们可以看到 Wes **Anderson** 和 Alfred **Hitchcock** 都是比较中性的术语,但它们在不同的语境中被提及。
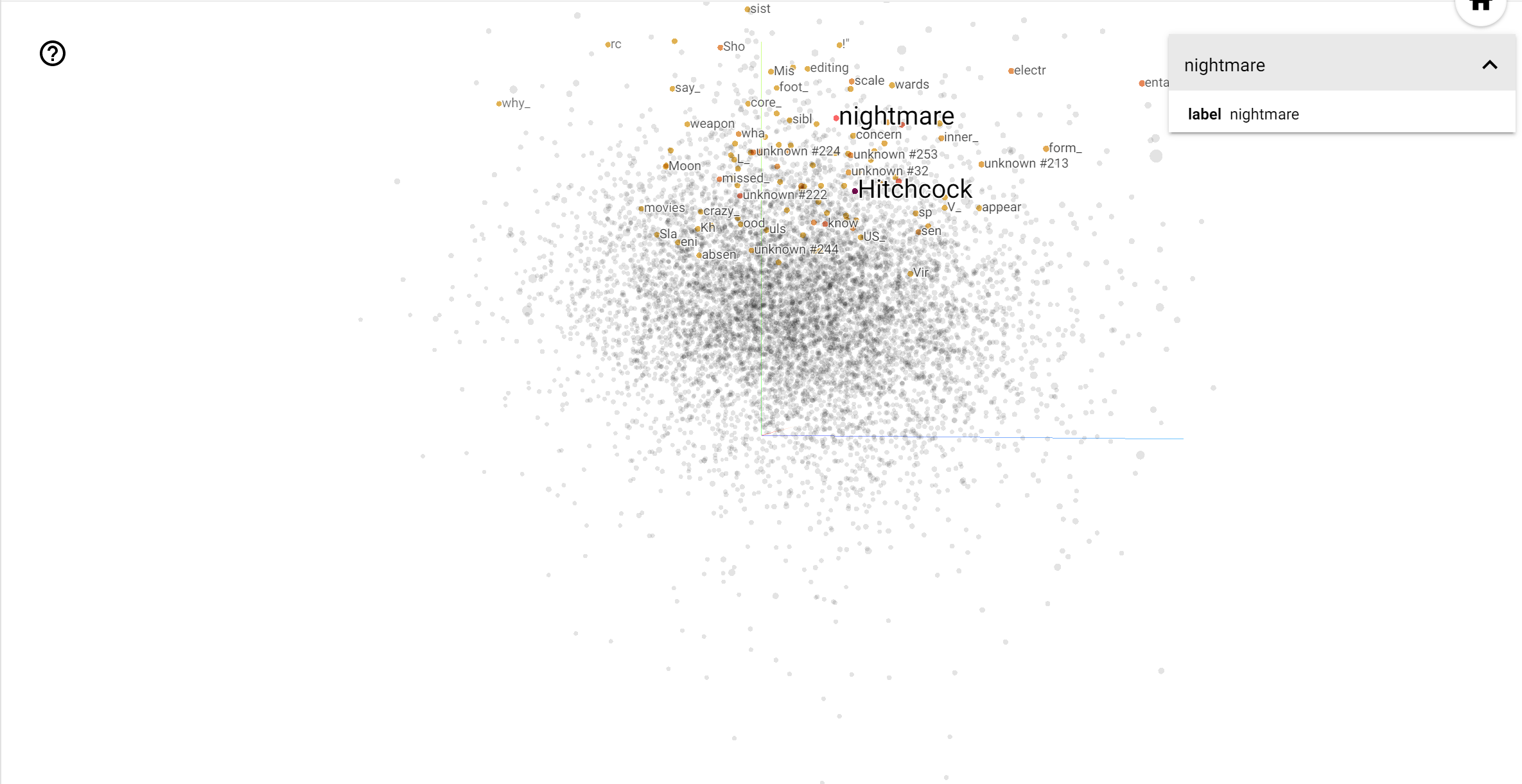
在这个空间中,希区柯克更接近像 nightmare 这样的词,这可能是因为他被称为“悬念大师”,而安德森更接近 heart 这个词,这与他一贯的细致入微和温馨风格相一致。